* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download REVIEW ANSWERS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
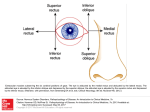
18_Eye 2/29/08 5:12 AM Page 157 4. Indicate which eye muscle would produce the following movements: a. You track an object as it moves from left to right b. You roll your eyes c. You look down to tie your shoes d. You look down at the feet of the person standing to your right 5. You have just had your vision checked. The optometrist tells you that you have 20/30 vision in your right eye and 20/40 in your left eye. What does this mean? 6. Which chamber lies between the cornea and the lens? What type of fluid would be in this chamber? 7. Explain how the lens changes shape for focusing. 8. Where does the optic nerve enter the eye? 9. What is the name of the area that immediately surrounds the fovea centralis? 10. Which cells are involved in color blindness? 11. If your retina was totally devoid of cones, would you be able to see at night? REVIEW ANSWERS 1. a. Sclera b. Choroid c. Retina d. Choroid 18–9 Eye Laboratory Exercise 157 18_Eye 2/29/08 5:12 AM Page 158 2. Excess tear production overloads the nasolacrimal sac. 3. Tears would drain over the lower eyelid & down the cheek. 4. a. Right lateral rectus, left medial rectus b. Superior & inferior rectus muscles and the superior and inferior obliques. c. Inferior rectus d. Superior obliques 5. 20/30 means you can see an object clearly from 20 feet which those with normal vision can see clearly at 30 feet. 20/40 means you can see an object clearly from 20 feet which those with normal vision can see clearly at 40 feet. You will need corrective lenses (eyeglasses or contact lenses). 6. The anterior chamber filled with aqueous humor. 7. Contraction of the ciliary muscle causes an increased tension in the suspensory ligaments which flattens the lens for distance viewing. When the ciliary muscle & suspensory ligaments are relaxed the lens thickens for close-up viewing. This change in shape is called accommodation. 8. Should read “Where does the optic nerve LEAVE the eye”?At the posterior retina. It is known as the optic disc (blind spot). 9. Macula lutea 10. Cones 11. Yes. You still have functioning rods. 158 Laboratory Exercise Eye 18–10