* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit Title / Grade Level Unit 3: The Basis of Life (Covering Chapters
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
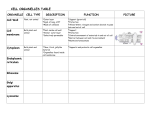
Unit Title / Grade Level Start Week / End Week Standard(s) Essential Question(s) Unit 3: The Basis of Life (Covering Chapters 8 through 11) 11/19 - 2/15 SP.1.1 Scientific Questions: Students recognize, formulate, justify, and revise scientific questions that can be addressed by science in order to construct explanations. LS.2.2 Cell Structure: Students understand that cells have internal structures that carry out specialized life functions, and that these internal structures vary depending on a cell’s function. LS.3.2 Interactions of Living Systems: Students understand that organisms in all ecosystems interact with and depend on each other, and that organisms with similar needs compete for limited resources. What are the characteristics of a living organism? How are living things classified and why is it important? What are the similarities and differences between human and plant cells? Why might it be difficult to treat a virus or a viral disease? Describe the processes that a cell undergoes to ensure its survival. Binomial Nomenclature Cell Wall Describe the processes used by cells and organisms to reproduce. Vocabulary Cell Cell Membrane Cell Theory Chloroplast Cytoplasm Genus Kingdom Organelle Ribosome Organic Compound Golgi Body Mitochondrion Organism Tissue Enzyme Active Transport Endocytosis Cellular Respiration Asexual reproduction Diffusion Exocytosis Fermentation Sexual reproduction Homeostasis Nucleus Organ System Virus Inorganic Compound Equilibrium Metabolism Mitosis Sperm Endoplasmic Reticulum Host Cell Organ Phylogeny Mixture Passive Transport Osmosis Photosynthesis Chromosome Egg Fertilization Meiosis Mutation Hybrid Genotype Zygote DNA Heredity Dominant Phenotype Diploid Gene Allele Recessive Homozygous Haploid RNA Genetics Punnett Square Heterozygous Performance Assessment Performance Assessment for Unit 3: Cell Membrane Project Directions: To make a 3-D model of the cell and cell membrane using common everyday materials. A model of an animal or plant cell will be made, labeled with the following organelles (where appropriate): Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Lysosome Nucleus Microtubules Marker Protein Cell Wall Nucleolus Channel Protein Nuclear Envelope Mitochondria Vacuole Golgi Body Ribosome Microfilaments Chloroplast Receptor Protein Phospholipids Centriole (Rough) Endoplasmic Reticulum Labeling: The cell type (plant or animal) should be labeled. All cell organelles and parts of the cell membrane should also be labeled. Identification of organelles should be done using flags made of toothpicks stuck in the appropriate organelle. The name of the structure can be written on the flag or a number can be used which corresponds to a key of the structures. Function Key: You must include a key for your model. The organelles should be listed and identified by the flags on your model. You should also include a brief explanation of the function of each organelle in your key. Cross Section of Cell Membrane: A second, smaller model of a cross section of a cell membrane will be made. You must show the phospholipid bilayer and the three types of cellular proteins. Be sure to label these and include them on your function key. Suggestions for Getting Started: Decide if you want to make an animal or plant cell for your model. Think of materials that would best represent the different organelles. Make a key of the organelles and their functions before you make the model. Materials used to represent organelles may include anything. Suggestions are to use what you have at home. Do not make this into an expensive project! Examples you could use would be wood, buttons, yarn, thread, food, (noodles, vegetables, etc) candy, plastic, paper, Styrofoam, etc. Grading: Points Possible Correctly labeling organelles 32 Function key of organelles 32 Correct model of the cell membrane 8 Correctly indicating plant or animal cell 3 Total Points: 75