* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
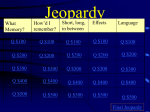
Download Brain Jeopardy Game
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Source amnesia wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Memory consolidation wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Misattribution of memory wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Childhood memory wikipedia , lookup
Sparse distributed memory wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive memory wikipedia , lookup
Socioeconomic status and memory wikipedia , lookup
Exceptional memory wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory (child testimony) wikipedia , lookup
Memory and aging wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Collective memory wikipedia , lookup
Hosted by Patrick Wall Parts Processing Retention Connections 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 What is the BRAINSTEM? This is the oldest and deepest area of the brain, sometimes called the “reptilian brain.” Row 1, Col 1 What is SENSORY REGISTER? The main function of this register is to screen out useless sensory input. 1,2 What is SEVEN? WORKING MEMORY has a functional limit. How many pieces of information can the average adult manage at one time? 1,3 What are MULTIPLE-CHOICE exams? These kinds of exams only test RECOGNITION— not RECALL skills. 1,4 What is the LIMBIC SYSTEM? Sometimes called the “old mammalian brain,” this area is the seat of emotions and sensory information. 2,1 What is SHORT-TERM MEMORY? “Immediate memory” and “working memory”are the two components of this type of memory. 2,2 What is CHUNKING? This is where the brain takes multiple items and considers them a single entity (as a way of bypassing the limitations of working memory). 2,3 What is CALLING on the FIRST HANDS to be raised? When teachers do this, it sends a signal to slower information retrievers that they can abort the process. 2,4 What is the CEREBRUM? This part of the brain controls thinking, memory, and speech. 3,1 What is IMMEDIATE MEMORY? This short-term memory component is where we put information until we decide what to do with it. 3,2 What is THIRTY? On average, adults can process items intently in working memory for about ___ minutes before becoming fatigued. 3,3 What is DURING SLEEP? This is WHEN information moves from short-term to long-term memory. 3,4 What are NEURONS? The technical name for nerve cells. 4,1 What is WORKING MEMORY? This component of shortterm memory is where we build, take apart, or rework ideas for eventual storage. 4,2 What are the FIRST and LAST portions? According to the Primacy-Recency effect, students are most likely to remember these portions of a lecture. 4,3 What is ACCOMMODATE DIVERSE LEARNING STYLES? Learning psychologists now speak of creating “multiple learning pathways” instead of this older expression. 4,4 What is the FRONTAL LOBE? Teens are slow to control their emotions because of late development in this part of the brain. 5,1 What are SENSE and RELEVANCE? These two criteria largely determine whether information is stored in long-term memory. 5,2 What is “FIRE until its WIRED!” Janet Zadina’s memorable phrase describing the learning process. 5,3 What is the CORPUS CALLOSUM? This connector gives females better communication BETWEEN brain hemispheres whereas males generally function more efficiently WITHIN a particular hemisphere. 5,4






















![[SENSORY LANGUAGE WRITING TOOL]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014348242_1-6458abd974b03da267bcaa1c7b2177cc-150x150.png)