* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10th Grade Genetics Content - Red Clay Secondary Science Wiki
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
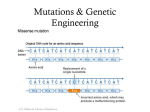
10th Grade Genetics Content K-U-D Topic: Storage of Genetic Information Which Standards are students learning in this unit? Standard 7.1.A Hereditary/genetic information in chromosomes is contained in molecules of DNA. Genes are sections of DNA that direct syntheses of specific proteins associated with traits in organisms. These consist of various combinations of four different nucleotides that encode this information through their sequences.(Essential) By the end of this unit, students will be able to… Know: Vocabulary: DNA Nucleotide Sugar-Phosphate backbone Genome Complementary base pair Understand: Do: The structure and constituent Isolate and observe DNA parts of the DNA molecule are from multiple sources (plant, directly related to its function. animal, bacteria) Describe the physical structure of a DNA molecule. Students can construct model of DNA Topic: Transmission of Genetic Information From Cell to Cell Which Standards are students learning in this unit? Standard 6.4.A Certain chemicals pathogens and high energy radiation seriously impair normal cell functions and the health of the organism (compact) Standard 7.1.C Mutations in DNA of organisms normally occur spontaneously at low rates, but can occur at higher rates (i.e., exposure to pathogens, radiation and some chemicals). Most mutations have no effect on the organisms, but some may be beneficial or harmful depending on the environment. (Essential) Standard 7.1.D Only random mutations in gametes can create the variation that is inherited by an organism’s offspring. Somatic mutations are not inherited, but may lead to cell death, uncontrolled growth, or cancer. (Important) Standard 7.1.E During the cell cycle, DNA of the parent cell replicates and the cell divides into two cells that are identical to the parent. This process is used for growth and repair of body tissues and for asexual reproduction.(Essential) By the end of this unit, students will be able to… Know: Vocabulary: Asexual reproduction Chromatid Chromosomes Mitosis Allele Crossing over Gamete Genes Meiosis Diploid Fertilization Haploid Independent assortment Karyotype Sexual reproduction Somatic cell Mutation Understand: Do: The cell cycle is an orderly process that results in new somatic cells that contain an exact copy of the DNA that make up the genes and chromosomes found in the parent somatic cells. Explain how the cell cycle contributes to reproduction and maintenance of the cell and/or organism. Explain how the type of cell (gamete or somatic cell) in which a mutation occurs determines heritability of the mutation. Explain how mutation and sexual reproduction increase variation in a population. Variation increases population’s survivability. a Topic: Expression of Genetic Material Which Standards are students learning in this unit? Standard 6.1.F Cells store and use information to guide their functions. DNA molecules in each cell carry coded instructions for synthesizing protein molecules. The protein molecules have important structural and regulatory functions. (Essential) Standard 6.4.B The scientific investigation of cellular chemistry enables the biotechnology industry to produce medicines foods and other products for the benefit of society (Essential) Standard 7.1.A Hereditary/genetic information in chromosomes is contained in molecules of DNA. Genes are sections of DNA that direct syntheses of specific proteins associated with traits in organisms. These consist of various combinations of four different nucleotides that encode this information through their sequences. (Essential) Standard 7.1.C Mutations in DNA of organisms normally occur spontaneously at low rates, but can occur at higher rates (i.e., exposure to pathogens, radiation and some chemicals). Most mutations have no effect on the organisms, but some may be beneficial or harmful depending on the environment. (Essential) Standard 7.2.A Evolution is a change in allelic frequencies of a population over time. The theory of evolution is supported by extensive biochemical, structural, embryological, and fossil evidence (Essential) Standard 7.2.E Organisms are classified into a hierarchy of groups and subgroups based on similarities in structure, comparisons in DNA and protein and evolutionary relationships. (Compact) Standard 7.2.G Biological evolution is the foundation for modern biology and is used to make predictions for medical, environmental, agricultural and other societal purposes. (Essential) Standard 7.3.A The expanding ability to manipulate genetic material, reproductive processes, and embryological development creates choices that raise ethical, legal, social, and public policy questions. (Compact) Standard 7.3.B Recombinant DNA technology, which is a form of genetic engineering, involves the insertion of DNA from one cell into a cell of a different organism where the inserted DNA is expressed. Genetic engineering is being applied in biology, agriculture, and medicine in order to meet human wants and needs. (Important) By the end of this unit, students will be able to… Know: Understand: Vocabulary: Mutations may be harmful, DNA beneficial, or have no impact on Codon the survival of the organism. Gene expression Nucleotide Genetic engineering is a process Protein by which a gene that is not Protein synthesis naturally occurring in an RNA organism