* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure and Function of Membranes
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
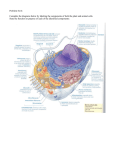
Structure and Function of Membranes Chapter 7 What you need to know! • Why membranes are selectively permeable. • The role of phospholipids, proteins, and carbohydrates in membranes. Plasma Membrane (PM) of animal/plant cells and organelles • Barrier between interior and exterior • Maintains homeostasis • Allow for compartmentalization (eukaryotes) • PM is selectively permeable for gas, H2O, entering nutrients, exiting waste • Blocks harmful substances, microorganisms • Controls ion exchange • Made from phospholipids Phospholipids • Phospholipids form a bilayer in aqueous solutions • the heads (phosphate groups) are polar (hydrophilic) and will form the two outer faces • the fatty acid tails are hydrophobic and point toward the inside Fluid Mosaic Model • Structure can be observed with EM • Mosaic of floating phospholipids with cholesterol, proteins, glycoproteins, and glycolipids embedded • Held together by hydrophobic/hydrophilic interaction and cytoskeleton attached to desmosomes. • Flexible and in constant motion – Think of a soap bubble skin rather than saran wrap • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rl5EmUQd kuI Fluidity: • Phospholipid molecules move around constantly • Fluidity regulated by different kinds of fatty acid (FA) tails: • More unsaturated FA, membrane stays fluid at lower temp (winter) • More saturated FA, membrane is more stable at high temperatures (summer) • Cholesterol embedded in animal membranes, keeps FA tails from twisting together Membrane Molecules • Integral – proteins that are embedded in the bilayer – – • contain hydrophilic ends and hydrophobic midsections to mimic the phospholipids Transmembrane proteins span the entirety of the bilayer (stick out on both ends) Peripheral proteins: not embedded but loosely attached (usually to integral proteins) Transmembrane Proteins 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Transport Enzymatic Signal transduction Cell-cell recognition Intercellular joining Attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix (ECM) Membrane Molecules • • Peripheral Proteins loosely connected on only one side of the membrane Membrane bound pigments in plants • • Chlorophylls Carotenoids Both sides of the membrane are not identical: • Cytoplasmic side • Extracellular side Animals: Extracellular Matrix (ECM) • Glycoproteins = carbohydrates attached to proteins for self recognition/immune system • Collagen fibers for connectivity Plants: Cell wall (1st, middle lamella, 2nd) Intrercellular Connections: Animals: • Tight Junctions: allowing movement of material across cell layer/preventing movement of material between cells: digestive system, epithelial cells • Desmosomes: tight connection of adjacent cells under high physical stress (muscle, cartilage), attached to cytoskeleton • Gap-Junctions: intercellular ion and small molecules transfer Intrercellular Connections: Plants: • Plasmodesma: channel between plant cells where ER goes through (desmotubule)