* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 13 - lanoue
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Mental chronometry wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
The brain of an average-sized adult weighs about three pounds,
yet the amount of information it contains is amazing!
Ch 13 – PNS &
Reflex Activity
Read 442, 445 – 464. Review eye anatomy & learn
structures and functions (complete 11 terms last slide).
1.
2.
3.
4.
Learning Objectives
Describe the major responsibilities of the PNS.
Recognize that reaction times are controlled with the
assistance of the PNS.
Discuss the 5 types of sensory receptors and what they
do.
Identify and explain the structures and function of the
eye.
Reaction Time
Need 2 Volunteers – 1 is the “catcher”; 1 drops ruler between their
partner’s fingers (the “dropper”)
Instructions for Volunteers:
The “Catcher” - Hold your thumb and index finger two inches apart
while your partner drops a ruler between them.
The “Dropper” – hold ruler vertical and drop it between your partner’s
thumb and index finger. The distance the ruler falls before he/she
stops it with his thumb and finger indicates their reaction time.
Repeat twice. Record the results.
Challenge: Try the experiment again while the catcher recites
addition or multiplication facts. Compare the results. What happened
to the reaction time? Why? NOTE: Our reaction time increases
when we are distracted.
With all of our senses, an __________ ______ is passed between
neurons and travels through the nerves, spinal cord, and brain.
PNS
• Motor (efferent)
division
• Sensory (afferent)
division
PNS
•Provides links to and from the _________ environment
•Conducts these impulses from receptors to the _____
PNS
• The peripheral nervous
system includes the _______
that extend from the brain and
the spinal cord. ("Peripheral"
means "by the surface or the
edge“)
• Our skin has receptors called
________________ that that
allow us to feel pressure and
touch, and __________ that
allow us to feel heat and cold
Other Receptors
• We also have receptors that respond to
light such as those in the retina of the eye
called ________________
• Those that allow us to smell or taste called
__________________
• Some that tell indicate potentially
dangerous stimuli (i.e., searing heat,
extreme cold, excessive pressure) that
could result in pain called ___________
Sensation versus Perception
Survival depends upon sensation and
perception.
• _________ is the awareness of changes
in the internal and external environment
• __________ is the conscious
interpretation of those stimuli
The Eye and Vision
• Vision is our dominant sense because ___
of all sensory receptors are in the eyes
and nearly ____ of the cerebral cortex is
involved in some aspect of visual
processing
• http://lightisreal.com/lightillusion.html?gclid
=CJPjl7Sx5I8CFQdEFQodan3R6w
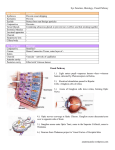
Eye Anatomy
Label your practice diagram
sclera
aqueous humor
choroid
retina
cornea
pupil
optic nerve
iris
lens
blind spot
vitreous humor
Homework & Study Practice
Instructions: Describe each structure and explain its function
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
cornea
pupil
iris
lens
aqueous humor
vitreous humor
sclera
choroid
retina
optic nerve
blind spot