* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
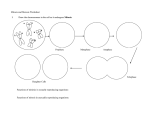
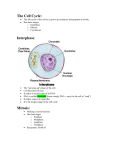
BI102: GENERAL BIOLOGY WINTER, 2007 MIDTERM #3B Student Name: 1. Which of these sequences correctly describes the cell cycle? A) G1 => G2 => S => prophase => metaphase => anaphase => telophase B) S => G2 => prophase => metaphase => anaphase => telophase => G1 C) G1 => S => G2 => prophase => anaphase => metaphase => telophase D) prophase => metaphase => telophase => anaphase => G1 => S => G2 E) G1 => S => G2 => metaphase => prophase => anaphase => telophase Answer questions 2 through 5 by matching the term on the left with the definition on the right 2. 3. 4. 5. centromere chromatid diploid cells homologs A. a single DNA molecule B. chromosomes with the same genes, but may have different alleles C. contain pairs of homologous chromosomes. D. point of attachment of the replicated arms of a chromosome. Using the following phases of the cell cycle as answers, pick the single most correct choice for each of the statements numbered 6 through 9. A. S B. G1 C. G2 D. Cytokinesis E. All of these 6) Spindle proteins are made. 7) DNA synthesis occurs. 8) Most cell growth occurs. 9) chromosomes composed of two attached chromatids Answer questions 10 through 13 by matching the following. Each choice may be used more than once. A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Telophase D. Anaphase E. Interphase 10) Chromosomes move to the equator 11) Chromosomes duplicate 12) Chromosomes shorten and thicken 13) Sister chromatids move to opposite poles 14) Homologous chromosomes pair up (synapsis) during A) mitosis. B) meiosis I. C) meiosis II. D) mitosis and meiosis II. E) protein synthesis. 15) Centromeres split during A) anaphase I and anaphase II of meiosis. B) anaphase of mitosis and anaphase I of meiosis. C) cytokinesis of mitosis and meiosis I D) the S portion of interphase. E) anaphase of mitosis and anaphase II of meiosis. 16) The chromosome number is reduced from diploid to haploid during A) mitosis. B) meiosis I. C) meiosis II. D) interphase. E) S phase of mitosis. 17) Haploid cells A) can result from meiosis. B) cannot be produced by mitosis. C) function as gametes or spores in sexually reproducing organisms. D) have one member of each pair of homologous chromosomes. E) Both choices A and C are correct. 18) If there are 12 chromosomes in a cell that has just completed meiosis II, what is the diploid number of chromosomes for that organism? A) 6 B) 12 C) 24 D) 24 pairs E) either 6 or 24, depending on the cell type 19) Chromosomes of a homologous pair separate from each other during A) anaphase I. B) metaphase I. C) prophase II D) anaphase II E) metaphase II. 20) Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Meiosis separates homologous chromosomes in a diploid cell to produce haploid daughter cells containing one copy of each type of chromosome. B) During prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange DNA. C) During meiosis II, paired homologous chromosomes move up to the equator of the cell. D) During anaphase I, homologous chromosomes separate. E) In meiosis II, the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate. Answer questions 21 through 25 by matching the following term to its number in either of these two diagrams. Each choice may be used more than once or not at all. A. DNA B. mRNA C. translation D. transcription E. protein Answer questions 26 through 28 by matching the following term to its number in either of these two diagrams. Each choice may be used more than once or not at all. A. anticodon B. peptide bond formation C. codon D. tRNA E. mRNA 29) Which is NOT found in DNA? A) adenine B) deoxyribose sugar C) phosphate group D) phospholipid group E) thymine 30) In Griffith's experiments, what happened when heat-killed S-strain pneumococcus were injected into a mouse along with live R-strain pneumococcus? A) DNA from the live R-strain was taken up by the heat-killed S-strain, converting them to R-strain and killing the mouse. B) DNA from the heat-killed S-strain was taken up by the live R-strain, converting them to S-strain and killing the mouse. C) Proteins released from the heat-killed S-strain killed the mouse. D) RNA from the heat-killed S-strain was translated into proteins that killed the mouse. E) nothing 31) The correct structure of a nucleotide is A) phosphate-5 carbon sugar-nitrogen base. B) phospholipid-sugar-base. C) phosphate-sugar-phosphate-sugar. D) adenine-thymine and guanine-cytosine. E) base-phosphate-glucose. 