* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Characteristics of Life
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Chromatophore wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
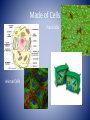
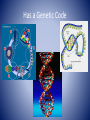
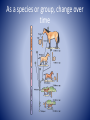
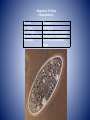
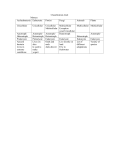
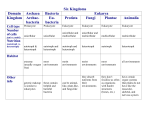
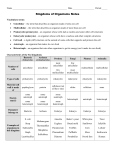
Characteristics of Life Biology • The science that studies life and seeks to understand the living world. Characteristics of Living Things • Must include ALL eight of the following in order to be considered. Made of Cells Plant Cells Animal Cells Reproduce Has a Genetic Code Grow and Develop Obtain & Use Energy Respond to their environment Maintain a stable internal environment HOMEOSTASIS As a species or group, change over time Survey of the Six Kingdoms of Life Kingdom 1: Archaebacteria Characteristics: Domain Cell Type Cell Number Mode of Nutrition Special Characteristic Examples Archaea Prokaryote Unicellular Autotroph or heterotroph Lives without oxygen Methanogens Kingdom 2: Eubacteria Characteristics: Domain Cell Type Cell Number Mode of Nutrition Examples Bacteria Prokaryote Unicellular Autotroph or heterotroph Streptococcus, Escherichia coli Kingdom 3: Protista Characteristics: Domain Cell Type Cell Number Mode of Nutrition Examples Eukarya Eukaryote Unicellular; some colonial Autotroph or heterotroph Amoeba, paramecium, algae Kingdom 4: Fungi Characteristics: Domain Cell Type Cell Number Mode of Nutrition Examples Eukarya Eukaryote Most multicellular; some unicellular Heterotroph Mushrooms, yeasts Kingdom 5: Plantae Characteristics: Domain Cell Type Cell Number Mode of Nutrition Examples Eukarya Eukaryote Multicellular Autotroph Mosses, Ferns, Flowering Plants Kingdom 6: Animalia Characteristics: Domain Cell Type Cell Number Mode of Nutrition Examples Eukarya Eukaryote Multicellular Heterotroph Sponges, Cnidaria, worms, insects, fishes, reptiles, birds, mammals