* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
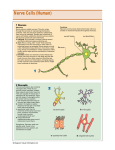
The Nervous System Chapter 11 Functions of the Nervous system I Sensory (input): Light Sound Touch Temperature Taste External Chemical Smell Internal Chemical Pressure Stretch Functions of the Nervous system II Integration: Integration means making sense of sensory input. Analyzing stimuli based on experience, learning, emotion & instinct and reacting in a useful way (you hope). Motor (output): The response to the sesnsory input and subsequent integration. Sending signals to the muscles and other organs of the body instructing them how to respond to the stimuli. The Basic Scheme Organization of the Nervous system The CNS compared with the PNS Support Cells of the Nervous system the Central Nervous System Astrocytes Microglia Oligodendrocytes Ependymal Cells the Peripheral Nervous System Schwann Cells (a.k.a. Neurolemmocytes) Satellite Cells Astrocytes & microglia Astrocytes & microglial cells protect the neurons of the CNS. Astrocytes & microglia Functions of astrocytes: 1. Connect neurons to capillaries. This makes up the “blood-brain barrier”. 2. Maintain the the electrochemical environment • Capture and recycle neurotransmitters • Absorb and return K+ and other ions. • Connected to one another and capable of communicating via gap junctions. Function of microglial cells: 1. Dendritic macrophages that phagocytize microbes and necrotic (dead) tissue. Ependymal Cells & oligodendrocytes Ependymal Cells & oligodendrocytes Functions: Ependymal Cells - Line the ventricles of the brain an central cnal of the spinal cord. They aid in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Oligodendrocytes - These cells have processes that wrap around the axons of neurons. This creates an insulation coating called a myelin sheath. Schwann Cells & satellite cells •These are the suport cells in the peripheral nervous system. •Schwann cells provide the myelin sheath for peripheral axons. •Satellite cells serve a slightly similar function to astrocytes, supporting the cell bodies of peripheral neurons. Neurons - the “action cells” Characteristics of neurons Long-lived Generally last a life time with 90% are formed by the time you are 6 years old. The rest are produced when as you go through puberty. Amitotic Until recently it was thought that neurons didn’t regenerate at all! Some may but generally what you have at adulthood is all you get. High metabolic rate This means high oxygen demand and lots of mitochondria. Neurons also require glucose. Myelin Myelin is a lipidrich component of the cell membranes of Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes. It acts kind of like the insulation on an electrical wire. The cycle of an Action Potential Anatomy of an Action Potential A Basic Neural Circuit Type of neurons Three structural classes of neurons Multipolar Most numerous Many dendrites Motor and association neurons Unipolar Second most numerous Rounded body with one process Somatic & general sensory neurons Bipolar Least common, found in special sensory organs Comparison of neuron types Functional categories of neurons