* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Why teach a course in bioinformatics?
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
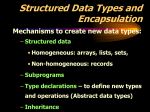
Why microarrays in a bioinformatics class? • • • • Design of chips Quantitation of signals Integration of the data Extraction of groups of genes with linked expression profiles (gene clustering) 2 important topics requiring computers: Data Integration • It’s important to link the data from the array experiment with other sequence databases (Genbank, SwissProt, etc). • If the activity of a gene has changed, you want to be able to view pre-existing information about the gene in order to explain the experimental results. • To exchange array data with other researchers, you need some standardized format. Gene Clustering Group together genes with similar patterns of expression: Clustering can be thought of as forming a phylogenetic tree of genes or tissues. Genes are near each other on the "gene tree" if they show a strong correlation across experiments, and tissues are near each other on the "tissue tree" if they have similar gene expression patterns. Important ?? • This opens the possibility of identifying patterns of coregulation among genes, which, in turn, reflects underlying regulatory mechanisms and function interrelationships. • PNAS -- Alon et al. 96 (12): 6745 • Pattern searching and gene clustering of promoter regions of Drosophila olfactory receptors • http://genomewww.stanford.edu/breast_cancer/mopo_clin ical/images/supplfig4.pdf The End Arrays: • Narrower terms include bead arrays, bead based arrays, bioarrays, bioelectronic arrays, cDNA arrays, cell arrays, DNA arrays, gene arrays, gene expression arrays, genome arrays, high density oligonucleotide arrays, hybridization arrays, microelectronic arrays, multiplex DNA hybridization arrays, nanoarrays, oligonucleotide arrays, oligosaccharide arrays, protein arrays, solution arrays, spotted arrays, tissue arrays, exon arrays, filter arrays, macroarrays, small molecule microarrays, suspension arrays, tiling arrays, transcript arrays. Related terms include arrayed library. See also chips, microarrays. • To me, the most important thing that has happened in recent years is the rapid development of DNA chips. Technologies have allowed highthroughput ‘transcriptome’ analysis. That capability was introduced in the ’90s, but since then, it has become much more powerful as the genome project progressed. There are now many transcriptome centers already set up or being established. People are using this technology for mapping gene Many microarray experiments are now being performed on human cells. • Genome is completely sequenced and well annotated. • Scientists are attempting to compare normal vs. diseased tissue.