* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Test 2 from 2012
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
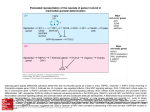
GENETICS TEST 2 - FALL 2012 This test has two parts. In Part 1, answer 5 of the 6 questions (15 pts each). Please indicate the questions you want me to grade. If there is any uncertainty I will grade the first five. All students must complete Part 2 (25 pts). Part 3 will be team-based, and will be completed in class on Monday. Parts 1 and 2 together will make up 85% of your test grade, Part 3 will be worth 15%. NAME: PART 1: Short Answer. Answer 5 of the following 6 questions. Question 1: Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase is an enzyme that is critical to glycolysis. Part of the amino acid sequence for the wild type glucose-6-phosphate isomerase enzyme is shown below, along with the same part of the protein as produced by four mutants, each of which contains a single, different point mutation. For each of the mutants, give a single DNA base change that could account for the observed change, and tell whether that change is a missense, nonsense, silent or frameshift mutation. A codon table can be found at the end of this test. Wild Type: Met-Glu-Lys-Ser-Ala Mutant 1: Met-Glu Mutant 2: Met-Lys-Lys-Ser-Ala Mutant 3: Met-Glu-Lys-Ser-Ala Mutant 4: Met-Arg-Glu-Ile-Gly Question 2: The following DNA sequence is the template/noncoding sequence from a portion of a eukaryotic gene that codes for amino acids. Introns are underlined and exons are designated by plain text. 3' ATGAGGACTTAAGGACCTGAGGGGCTGATAAAA 5' A) Give the sequence of the mRNA that would be produced by this gene B) If the splice site for the first exon was mutated so that it was no longer functional, what would you expect the specific impact to be on the resulting mRNA? C) Do you think this mutation will impact protein function? Explain. Question 3: The following DNA sequence is that of the coding strand of a gene. Transcription starts at base 10 in this sequence. 5' ACGTACATACCATATAACCGCTAGATGCACGAAGATCCCGGGTCAACATTTGCATAA 3' A). Give the first ten bases of the RNA produced by this gene. B). Give the first 5 amino acids translated from this gene. C). If a T was inserted at base number 11, what would be the impact on the protein product? Explain your answer. Question 5: The biochemical pathway for the synthesis of the color purple in flowers is shown below: Colorless Gene R Red Blue Gene B Purple Colorless What phenotype (color) would you expect flowers to have if they were homozygous for the following mutations? Explain each answer 1) A down promoter mutation in gene R 2) An up promoter mutation in gene B 3) A frameshift mutation early in gene R Question 6: Very briefly describe how three different types of point mutations could impact a phenotype. You do not need to know the names of the different point mutations, nor the names of specific genetic traits involved. Rather, tell hypothetically how different types of point mutations could influence phenotypes. PART TWO: All students must answer this question. The diagram below is of a Western Blot that shows, in lane 1, Sox9 protein expression in a normal human male and, in lane 2, Sox9 protein expression in a normal human female. 1 2 3 4 1). Based on this data, what can you conclude about the expression of Sox9 in normal human males versus females? 2) SRY is a Y-linked gene that codes for a transcription factor that is required for SOX9 transcription. In Lane 3, draw the Sox9 protein product, if any, that you would expect to see in a human male who has a nonsense mutation early in their SRY gene. Based on your conclusions in 1), what sex would you expect this individual to be? 3). Explain your answer to #2 4) In Lane 4, draw the Sox9 protein product, if any, that you would expect to see in a female who has a Gain of Function mutation that causes male levels of SOX9 expression. 5). Based on your conclusions in 1), what sex would you expect this individual to be? Explain.