* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Xeroderma Pigmentosum(XP)
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
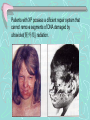
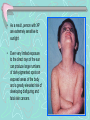
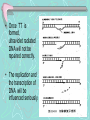
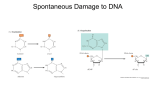
Xeroderma Pigmentosum(XP) 着色性干皮病 • We owe our lives to light from the sun,which provides the energy captured during photosynthesis (光合作用). • But the sun also emits a constant stream of ultraviolet rays that ages and mutates the cells of our skin. • The hazardous effects of the sun are most dramatically illustrated by the rare recessive genetic disorder , Xeroderma Pigmentosum(XP) . Patients with XP possess a dificient repair system that cannot remove segments of DNA damaged by ultraviolet(紫外线) radiation. • As a result ,person with XP are extremely sensitive to sunlight • Even very limited exposure to the direct rays of the sun can produce large numbers of dark-pigmented spots on exposed areas of the body and a greatly elevated risk of developing disfiguring and fatal skin cancers. The mechanism about XP ------nucleotide excision repair deficiency (核苷酸切除修复缺陷) • When subjected to ultraviolet radiation ,adjacent(相邻 的) pyrimidines(嘧啶) on a DNA strand have a tendency to interact with one another to form a covalent(共价的) dimer complex.(example as TT--胸腺嘧啶二具体) • Once TT is formed, ultraviolet radiated DNA will not be repaired correctly. • The replication and the transcription of DNA will be influenced seriously. • THF II H--- a crucial link between transcription and DNA repair • XPB and XPD are two subunits of THF II H • In persons with XP who carry specific mutations in the XPD gene. • XPD gene encodes a subunit of the TFII H required for transcription initiation(起始) • So, Mutations in XPD could lead to defect(缺陷) in both DNA repair and transcription nucleotide excision repair How to help XP patients? • Some help for XP patients may be on the way in the form of skin creams that contain DNA repair enzymes. • The enzyme are contained in liposomes(脂质体) that can apparently penetrate (穿过) the outer layer of the skin and participate in repair pathways • XP is a very rare condition ,but colon cancer(结肠 癌) is relatively common. • It is estimated that up to 15 percent of colon cancer cases can be attributed to mutations in the genes that encode the proteins required for mismatch repair. • Mutations that cripple the mismatch repair system inevitably lead to higher mutation rate in other genes because mistakes made during replication are not corrected.