32) The two polynucleotide chains in a DNA molecule are attracted to each other by A) covalent bonds between carbon atoms. B) covalent bonds between phosphates & sugars. C). hydrogen bonds between bases D) ionic bonds between "R" groups in amino acids E). peptide bonds between amino acids. 33) The DNA of a certain organism has guanine as 30% of its bases. What percentage of its bases would be adenine? A) 0% B) 10% C) 20% D) 30% E) 40% 34) In the comparison of a DNA molecule to a twisted ladder, the uprights of the ladder represent A) hydrogen bonds between bases. B) deoxyribose linked to phosphates. C) deoxyribose linked to sulfates. D) nitrogenous bases linked to phosphates. E) nitrogenous bases linked together. 35) The sequence of subunits in the DNA "backbone" is A) --base--phosphate--base--phosphate--base--phosphate-. B) --phosphate--sugar--phosphate--sugar--phosphate--sugar. C) --sugar--base--sugar--base--sugar--base--sugar--base-. D) --base--sugar--phosphate--base--sugar--phosphate-. E) --base--phosphate--sugar--base--phosphate--sugar-. 36) How does the Watson and Crick model of DNA structure help explain DNA replication? A) Deoxyribose sugar always bonds to a nitrogenous base. B) Four types of bases are found in DNA. C) Phosphate groups always bond to deoxyribose sugar. D) Precise base pairing allows the base sequence to be copied. E) The number of purines equals the number of pyrimidines. 37) Which of the following is TRUE about the accuracy of DNA replication? A) Many errors are made during DNA replication, but this does not matter because repair enzymes will mend the errors. B) Many errors are made during DNA replication, but this does not matter because of the immense size of the DNA molecule. C) The few errors made by DNA polymerase are usually corrected by repair enzymes. D) DNA polymerase makes very few errors, so no repair enzymes are needed. E) DNA polymerase always makes a perfect copy of the original DNA. Answer questions 38 through 40 by matching the following term to its number in the diagrams. Each choice may be used more than once or not at all. A. 3’ end B. origin of replication C. helicase D. 5’ end E. makes sure that complementary base pairing occurs 41) According to the Law of Segregation, in an organism with the genotype Aa A) all the gametes will have gene a. B) half the gametes will have A and half will have a C). all the gametes will have gene A D) 3/4 of the gametes will have A and 1/4 will have a. E) 1/4 of the gametes will have A and 3/4 will have a. 42) When genes are linked, the reason a few of the recombinant genotypes still occur in the offspring is because of A) crossing over. B) linkage. C). mutation D) natural selection. E) independent assortment. 43) Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Individuals with the same genotype might have different phenotypes. B) Matings between individuals with dominant phenotypes cannot produce offspring with recessive phenotypes. C) Matings between individuals with recessive phenotypes usually do not produce offspring with dominant phenotypes. D) Individuals with the same phenotype might have different genotypes. E) All of the above choices are correct. Answer questions 44 through 47 by matching the following. Each choice may be used more than once A. Genotype B. Incomplete dominance C. Heterozygote D. Homozygote E. Phenotype 44) An individual having 2 identical alleles at a particular locus. 46) The entire genetic constitution of an individual. 45) The Bb individual. 47) The appearance of a Bb individual. 48) The failure of chromosomes to segregate properly during meiosis is called A) nondisjunction. B) translocation. C) replication. E) independent assortment. D) inversion. Answer numbers 49 and 50 by filling in selection “A” on your answer sheet if the answer is true an “B” if the statement is false 49) Females who receive sex-linked genes always express them. 50) Only males can express sex-linked traits. 51. Diagram a cross between heterozygotes for both the “B” and the “E” genes if the e gene is sex linked Only answers within the boxes will be graded Genotypic ratio: Phenotypic ratio: 52. Determine the genotype and phenotype of the parents that produced a litter with equal numbers of yellow and chocolate puppies The boxes below are provided for your assistance – you don’t have to use them if you don’t need to in order to answer the question. Genotypic ratio: Phenotypic ratio: