* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DEF: colored body
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
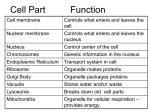
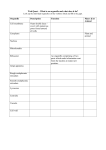
Name: Date: Period: CW#: Cell Organelles: Cells take on a variety of shapes and sizes based on their function. For example, plant cells, that specialize in photosynthesis and that lack the ability to move, appear very different from cells found in the sides of our cheeks. Similarly, nerve cells that function to send messages throughout our body appear very different from white blood cells that protect our body from infection. However, even with all of these differences, there are many similarities among all cells. In the following activity, you record the size of the organelle (in the scale provided), address the function of this organelle, and make an analogy of this organelle to something more familiar to you. Organelle Name/Image Size/Shape Function This is the size of the plant cell. This is the outermost part of a plant cell. This is the part of a plant cell that gives the cell shape and helps to support the plant. The cell wall is made of cellulose – a tough molecule that is hard to break down through digestion. Cell Wall – PLANTS and FUNGI Cell Membrane Analogy This organelle is like a/n: because: Homeostasis This is the size of the cell. The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is the outermost part of an animal cell. This part of ALL cells allows some, but not all things INTO and OUT of the cell. This watery liquid fills the entirety of the cell membrane. Fills up the cell to give the cell structure. It provides a watery environment for all cell functions. (Mostly water) Homeostasis This protects the cell as well (especially animal cells). This organelle is like a: because: Homeostasis This organelle is like a: because: DEF: cell, liquid Cytoplasm 2 m x 8m oval shaped Chloroplasts - PLANTS one, to many, in a PLANT cell, membranes inside Create sugar or carbohydrates using water, sun and CO2. This organelle is like a: METABOLISM because: They break down or use sugar to make ATP. This organelle is like a: DEF: colored body 1 m x 2m oval shaped many in a cell ATP is the energy units used by cells to do work. membranes inside METABOLISM 21 nm in diameter These make PROTEINS from smaller pieces called amino acids (the instructions for making PROTEIN come form DNA) because: Mitochondria 2 subunits float in the cytoplasm OR are attached to the ER This organelle is like a: because: HOMEOSTASIS Ribosomes Big membrane found all over the cell, generally near the nucleus. Starts packaging process for proteins and sends the package to the Golgi Apparatus. HOMEOSTASIS Endoplasmic Reticulum This organelle is like a: because: Big membrane found everyone in the cell – always near the ER. Transports materials around the cell and out of the cell. This organelle is like a: MAKES VESICLES! because: HOMEOSTASIS Golgi Apparatus 200 nm in diameter on average. These can hold water, food, waste, digestive enzymes/proteins… Circular bubbles all over cells. For removal or storage of these items… HOMEOSTASIS This organelle is like a: because: Vesicles/Vacuoles 25 nm by 1 nm throughout the cell These proteins give a cell support and structure. They are used to help a cell move AND to move things around a cell. This organelle is like a: because: HOMEOSTASIS Microtubules/filaments & Cytoskeleton 15 to 80 m – the size depends on how much water is in the plant cell. Large water sacks that help give a plant its structure – it helps the plant stand up straight and not WILT. HOMEOSTASIS Central Vacuole – PLANTS This organelle is like a: because: 5m in diameter, usually round like a ball This holds the DNA and keeps it safe. This is where RNA is made. This organelle is like a: HOMEOSTASIS because: These holes allow things in and out of the nucleus. This organelle is like a: Nucleus 50 nm in diameter – these are holes in the nucleus membrane DNA is too big to fit through these holes. RNA can fit through these holes. because: HOMEOSTASIS Nuclear Pores Small dark patch inside the nucleus This is the site of DNA transcription (parts of DNA are copied into a different form called RNA). HOMEOSTASIS+ This organelle is like a: because: Nucleolus 2 nm by 6 cm! (average human) This is the CODE or instructions for making PROTEINS (all cell structures and all cell functions!). This organelle is like a: long, long molecule Chromatin/Chromosomes and DNA HEREDITY because: Long, thin, tail-like structure (made of microtubules) This helps a cell to move or swim. This organelle is like a: HOMEOSTASIS because: Flagella – mostly ANIMALS Short and finger-like projections from a cell membrane These microvilli help a cell to This organelle is like a: increase its surface area (for bringing food/waste into and out of a cell). Also, these can move to help move OTHER things to cells in because: different directions. HOMEOSTASIS Microvilli – mostly ANIMALS Bundles of microtubules Used in cell division – anchors microtubules to form a web of them inside a cell to help pull things apart to separate into two cells. This organelle is like a: because: Centrioles – mostly ANIMALS REPRODUCTION Small hairs Cilia – mostly ANIMALS These help a cell to move or swim. This organelle is like a: HOMEOSTASIS because: