* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Scientists, Cell Theory and Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
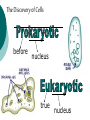
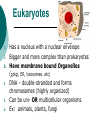
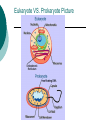
Cell Theory and Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote What is a Cell? Cell – Basic unit of living things. Organisms are either: Unicellular – made of one cell such as bacteria and amoebas. OR Multicellular – made of many cells such as plants and animals. Scientists to Remember Robert Hooke (1665) – Observed “cells” in cork Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1674) Father of Microscopy Saw tiny living things in pond water. Cell Theory Confirmed discoveries that all scientists believe to be true about cells: 1. Cells are the basic unit of life. 2. All living things are made of cells. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. Microscopes Light Microscope – magnifies tiny organisms up to 1,000 times. -Uses light and lenses. -We use these. Electron Microscope – magnifies up to a million times. -Uses electrons. The Discovery of Cells before nucleus true nucleus Eukaryotes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Has a nucleus with a nuclear envelope Bigger and more complex than prokaryotes Have membrane bound Organelles (golgi, ER, lysosomes…etc) DNA – double-stranded and forms chromosomes (highly organized) Can be uni- OR multicellular organisms Ex: animals, plants, fungi Prokaryotes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. NO nucleus NO membrane bound organelles (just ribosomes) ALL are unicellular Smaller than eukaryotic cells Forerunner to eukaryotic cells (smaller and more simple) DNA – single strand and circular Ex: ALL Bacteria Similarities 1. Contain all four biomolecules (lipids, carbs, proteins, and nucleic acids) 1. Have ribosomes 2. Have DNA 3. Similar Metabolism 4. Can be unicellular 5. Have cell/plasma membranes or cell wall Eukaryote VS. Prokaryote Picture