Arriving at a correlation between the flagellar arrangement and
... were notably seen; cells with gas vesicles and those that harbored flagella. Gas vesicles are found rampantly among the unicellular organisms; but, flagella are found equally among both the unicellular and multicellular organisms. The latter might have originated from groups of single cells that nee ...
... were notably seen; cells with gas vesicles and those that harbored flagella. Gas vesicles are found rampantly among the unicellular organisms; but, flagella are found equally among both the unicellular and multicellular organisms. The latter might have originated from groups of single cells that nee ...
ppt
... organics from environment. Only done by bacteria. - photoautotrophs: use light as source of energy, and use this energy to fix carbon dioxide. bacteria and some eukaryotes. - chemoheterotrophs: get energy and carbon from organics they consume. bacteria and some eukaryotes. ...
... organics from environment. Only done by bacteria. - photoautotrophs: use light as source of energy, and use this energy to fix carbon dioxide. bacteria and some eukaryotes. - chemoheterotrophs: get energy and carbon from organics they consume. bacteria and some eukaryotes. ...
Fungi - Dr Magrann
... Fungi can be found anywhere from athlete’s foot to spoiled food, and even on our dinner plate. There are more than one million species of fungi, many of which are just mushrooms. Fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants. The few fungi that are single celled are called yeasts; most fu ...
... Fungi can be found anywhere from athlete’s foot to spoiled food, and even on our dinner plate. There are more than one million species of fungi, many of which are just mushrooms. Fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants. The few fungi that are single celled are called yeasts; most fu ...
Figure 16.6C
... • Evolved about 1.7 billion years ago Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... • Evolved about 1.7 billion years ago Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
here
... basis for constructing a system of organisms. The system we develop will be one that is completely restructured at the highest levels. Haeckel in 1866 (6) formally challenged the aboriginal plant/animal division of the living world. He recognized that the single-celled forms, the protists, did not f ...
... basis for constructing a system of organisms. The system we develop will be one that is completely restructured at the highest levels. Haeckel in 1866 (6) formally challenged the aboriginal plant/animal division of the living world. He recognized that the single-celled forms, the protists, did not f ...
Bacterial but not protist gut microbiota align with ecological
... but also suggesting a role of protist diversity in the evolution of bacterial diversity ...
... but also suggesting a role of protist diversity in the evolution of bacterial diversity ...
Microbiology Section C
... (ii) State a function of B. (iii) State a function of C. (iv) What term is used to describe the nutrition of Rhizopus? Explain the importance of this type of nutrition in nature. (v) To what kingdom does Rhizopus belong? (vi) Name another organism that you have studied in your biology course that be ...
... (ii) State a function of B. (iii) State a function of C. (iv) What term is used to describe the nutrition of Rhizopus? Explain the importance of this type of nutrition in nature. (v) To what kingdom does Rhizopus belong? (vi) Name another organism that you have studied in your biology course that be ...
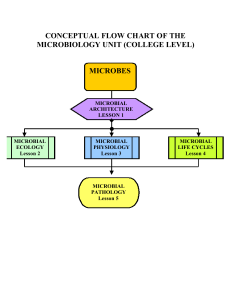
conceptual flow chart of the microbiology unit (college level) microbes
... the use of a microscope to see. There are many different species of microorganisms that have been classified or put into similar groups based on the possession of certain characteristics. This is called taxonomy (the science of classifying things) and the largest classification group is called the K ...
... the use of a microscope to see. There are many different species of microorganisms that have been classified or put into similar groups based on the possession of certain characteristics. This is called taxonomy (the science of classifying things) and the largest classification group is called the K ...
Notes on some Parasitic Protists.
... and I think my organism must go where it goes. Both forms will probably have to be removed—perhaps, as Schaudinn suggested, to the genus Dispora, Kern. The large size of these organisms, their life-history and formation of two spores, all distinguish them from the ordinary Bacilli. The specific name ...
... and I think my organism must go where it goes. Both forms will probably have to be removed—perhaps, as Schaudinn suggested, to the genus Dispora, Kern. The large size of these organisms, their life-history and formation of two spores, all distinguish them from the ordinary Bacilli. The specific name ...
