* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - OG-Science
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
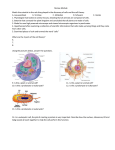
Studyguide for Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Things to study for your test: this study guide, your notes and note sheets from Power points, lab handouts, vocabulary words, key concepts from book, cell analogy worksheet (A cell is like a factory…) 1. In many cells, the structure that controls the cell’s activities is the a. Cell membrane b. Organelle c. Nucleolus d. Nucleus 2. Despite differences in size and shape, all cells have DNA and a a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Mitochondrion d. Nucleus 3. What distinguishes a eukaryotic cell from a prokaryotic cells is the presence of a a. Cell wall b. Nucleus c. DNA d. Ribosomes 4. Create a table that summarizes the contributions made to the cell theory by Robert Hooke, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow. 5. What was significant about Anton van Leeuwenhoek? 6. If you wanted to observe a living organism – an amoeba, for example – which type of microscope would you use? 7. In eukaryotic cells, chromosomes carrying genetic information are found in the a. Ribosomes b. Lysosomes c. Nucleus d. Cell membrane 8. The organelles that break down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into small molecules that can be used by the cell are called a. Vacuoles b. Lysosomes c. Ribosomes d. Microfilaments 9. How do microfilaments help cellular movement? 10. Cell membranes consist mainly of a. Lipid bilayers b. Protein pumps c. Carbohydrates d. Proteins 11. Draw a cell nucleus. Label and give the functions of: chromatin, nucleolus, and nuclear envelope. 12. What is the function of a ribosome? 13. Describe the role of the Golgi apparatus. 14. The pancreas, an organ present in certain animals, produces enzymes used elsewhere in the animals’ digestive systems. Which type of cell structure(s) might produce those enzymes? Explain your answer. 15. For each of the following, indicate if the structure is found only in eukaryotes, or it if is found in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. a. Cell membrane - Prokaryote Eukaryote b. Mitochondria - Prokaryote Eukaryote c. Ribosome Prokaryote Eukaryote d. Golgi apparatus - Prokaryote Eukaryote e. Nucleus Prokaryote Eukaryote f. Cytoplasm Prokaryote Eukaryote g. DNA Prokaryote Eukaryote 16. The movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane is a. Exocytosis b. Phagocytosis c. Endocytosis d. Osmosis 17. A substance that moves by passive transport tends to move a. Away from the area of equilibrium b. Away from the area that’s less concentrated c. Away from the area that’s more concentrated d. Toward the area that’s more concentrated 18. Describe the process of diffusion, including the word equilibrium in your answer. 19. What is the relationship between diffusion and osmosis? 20. What is the difference between passive and active transport? 21. What would happen to a sample of your red blood cells if they were placed in a hypotonic solution? Explain. (Remember, hypotonic is describing where solutes are. If the solution is hypotonic, does it have more solutes or more water?) 22. Which of the following is true of ALL single-celled organisms? a. All are prokaryotic b. All are bacteria c. All reproduce d. All have a nucleus 23. Tissues are composed of a group of a. Similar cells b. Related organelles c. Organ systems d. Related organs 24. Explain the relationship among cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. 25. Describe the relationship among cell specialization, multi-cellular organisms, and homeostasis. 26. Would you expect skin cells to contain more or fewer mitochondria than muscle cells? Explain your answer Can you give an answer to each of the Chapter’s Key Questions? Find each one in the book at the beginning of the section and see if you can answer it without looking it up! Then check the answer in that section to see if you were right! Vocabulary Ch 7 Words Cell Lipid bilayer Cell theory Selectively permeable Cell membrane Diffusion Nucleus Facilitated diffusion Eukaryote Aquaporin Prokaryote Osmosis Cytoplasm Isotonic Organelle Hypertonic Vacuole Hypotonic Lysosome Osmotic pressure Cytoskeleton Homeostasis Centriole Tissue Ribosome Organ Endoplasmic reticulum Organ system Golgi apparatus Receptor Chloroplast Cell junction (not vocab word, but know Mitochondrion this! Cell wall