* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell: Smallest Unit of Life
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
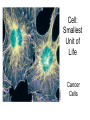
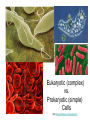
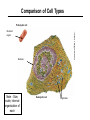
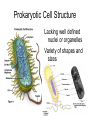
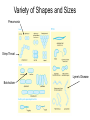
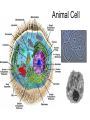
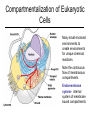
1,000 Cell: Smallest Unit of Life Cancer Cells SEM 2,000 Eukaryotic (complex) vs. Prokaryotic (simple) Cells http://www.cellsalive.com/howbig.htm How Life is Organized Eukaryotic Cell Plan How Life is Organized Prokaryotic Cell Plan Eukaryotic Cell Plan Comparison of Cell Types Prokaryotic cell Colorized TEM 15,000 Nucleoid region Nucleus Note - Size, scale, internal organization of each Eukaryotic cell Organelles Scale of Life Cells are limited in size because of surface area to volume ratio Too large a cell too much volume and not enough exchange with environment Smaller cells less volume so easier for cell membrane to meet metabolic demand of the cell Prokaryotic Cell Structure Lacking well defined nuclei or organelles Variety of shapes and sizes Variety of Shapes and Sizes Pneumonia Strep Throat Lyme’s Disease Botchulism Animal Cell Compartmentalization of Eukaryotic Cells Many small enclosed environments to create environments for unique chemical reactions. Note the continuous flow of membranous compartments Endomembrane system- internal system of membrane bound compartments Plant Cell Note the differences in structure to animal cell. What are similarities?