* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Six Kingdoms
Survey
Document related concepts
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids wikipedia , lookup
Horizontal gene transfer wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
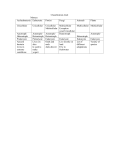
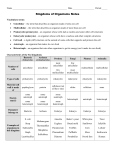
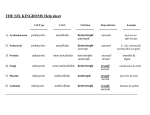
Six Kingdoms Domain Kingdom Cell type Number of cells (uni vs. multi) Archaea Archaebacteria Prokaryote Bacteria Eubacteria Protista Eukarya Fungi Plantae Animalia Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote unicellular unicellular unicellular and multicellular unicellular and multicellular multicellular multicellular autotroph & heterotroph autotroph and heterotroph autotroph and heterotroph heterotroph autotroph heterotroph extreme most (usually oxygen environments free) moist environments moist environments most environments all environments they absorb nutrients from their environments they don’t fossilize as often as organisms with harder structures (bones, etc.) have certain organ systems that plants do not have like the muscular, skeletal, and nervous system Nutrition (autotroph vs. heterotroph) Habitat Other info genetic makeup is similar to eukaryotes these contain helpful and harmful bacteria can be animallike, plant-like, and fungi-like Definitions: Unicellular: a single-celled organism Multicellular: an organism made of two or more cells Autotroph: an organism that produces its own food Heterotroph: an organism that has to consume other organisms for food