Open Questions on the Origin of Eukaryotes
... Box 3. Symbiosis in Evolution: The Case of Mitochondria The idea that some membrane-bound organelles derive from endosymbiotic bacteria dates back to the early twentieth century, when Konstantin Mereschkowsky proposed such an evolutionary origin for chloroplasts (but also the nucleus) [21]. Several ...
... Box 3. Symbiosis in Evolution: The Case of Mitochondria The idea that some membrane-bound organelles derive from endosymbiotic bacteria dates back to the early twentieth century, when Konstantin Mereschkowsky proposed such an evolutionary origin for chloroplasts (but also the nucleus) [21]. Several ...
Glencoe Biology
... The broadest category in the classification used by most biologists is the domain. The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms and three domains. The three domains are Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. The six kingdoms are Bacteria, Archaea, Protists, Fungi, Plantae, ...
... The broadest category in the classification used by most biologists is the domain. The most widely used biological classification system has six kingdoms and three domains. The three domains are Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. The six kingdoms are Bacteria, Archaea, Protists, Fungi, Plantae, ...
Chapter 5 Gases
... Using a very simple model of disease spread, Oskar Hallatschek, assistant professor of physics, proved that one common assumption is actually wrong. Most models have taken for granted that if disease vectors, such as humans, have any chance of "jumping" outside the initial outbreak area -- by plane ...
... Using a very simple model of disease spread, Oskar Hallatschek, assistant professor of physics, proved that one common assumption is actually wrong. Most models have taken for granted that if disease vectors, such as humans, have any chance of "jumping" outside the initial outbreak area -- by plane ...
CHAP
... fruiting body. The fruiting body is nothing more than a reproductive hyphae. 2. Budding Only unicellular fungi like yeast reproduce by budding. In budding, a new cell forms inside a parent cell. The new cell eventually makes it way out of the parent cell and lives on its own. The new cell is identic ...
... fruiting body. The fruiting body is nothing more than a reproductive hyphae. 2. Budding Only unicellular fungi like yeast reproduce by budding. In budding, a new cell forms inside a parent cell. The new cell eventually makes it way out of the parent cell and lives on its own. The new cell is identic ...
Indezine Template
... Nature of Microorganisms • Pathogens: microorganisms that cause disease • most microorganisms are harmless • some microorganisms found in the body are beneficial to us • when a microorganism enters a part of the body other than where it is intended to be, it can be harmful • eg. E. coli from the co ...
... Nature of Microorganisms • Pathogens: microorganisms that cause disease • most microorganisms are harmless • some microorganisms found in the body are beneficial to us • when a microorganism enters a part of the body other than where it is intended to be, it can be harmful • eg. E. coli from the co ...
17.1 The Linnaean System of Classification
... • contains single-celled (unicellular) prokaryotes • cell walls are diverse but chemically different from bacteria • produce asexually • differences discovered by studying RNA • known for living in extreme environments (methanogens in anaerobic swamps, helophiles in salt lakes, thermacidophiles in h ...
... • contains single-celled (unicellular) prokaryotes • cell walls are diverse but chemically different from bacteria • produce asexually • differences discovered by studying RNA • known for living in extreme environments (methanogens in anaerobic swamps, helophiles in salt lakes, thermacidophiles in h ...
Lecture Slides
... – Synthesized the entire genome of Mycoplasma genitalium, a species of bacteria found naturally in the human urinary tract – Transplanted the complete genome of one species of Mycoplasma bacteria into another ...
... – Synthesized the entire genome of Mycoplasma genitalium, a species of bacteria found naturally in the human urinary tract – Transplanted the complete genome of one species of Mycoplasma bacteria into another ...
Microbiology Questions
... 41. Name a fungus, other than yeast, that you studied during your course. 42. What are symbiotic bacteria? 43. What is fermentation? 44. To which kingdom does Rhizopus belong? 45. Name the container in which you grew the leaf yeast. 46. Give an example of a beneficial organism and of a harmful organ ...
... 41. Name a fungus, other than yeast, that you studied during your course. 42. What are symbiotic bacteria? 43. What is fermentation? 44. To which kingdom does Rhizopus belong? 45. Name the container in which you grew the leaf yeast. 46. Give an example of a beneficial organism and of a harmful organ ...
Short Exam Questions
... 56. Some bacteria are anaerobic. What does this mean? 57. What are pathogenic bacteria? 58. Give two example of the economic importance of bacteria. 59. Explain how Rhizopus gets its food. 60. What form of heterotrophic nutrition does Rhizopus have? 61. Outline the importance of this type of nutriti ...
