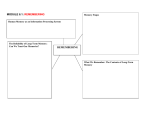
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download on Memory
Cognitive interview wikipedia , lookup
William Clancey wikipedia , lookup
Procedural memory wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Implicit memory wikipedia , lookup
De novo protein synthesis theory of memory formation wikipedia , lookup
Effects of alcohol on memory wikipedia , lookup
Multiple trace theory wikipedia , lookup
Socioeconomic status and memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory error wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Sparse distributed memory wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive memory wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Source amnesia wikipedia , lookup
Art of memory wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory wikipedia , lookup
Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model wikipedia , lookup
Memory and aging wikipedia , lookup
Traumatic memories wikipedia , lookup
Music-related memory wikipedia , lookup
Exceptional memory wikipedia , lookup
Childhood memory wikipedia , lookup
Remember versus know judgements wikipedia , lookup
Misattribution of memory wikipedia , lookup
Collective memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory (child testimony) wikipedia , lookup
Episodic-like memory wikipedia , lookup