* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download word
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Chloroplast DNA wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
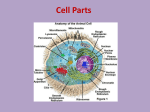
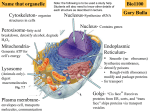
BL 424 Study guide Test 2 (Chapts 8-12) post as word file Organelles and structures/components: components and function Nucleus - Nucleolus - Nuclear membrane - Nuclear Pore complex - Nuclear lamina Ribosome - polysome Proteasome Endoplasmic reticulum - ERGIC Golgi Lysosome Plasma membrane Mitochondria – Matrix- intermembrane space Chloroplast – stroma – thylakoid space, thylakoid membranes Chromoplasts, etioplast, leucoplasts Peroxisome Electron transport chains for oxidative respiration, photosynthesis Cytoskeleton Special signals on mRNA; RNA-RNA hybrids Shine-Delgarno sequence poylA, CAP ribosome scanning for 1st AUG tRNA: mRNA pairing SnoRNAs Micro RNAs or RNAi Primary transcript of rRNA genes vs. final products Special signals on proteins for transport, location etc. NLS, Nuclear Localization sequence; NES, nuclear export sequence KDEL sequence Signal sequence Internal stop-transfer signals GPI anchor Presequence Transit peptide Internal signal sequence Mannose 6 phosphate Modifications to proteins or RNAs and enzymes that do the reactions Phosphorylation – phosphatases, kinases and role of ATP Ubituitination – ubituitin ligase S-S bonds – protein disulfide isomerase Binding of GTP vs. GDP by Ras, Ran, Rab proteins Glycosylation – glycosyl transferase; removal of sugars by glycosidase;N-linked vs. O-linked Addition of lipids Role of chaperones – why are they called ‘heat-shock proteins’ Proteolysis – by signal peptidase, by proteasome Amino acyl tRNA synthetases Splicing of rRNA precursors – primary transcript to processed product Binding of GTP vs. GDP by Actin, by microtubules Matrix processing peptidase, stroma processing peptidase, signal peptidase New terms/ complexes SnRNAs Lamins Flippase SV40 T antigen BiP Mitochondria use some different genetic codes Mitochondria and chloroplasts have genomes ATP synthase Clathrin treadmilling Mechanisms/ transport complexes Translocase Tom complex Tim complex Guidance complex Toc complex Tic complex SRP particle Karyopherins Importins Exportins Actin – subunits, polymerization Actin binding proteins – a-actinin, spectrin, ankyrin, dystrophin Myosin II role, examples of actin-myosin contraction Sarcomere structure Intermediate filaments – subunits, polymerization - keratin Microtubules – subunits, polymerization Microtubule associated proteins – how function Microtubule motor proteins – kinesin, dynein – what they move and what end Adherens junctions, focal adhesions, adhesion belt Cadherins, Desmosomes, Microvilli, pseudopodia, fibroblasts moving Centrosome, centriole Cilia, flagella Chemiosmotic mechanism – compartments in prokaryotes, mitochondria, chloroplast Some lipids Ceramide Cholesterol Sphingomyelin Phospholipids Some drugs and what they affect Cytocholasins Phalloidin Vinblastine Taxol colchicine Human diseases so far: 8 of them by students Basic facts – protein/ mRNA defect – basic characteristics of disease Other human diseases discussed in book How are lipids synthesized – from cytosolic aqueous-soluble precursors and inserted into membranes Topology of compartments – from lumen of ER to Golgi to outside of cell From nucleus to where? General concepts: Consider integral membrane protein in the ER, versus a secreted protein or a nuclear protein. How are they targeted to their locations? What about a ribosomal protein? Draw structure of eukaryotic cell, clearly indicating major subcellular structures, and organelles Opportunities for regulation – of RNA transport, of translation, of post-translational modifications to the protein, of protein transport, protein activity Consider how ribosomes end up on the rough ER versus remaining free ribosomes Consider the cellular compartments transversed by a protein destined for different final destinations – role of aa sequence, modifications, enzymes. Consider what might happen to mutated protein (also pathways for degradation) Clathrin-coated vesicles Consider the basic import of proteins into nucleus, and the role of Ran, importins Consider import into mitochondria, into chloroplasts Consider what catalyzes the peptide bond on the ribosome – evidence for rRNA Models for movement on microtubules Models for actin/myosin and muscle contraction Consider transport of vesicles through cells, separation of chromosomes at mitosis Numbers – if an amino acid weights 110 daltons, then a polypeptide of 20 kD (20,000 daltons) has _____ amino acids. (about largest size that can passively diffuse through nuclear pore; most proteins need to be actively transported through nuclear pore).