* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gene Section SRSF3 (serine/arginine rich splicing factor 3) -
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Alternative splicing wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
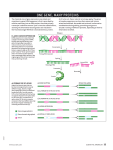
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology INIST-CNRS OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL Gene Section Short Communication SRSF3 (serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 3) Rong Jia, Zhi-Ming Zheng School of Stomatology Wuhan University, PR. China (RJ), Tumor Virus RNA Biology Section, HIV and AIDS Malignancy Branch, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, NIH, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA (ZMZ) Published in Atlas Database: May 2012 Online updated version : http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Genes/SRSF3ID42279ch6p21.html DOI: 10.4267/2042/48232 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2012 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Identity Expression Other names: SFRS3, SRp20 HGNC (Hugo): SRSF3 Location: 6p21.31 Expression of SRSF3 varies significantly in different cell types. For example, the expression of SRSF3 is abundant in the undifferentiated or intermediately differentiated keratinocytes in the basal and parabasal layers, but drops significantly in terminally differentiated keratinocytes in the superficial layers of the cervix or skin. In general, normal cells like muscle or nerve cells have no or little expression of SRSF3. In contrast, malignant tumor cells express remarkable amount of SRSF3 when compared to their normal counterparts. DNA/RNA Description SRSF3 gene contains 6 exons and spans 10155 bp on the plus (+) strand of the short arm of chromosome 6. Transcription SRSF3 mRNA is in size of 3144 nts and encodes a protein with 164 amino acid residues. By including an alternative exon between exon 3 and exon 4, SRSF3 pre-mRNA could generate additional isoform of SRSF3 transcript. Localisation SRSF3 is a shuttling protein between nucleus and cytoplasm. Pseudogene Function No. SRSF3 is a splicing factor and involved in the regulation of RNA splicing. It affects alternative splicing by interacting with RNA cis-elements in a concentration and cell differentiationdependent manner. Protein Description 164 amino acid residues, 20 kDa. Diagram of genomic structure of SRSF3 gene. The numbers above the diagram are the nucleotide positions in SRSF3 gene. The open boxes and broken lines represent exons and introns, respectively. Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2012; 16(11) 838 SRSF3 (serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 3) Jia R, Zheng ZM Diagram of protein structure of SRSF3. The numbers below the diagram are the amino acid positions in SRSF3 protein. SRSF3 has an RNA recognition motifs (RRM) in the N-terminus and an arginine/serine-rich domain (RS) at the C-terminus. RRM motif identifies and binds specific RNA sequences. RS domain interacts with other proteins and facilitates recruitment of the spliceosomal components. The serine residues of the RS domain can be phosphorylated. Moreover, SRSF3 plays important roles in RNA export from nuclear to cytoplasm, termination of transcription, alternative RNA polyadenylation, and protein translation. SRSF3 is required for embryonic development and cell cycle progression. SRSF3 at increased expression is tumorigenic and is required for tumor initiation, progression, and maintenance. Alternative splicing of pre-mRNA SRSF3 controls viral early to late switch by regulation of gene expression of bovine papillomavirus type 1 and human papillomavirus through interaction with A/Crich RNA elements (Jia et al., 2009). SRSF3 promotes the inclusion of exon 4 of its own mRNA and reduces the expression of full length SRSF3 protein (Juma and Nielsen, 1997). SRSF3 activates the inclusion of exon 10 of PK-M gene to promote the expression of oncogenic M2 isoform (Wang et al., 2012). SRSF3 inhibits the inclusion of a fibronectin cassette exon in the mature mRNA by interacting with RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain (de la Mata and Kornblihtt, 2006). Termination of transcription SRSF3 plays a role in termination of transcription