... 56. Some bacteria are anaerobic. What does this mean? 57. What are pathogenic bacteria? 58. Give two example of the economic importance of bacteria. 59. Explain how Rhizopus gets its food. 60. What form of heterotrophic nutrition does Rhizopus have? 61. Outline the importance of this type of nutriti ...
Chapter 15 Notes
... The Diversity of Protists – Other protists are heterotrophs. – Some protists eat bacteria or other protists. – Other protists are fungus-like and obtain organic molecules by absorption. – Parasites derive their nutrition from a living host, which is harmed by the interaction. Parasitic trypanosomes ...
... The Diversity of Protists – Other protists are heterotrophs. – Some protists eat bacteria or other protists. – Other protists are fungus-like and obtain organic molecules by absorption. – Parasites derive their nutrition from a living host, which is harmed by the interaction. Parasitic trypanosomes ...
Top 10 Bacterial Infections
... nitrogen into nitrates or nitrites as part of their metabolism, and the resulting products are released into the environment. Some plants, such as liverworts, cycads, and legumes have taken special advantage of this process by modifying their structure to house the basteria in their own tissues. Oth ...
... nitrogen into nitrates or nitrites as part of their metabolism, and the resulting products are released into the environment. Some plants, such as liverworts, cycads, and legumes have taken special advantage of this process by modifying their structure to house the basteria in their own tissues. Oth ...
Five kingdoms
... 5. Ciliophora are distinguished by their cilia, which they use for moving and other functions. Because of specialized structures, such as mouths, anal pores, contractile vacuoles (for water balance), two kinds of nuclei (one large macronucleus and several small micronuclei), and other features, the ...
... 5. Ciliophora are distinguished by their cilia, which they use for moving and other functions. Because of specialized structures, such as mouths, anal pores, contractile vacuoles (for water balance), two kinds of nuclei (one large macronucleus and several small micronuclei), and other features, the ...
Microbiology Questions
... 33. What term is used to describe the nutrition of Rhizopus? Explain the importance of this type of nutrition in nature. 34. To what kingdom does Rhizopus belong? 35. Name another organism that you have studied in your biology course that belongs to the same kingdom as Rhizopus. 36. Distinguish ...
... 33. What term is used to describe the nutrition of Rhizopus? Explain the importance of this type of nutrition in nature. 34. To what kingdom does Rhizopus belong? 35. Name another organism that you have studied in your biology course that belongs to the same kingdom as Rhizopus. 36. Distinguish ...
Protist

In all biological taxonomy schemes, protists (/ˈproʊtɨst/) were a large group of diverse eukaryotic microorganisms, mainly unicellular animals and plants, that do not form tissues. Formerly, these were assigned to the now-obsolete kingdom Protista. However in modern taxonomy the Protista are understood to be paraphyletic (not a clade), so the term remains in use only for convenience, similar to ""invertebrate"". An equivalent term Protoctista is used for these organisms by various organisations and institutions. Molecular analyses in modern taxonomy have been used to redistribute former members of this group into diverse and sometimes distantly related phyla. When used, the term “protists” is now considered to mean similar-appearing but diverse phyla that are not related through an exclusive common ancestor, and which have different life cycles, trophic levels, modes of locomotion, and cellular structures. Besides their relatively simple levels of organization, the protists do not have much in common.The term protista was first used by Ernst Haeckel in 1866. Protists were traditionally subdivided into several groups based on similarities to the ""higher"" kingdoms: the unicellular ""animal-like"" protozoa, the ""plant-like"" protophyta (mostly unicellular algae), and the ""fungus-like"" slime molds and water molds. These traditional subdivisions, largely based on superficial commonalities, have been replaced by classifications based on phylogenetics (evolutionary relatedness among organisms). However, the older terms are still used as informal names to describe the morphology and ecology of various protists.Protists live in almost any environment that contains liquid water. Many protists, such as algae, are photosynthetic and are vital primary producers in ecosystems, particularly in the ocean as part of the plankton. Other protists include pathogenic species such as the kinetoplastid Trypanosoma brucei, which causes sleeping sickness and species of the apicomplexan Plasmodium which cause malaria.