* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MolecularBiology1APLab6
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
DNA barcoding wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
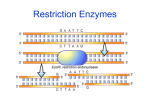
Molecular Biology Part I: Restriction Enzymes AP Lab 6 What you need to know! • http://www.phschool.com/science/biol ogy_place/labbench/lab6/intro.html Bacteria Contain: • 1 chromosome • 1 or more plasmids • Restriction enzymes Plasmids • Small, circular DNA pieces • Contain random DNA fragments that are collected or exchanged w/ other bacteria • Contain nonsense information • Sometimes contain useful information like antibiotic resistance Restriction Enzymes (RE) • Enzymes that cut DNA at very specific base sequences (often palindromes) • Make blunt or sticky ends • Evolved to combat invasive DNA from viruses • Does not cut bacterium’s DNA because it’s missing correct DNA sequence • Different bacterial strains have different RE RE Nomenclature • Named after the bacteria it comes from • First capital letter is of the genus • Lower case letters are the species • Next capital letter is the strain • The number is the order of discovery within the particular bacteria Example: EcoRI E = Escherichia co = coli R = RY13 EcoRI • Cleaves double stranded DNA at GAATTC • Cuts between the G and A on the top and bottom strand G|A A T T C C T T A A|G • This creates a sticky end • Other RE can create blunt ends – i.e. C C|G G G G|C C Genetic Engineering • RE fragments can be “glued” back together using ligase Biotech supply vendors offer: • Purified RE in a large variety • Plasmids with published restriction maps