* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 8 Cell Membrane
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
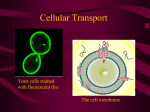
DUBLIN HIGH SCHOOL AP BIOLOGY CH. 8 STUDY GUIDE: CELL MEMBRANES KEY TERMS plasma(=cell) membrane isotonic fluid-mosaic model crenation phospholipid plasmolysis integral(=imbedded) protein lysis peripheral protein facilitated diffusion membrane channel gated channel transport protein membrane pump diffusion active transport passive transport sodium-potassium pump osmosis endocytosis selectively permeable phagocytosis osmotic concentration pinocytosis osmotic pressure(=potential) pseudopodia hypertonic exocytosis hypotonic 1 WORDS ROOTS amphi - = dual (amphipathic molecule: a molecule that has both a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic region) aqua - = water; - pori = a small opening (aquaporin: a transport protein in the plasma membrane of a plant or animal cell that specifically facilitates the diffusion of water across a membrane) co - = together; trans - = across (cotransport: the coupling of the “downhill” diffusion of one substance to the “uphill” transport of another against its own concentration gradient) electro- = electricity; - genic = producing (electrogenic pump: an ion transport prottein generating voltage across a membrane) endo - = inner; cyto - = cell (endocytosis: the movement of materials into a cell. Cell-eating) exo - = outer (exocytosis: the movement of materials out of a cell) hyper - = exceeding; - tonus = tension (hypertonic: a solution with a higher concentration of solutes) hypo - = lower (hypotonic: a solution with a lower concentration of solutes) iso - = same (isotonic: solutions with equal concetrations of solutes) phago - = eat (phagocytosis: cell eating) pino - = drink (pinocytosis: cell drinking) plasm - = molded; - lyso = loosen (plasmolysis: a phenomenon in walled cells in which the cytoplasm shrivels and the plasma membrane pulls away from the cell wall when the cell loses water to a hypertonic environment) QUESTIONS 1. Describe the processes of diffusion. 2. How does the random movement of molecules bring about an even distribution of molecules throughout the system? 3. Describe the processes of osmosis. 2 4. Using a diagram describe the fluid-mosaic model of the cell membrane. Indicate the following; phospholipid molecules, hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends, types of membrane proteins and glycoproteins. List substances to which the membrane is relatively permeable and those substances to which it is relatively impermeable. 5. Why is the term mosaic used to describe the fluid-mosaic model of the cell membrane? 6. Define the terms hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic and explain what would happen to a cell if it were placed in each of these solutions. 7. Describe the role of membrane proteins in movement of materials through membranes. Discuss integral proteins, and membrane pumps. 8. Distinguish between simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport and indicate the significance of these processes to the life of the cell. 9. Describe and diagram the sodium/potassium pump of the cell membrane. 10. Describe the processes of phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and exocytosis. 11. Describe how cells recognize each other, include a description of the role of oligosaccharides, glycoproteins and glycolipids. 12. Differentiate between hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic. Use the example of red blood cells in pure water, in blood and in 5% salt water. 13. Why is it incorrect to say that a 1% salt solution is isotonic? 14. Justify the conclusion that differences in ion concentration between cells and their surroundings indicates that cells regulate the passage of materials across membranes. 15. In addition to the cell membrane, what membranous structures are included in the endomembrane system? 16. In simple terms, using simple English, describe turgidity. 3