* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ch. 17 DNA mutations and repair
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
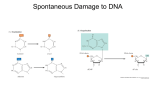
DNA Mutations and Repair Chapter 17 pp. 481- Mutation Rates and Frequency 1 to 10 mutations per million gametes Incidence within a group For example: swine flu incidence in the U.S Causes of Mutations Spontaneous Induced Environmentally Induced DNA changes Intercalating agents Insert and distort DNA Radiation Hiroshima (Aug. 6th, 1945) (Techa River) Thymine Dimers SOS Chemicals and Reactions Leading to Mutations alklyating Deamination Adds OH Oxidative radicals Reactive forms of oxygen can lead to these radicals Detecting mutations with the AMES test THE AMES TEST Salmonella typimurium AMES TEST 2-aminofluorene Saccharin Aflatoxin Aflatoxin B1 DNA Repair: general characteristics Double stranded DNA Redundancy of pathways Types of DNA repair Mismatch repair Direct Repair Base-Excision Repair Nucleotide Excision Repair Mismatch repair Mut H Recognize GATC hemi-methylation Mut S Mut L A closer look at mismatch repair DIRECT REVERSAL REPAIR Direct Repair BASE EXCISION REPAIR BASE EXCISION REPAIR Nucleotide Excision Repair Diseases of DNA repair! Xeroderma pigmentosum Autosomal recessive Hereditary Non-Polyposis Colon Cancer HNPCC 15% of all colon cancers Li-Fraumeni P-53 mutation The End