* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
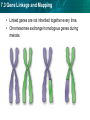
7.3 Gene Linkage and Mapping KEY CONCEPT Genes can be mapped to specific locations on chromosomes. 7.3 Gene Linkage and Mapping Gene linkage was explained through fruit flies. • Morgan found that linked traits are on the same chromosome. • Chromosomes, not genes, assort independently during meiosis. Wild type Mutant 7.3 Gene Linkage and Mapping • Linked genes are not inherited together every time. • Chromosomes exchange homologous genes during meiosis. 7.3 Gene Linkage and Mapping Linkage maps estimate distances between genes. • The closer together two genes are, the more likely they will be inherited together. • Cross-over frequencies are related to distances between genes. – The higher the frequency, the further the genes are apart • Linkage maps show the relative locations of genes. 7.3 Gene Linkage and Mapping • Cross-over frequencies can be converted into map units. • Ex: A 5% cross-over frequency equals 5 map units. – gene A and gene B cross over 6.0 percent of the time – gene B and gene C cross over 12.5 percent of the time – gene A and gene C cross over 18.5 percent of the time 7.3 Gene Linkage and Mapping Draw a linkage map based on the following cross over percentages: • A – B = 8% • B – C = 10% • A – C = 2% 8.0 B 2.0 A 8.0 + 2.0 = 10.0 C