is inserted into its tRNA genome thereby altering the mRNA organism’s phenotype. rRNA transcription Translation Chromosome Gene expression Mutations in DNA sequences of a gene may or may not affect the expression of the gene. Do: Illustrate how a sequence of DNA nucleotides codes for a specific sequence of amino acids. Predict the possible outcome of specific genetic mutations or of a specific genetic modification carried out by humans. Topic: Transmission of Genetic Information from Generation to Generation Which Standards are students learning in this unit? Standard 6.4.B The scientific investigation of cellular chemistry enables the biotechnology industry to produce medicines foods and other products for the benefit of society (Essential) Standard 7.1.A Hereditary/genetic information in chromosomes is contained in molecules of DNA. Genes are sections of DNA that direct syntheses of specific proteins associated with traits in organisms. These consist of various combinations of four different nucleotides that encode this information through their sequences. (Essential) Standard 7.1.D Only random mutations in germ cells (gametes) can create the variation that is inherited by an organism’s offspring. Somatic mutations are not inherited, but may lead to cell death, uncontrolled cell growth or cancer. (Important) Standard 7.1.F Meiosis is the production of sex cells (gametes). The production and release of these gametes is controlled by hormones. In meiosis, the number of chromosomes is reduced by one-half and chromosomes may randomly exchange homologous parts to create new chromosomes with combinations not necessarily found in the parent cell. (Essential) Standard 7.1.G Upon fertilization, the fusion of the gametes restores the original chromosome number, and new gene combinations lead to increased genetic variation, which, in turn, increases the likelihood of survival of the species. (Essential) Standard 7.1.I Embryological development in plants and animals involves a series of orderly changes in which cells divide and differentiate. Development is controlled by genes whose expression is influenced by internal factors (i.e., hormones) and may also be influenced by environmental factors (i.e., nutrition, alcohol, radiation, drugs, and pathogens). Alteration in this balance may interfere with normal growth and development. (Compact) By the end of this unit, students will be able to… Know: Understand: Vocabulary: Organisms reproduce, develop, have predictable life cycles, and Allele pass on heritable traits to their Dominant offspring. Gene Genotype The development of technology Phenotype has allowed us to apply our Punnett square knowledge of genetics, Recessive reproduction, development and Co-dominance evolution to meet human needs Heterozygous and wants. Homozygous Incomplete dominance Karyotypes Sex-linked trait Trisomy Do: Use Punnett squares, including dihybrid crosses, and pedigree charts to determine probabilities and patterns of inheritance (i.e. dominant/recessive, codominance, sex-linkage, multiallele inheritance) Analyze a karyotype to determine chromosome numbers and pairs. Compare normal and abnormal karyotypes. Use characteristics of offspring can help determine the genotype of parent organisms. (phenotypes) Topic: Patterns of Inheritance/Bioethical Issues Which Standards are students learning in this unit? Standard 6.4.D Biotechnology is a growing international field of research and industry. Many scientists including those in Delaware are conducting cutting edge research in the field of biotechnology. (Compact) Standard 7.1.A Hereditary/genetic information in chromosomes is contained in molecules of DNA. Genes are sections of DNA that direct syntheses of specific proteins associated with traits in organisms. These consist of various combinations of four different nucleotides that encode this information through their sequences. (Essential) Standard 7.1.B Known patterns of inheritance can be used to make predictions about genetic variation. (Important) Standard 7.1.H The sex chromosomes contain different genes, and therefore, certain traits will show patterns of inheritance based on gender. (Important) Standard 7.2.G Biological evolution is the foundation for modern biology and is used to make predictions for medical, environmental, agricultural and other societal purposes. (Essential) Standard 7.3.A The expanding ability to manipulate genetic material, reproductive processes, and embryological development creates choices that raise ethical, legal, social, and public policy questions. (Compact) Standard 7.3.B Recombinant DNA technology, which is a form of genetic engineering, involves the insertion of DNA from one cell into a cell of a different organism where the inserted DNA is expressed. Genetic engineering is being applied in biology, agriculture, and medicine in order to meet human wants and needs. (Important) By the end of this unit, students will be able to… Know: Understand: Vocabulary: By understanding the structure and function of DNA and the DNA processes by which DNA directs Electrophoresis cell activities, scientists can Genetic modification manipulate the code to create new combinations of traits and new varieties of organisms. Knowing how to modify genetic code does not answer the question of what will happen once the genes are inserted into the general population. Do: Evaluate the risks and benefits of various ethical, social and legal scenarios that arise from the ability to manipulate genetic material and reproductive processes.