* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
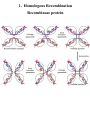
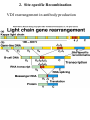
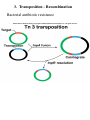
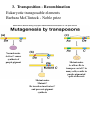
DNA/RNA Metabolism Blackburn & Gait, Ch. 5 Neidle, Ch. 4 Recombination • understand basics of the reaction • know advantages/disadvantages of recombination • understand how recombinase protein works • know structure of Holliday junction (X-shaped) • know different types of recombination Recombination • Enables the limited exchange of genetic material between paired chromosomes • Occurs between intact double helices • Damage to DNA can stimulate recombination • Enables the immune system to generate a diversity of protein antibodies from a limited set of genes • Enables viruses to integrate their genetic material into a host’s genome • Enables host organism to assort alleles (differing copies of same gene) into novel groups - favorable & unfavorable alleles can be shuffled randomly • Enables repair of a damaged gene in an otherwise favorable chromosome • Enables regulation of gene expression • Enables rearrangement of antibody genes • Can lead to cancers - example: Burkitt’s lymphoma caused by translocation between ch. 8 and 14 Recombination • THREE main categories 1. Homologous recombination takes place between similar sequences 2. Site-specific recombination Limited sequence similarity between recombining DNAs 3. Transposition movement of a DNA element from one position to another, little sequence similarity needed called “illegitimate recombination” 1. Homologous Recombination 1. Homologous Recombination Recombinase protein • One example is that of Cre recombinase from a bacteriophage (virus that infects bacteria) • The enzyme mediates strand cleavage and exchange between two pieces of DNA • An intermediate (half reacted) configuration of the DNA is called a Holliday junction (X-shaped) 1. Homologous Recombination Recombinase protein 1. Homologous Recombination 2. Site-specific Recombination Lambda phage integration and excision 2. Site-specific Recombination VDJ rearrangement in antibody production 3. Transposition - Recombination Bacterial antibiotic resistance 3. Transposition - Recombination Eukaryotic transposable elements Barbara McClintock - Noble prize Normal maize Active C causes synthesis of purple pigment Mutant maize Ac allows Ds to transpose out of C in many cells, results in purple pigmented spots on kernels Mutant maize Mutant C Ds insertion inactivates C and prevents pigment synthesis