* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Blast-related ocular trauma wikipedia , lookup
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment due to intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Dry eye syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Corneal transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Cataract surgery wikipedia , lookup
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
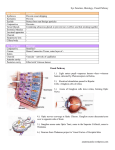
Stamp Anatomy of the Eye 1. Color the following structures: Sclera (yellow), choroid (pink), retina (light blue), lens (purple), pupil (black), cornea (red), Iris (orange) and vitreous body (green) 2. What are the three layers of the eye? And what does each layer consist of? For number 3-22 use the terms in the box to fill in the blanks. Aqueous humor, choroid, ciliary muscle, cones, cornea, fovea centralis, intraocular pressure, iris, lateral rectus muscle, lens, medial rectus muscle, orbicularis oculi, optic disk, optic nerve, pupil, rods, sclera, vitreous body, vitreous humor. 3. ______________________ these cells give rise to color vision, mediate fine detail vision and work in “brighter” light than their counterparts. 4. ______________________ is the beginning of the optic pathway and contains light sensitive cells and neurons which transmit visual impulses to the brain via sensory cells and optic nerves. 5. ______________________ is a thin membrane that lines most of the internal surface of the sclera and contains many blood vessels that help nourish the retina. 6. ______________________ the contraction of this muscle causes the eye to move inward. 7. ________________________ gives shape to the eye, protects the inner parts of the eye, maintains the size of the eye and attaches to muscles that move the eye. This structure is commonly called the “white of the eye”. 8. ______________________ is a clear fluid which provide nourishment for the eye and circulates through both chambers of the eye. 9. ______________________ the contraction of this muscle causes the eye to move outward. 10. ______________________ allow us to see shades of grey and work in low light. 11. __________________ is a hole in the iris through which light passes. This structure changes in diameter in response to changes in the amount of light. 12. ______________________ alters the shape of the lens when viewing objects up close or at a distance. 13. ______________________ the pressure of the fluid inside the eyeball and is maintained by a balance between the production and drainage of the aqueous humor. 14. ___________________ this structure is curved so light bends as it goes through. 15. ____________________________ is the colored part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil. 16. ______________________ allows the eyelids to open and close. 17. ______________________ this area is responsible for sharp central vision which is needed for reading, driving, etc. There is a high concentration of cone cells but rod cells are not present. 18. ____________________ is a hole in the iris which light passes through. 19. ______________________ transmits visual data to the brain. 20. ______________________ prevents the eye from collapsing and hold the retina flush against the choroid. This structure is filled with __________________________. 21. ______________________ is also known as the blind spot due to the fact that this area of the eye lacks both rods and cones. 22. _____________________ refracts light and focuses images onto the retina, this allows us to see clearly. 23. What are the two types of photoreceptors found in the eye? 24. What do zonular fibers do? 25. Which muscles move the eye up and down? 26. T or F The degree of the corneal curvature varies in individuals and helps focus light rays onto the retina