* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Epigenetic clock wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA paternity testing wikipedia , lookup
DNA barcoding wikipedia , lookup
DNA methylation wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
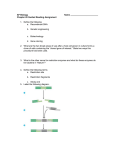
9.1 Manipulating DNA KEY CONCEPT Biotechnology relies on cutting DNA at specific places. WHAT ARE RESTRICTION ENZYMES? Restriction Enyzmes – molecular scissors able to cut DNA HOW DO RESTRICTION ENZYMES WORK? Usually cut DNA at a “palindrome” such as GAATTC. Palindrome – word or phrase when spelled backwords, spells the same word or phrase Ex. BOB MADAM I’M ADAM A Toyota! Race fast, safe car. A Toyota 5’ 3’ GAATTC | | | | | | 3’ CTTAAG 5’ “Restriction site” or “Recognition Sequence” HOW DO RESTRICTION ENZYMES WORK? RE’s cut DNA’s phosphodiester bonds and hydrogen bonds. HOW DO RESTRICTION ENZYMES WORK? - RE’s generate two different types of “cuts” - Sticky ends - Blunt cuts. WHERE DO RE’S COME FROM? Bacteria “Immune system” to protect against bacteriophages (bacteria-infecting viruses like Lambda). HOW ARE RE’S NAMED? After bacteria which produces them. EcoRI HindIII Genus Escherichia Haemophilus Bacillus Species coli influenzae amylo. Strain R d H Order Isolated I III I Recognition Site G^AATTC A^AGCTT BamHI G^GATGC HOW DO RESTRICTION ENZYMES WORK? Must provide correct temperature and buffer (salt, pH) for enzyme to work. Mimics cellular conditions of bacteria they come from. Restriction enzymes, DNA, and Electrophoresis • DNA normally comes in “Genome sized” lengths (usually several million bp in length.) • These are the “elephants” in the race through the agarose and cant enter the gel matrix when they are this big. • Restriction enzymes made possible the cutting of DNA into smaller fragments together with their separation and visualization by agarose gel electrophoresis. Restriction Sites as “Molecular Signposts” • Using two, or more different restriction enzymes on a DNA fragment enables those restriction sites to be mapped onto that DNA fragment. Eco Digest Eco cuts to yield two DNA fragments Eco Bgl also cuts to yield two DNA fragments. But where is the Bgl site in relation to the Eco site? Bgl Digest Bgl Eco Or Eco Bgl A restriction digest with both Eco and Bgl enzymes provides the answer. Eco Bgl Double Digest Shows it must be: Eco Bgl Your Turn: • DNA- Off to the Races • Restriction Enzyme mapping challenge. WHAT ARE RE’S USED FOR? Genetic engineering – pasting together DNA from two different organisms. HOW DO RESTRICTION ENZYMES WORK? Which are more useful in genetic engineering? RE’s that generate sticky ends or ones that produce blunt cuts? STICKY ENDS HOW IS DNA PASTED TOGETHER? Ligase – another enzyme which reconnects phosphodiester bonds. RE Video restriction enzymes.exe Bill Nye on Restriction Enzymes Videos and Animations http://www.dnai.org/b/ Click on “Techniques” then “Cutting and Pasting” and view the 2D animation and 3D Cartoon Video to see Restriction enzymes in action WHAT ELSE ARE RE’S USED FOR? Forensics – DNA Fingerprinting for crime scene investigation and paternity testing. Everyone’s DNA has a different sequence – even though only 0.1% different. How frequently would EcoRI cut DNA? 6 4 = once every 4096 bp Lambda (48,514 bp) would expect about 12 EcoRI sites THOUGHT QUESTION Bacteria are prokaryotes. Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus. Both DNA and RE’s are in cytoplasm. Why isn’t bacterial DNA cut by RE’s? Methylation See board In humans, methyl groups are used to tag genes to turn them on or off. Stay tuned. 9.1 Manipulating DNA Scientists use several techniques to manipulate DNA. • Chemicals, computers, and bacteria are used to work with DNA. • Scientists use these tools in genetics research and biotechnology. 9.1 Manipulating DNA Restriction enzymes cut DNA. • Restriction enzymes act as “molecular scissors.” – come from various types of bacteria – allow scientists to more easily study and manipulate genes – cut DNA at a specific nucleotide sequence called a restriction site 9.1 Manipulating DNA • Different restriction enzymes cut DNA in different ways. – each enzyme has a different restriction site 9.1 Manipulating DNA – some cut straight across and leave “blunt ends” – some make staggered cuts and leave “sticky ends” 9.1 Manipulating DNA Restriction maps show the lengths of DNA fragments. • Gel electrophoresis is used to separate DNA fragments by size. – A DNA sample is cut with restriction enzymes. – Electrical current pulls DNA fragments through a gel. 9.1 Manipulating DNA – Smaller fragments move faster and travel farther than larger fragments. – Fragments of different sizes appear as bands on the gel. 9.1 Manipulating DNA • A restriction map shows the lengths of DNA fragments between restriction sites. – only indicate size, not DNA sequence – useful in genetic engineering – used to study mutations