by binding to RNA downstream of the cleavage site, facilitating its degradation, and the release of Pol II from template DNA (Cui et al., 2008). Alternative polyadenylation The 3'-terminal exon 4 of calcitonin pre-mRNA contains an alternative polyadenylation site. SRSF3 affects the inclusion of exon 4 and alternative polyadenylation by the interaction with CstF (Lou et al., 1998). RNA export SRSF3 associates with TAP promoting the export of intronless mRNA of histone H2a gene by interacting with a 22-nt RNA element (Huang et al., 2003; Huang and Steitz, 2001). Protein translation SRSF3 is required for poliovirus translation initiation. SRSF3 binds to internal ribosome entry site (IRES) of a viral RNA by interaction with PCBP2 (Bedard et al., 2007). SR (serine/arginine-rich) family and shares a high homology with other members. All of SR proteins contain at least one RRM and one downstream RS domain enriched in repeating arginine-serine dipeptides. Mutations Note There is one mutation which causes amino acid residue change according to NCBI dbSNP database. Implicated in Cancer Note SRSF3 is a protooncogene. Overexpression of SRSF3 has been found in various cancers, including cervix, lung, breast, stomach, skin, bladder, colon, liver, thyroid, and kidney; and in various soft tissue tumors, including B-cell lymphoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, hemangioendothelioma, hemangiopericytoma, neurofibroma, neurilemmoma, liposarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, histiocytoma, and synovial sarcoma. SRSF3 at overexpression has transformation activity for MEF/3T3 cells, a mouse embroynic fibroblast cell line. SRSF3 controls cell cycle progression and thereby cell proliferation presumably by regulating the expression of forkhead box transcription factor M1 (FoxM1), PLK1 and Cdc25B. References Jumaa H, Nielsen PJ. The splicing factor SRp20 modifies splicing of its own mRNA and ASF/SF2 antagonizes this regulation. EMBO J. 1997 Aug 15;16(16):5077-85 Lou H, Neugebauer KM, Gagel RF, Berget SM. Regulation of alternative polyadenylation by U1 snRNPs and SRp20. Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Sep;18(9):4977-85 Huang Y, Steitz JA. Splicing factors SRp20 and 9G8 promote the nucleocytoplasmic export of mRNA. Mol Cell. 2001 Apr;7(4):899-905 Homology Huang Y, Gattoni R, Stévenin J, Steitz JA. SR splicing factors serve as adapter proteins for TAP-dependent mRNA export. Mol Cell. 2003 Mar;11(3):837-43 Human SRSF3 protein is highly conserved in chimpanzee, dog, sheep, cow, mouse, rat, chicken, zebrafish and so on. SRSF3 is the smallest member of de la Mata M, Kornblihtt AR. RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain mediates regulation of alternative splicing by SRp20. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006 Nov;13(11):973-80 Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2012; 16(11) 839 SRSF3 (serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 3) Jia R, Zheng ZM Bedard KM, Daijogo S, Semler BL. A nucleo-cytoplasmic SR protein functions in viral IRES-mediated translation initiation. EMBO J. 2007 Jan 24;26(2):459-67 Jia R, Li C, McCoy JP, Deng CX, Zheng ZM. SRp20 is a protooncogene critical for cell proliferation and tumor induction and maintenance. Int J Biol Sci. 2010 Dec 15;6(7):806-26 Cui M, Allen MA, Larsen A, Macmorris M, Han M, Blumenthal T. Genes involved in pre-mRNA 3'-end formation and transcription termination revealed by a lin-15 operon Muv suppressor screen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Oct 28;105(43):16665-70 Wang Z, Chatterjee D, Jeon HY, Akerman M, Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Krainer AR. Exon-centric regulation of pyruvate kinase M alternative splicing via mutually exclusive exons. J Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Apr;4(2):79-87 This article should be referenced as such: Jia R, Liu X, Tao M, Kruhlak M, Guo M, Meyers C, Baker CC, Zheng ZM. Control of the papillomavirus early-to-late switch by differentially expressed SRp20. J Virol. 2009 Jan;83(1):167-80 Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2012; 16(11) Jia R, Zheng ZM. SRSF3 (serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 3). Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2012; 16(11):838840. 840