* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Respiration
Mitochondrial replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
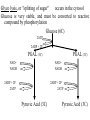
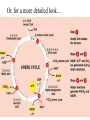
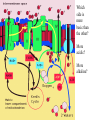
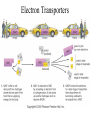
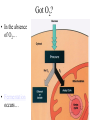
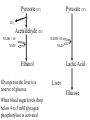
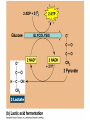
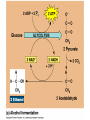
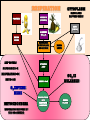
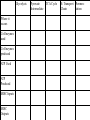
Respiration A Dr. Production Energy Concepts • Thermodynamics & Reaction Rates • RESPIRATION a process where organic (food) molecules are oxidized & broken down to release E • Glycolysis is the 1o source of e- for the citric acid and etransport chain • CH2O + O2 CO2 + H2O + Energy • Has both an anaerobic phase and an aerobic phase • Associated with Mitochondria found in eukaryotic cells • Respiration is a multi-step process that occurs in several places in the mitochondria. So it is important that you know the anatomy of the mitochondria Glyco lysis, or "splitting of sugar" occurs in the cytosol Glucose is very stable, and must be converted to reactive compound by phosphorylation Glucose (6C) 2ATP 2ADP + 2P PGAL (3C) NAD+ NADH PGAL (3C) NAD+ NADH 2ADP + 2P 2ATP 2ADP + 2P 2ATP Pyruvic Acid (3C) Pyruvic Acid (3C) Redox Reactions • How NAD+ Works Glycolysis • net gain +2ATP, 2% total E in 1 molecule glucose, only 7% of E released • 2ADP 2ATP • 2NAD+ 2NADH + 2H+ • 1 Glucose 2Pyruvate Pyruvic Acid vs Pyruvate Draw pyruvate Conversion of Pyruvate • Conversion of Pyruvate occurs in the mitochondrial membrane Identify the components of Acetyl CoA TCA/Citric Acid/Krebs Cycle • Citric Acid Cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix • each molecule acetyl Co-A yields the following from one molecule of glucose: 3NADH+ + H + 1FADH2 1ATP 2CO2 Or, for a more detailed look… The Electron Transport Chain E- Transport Chain occurs across the inner mitochondrial membrane and in the inter-membrane space It uses O2 to transfer e- from 10NADH + H+ and 2FADH2 It separates H into e- and H+, carries e- away from H+ gradient Which side is more basic than the other? More acidic? More alkaline? ATPase attached to H + channels and uses kinetic E of H+ to join ADP + P this is called "chemiosmotic ATP synthesis" each NADH+ + H + produces 3ATP = 30 ATP each FADH2 produces 2ATP = 4 ATP Glycolysis = 2 ATP Kreb’s Cycle = 2 ATP ATP Synthetase The Movie Electron Transporters Got O2? • In the absence of O2… • Fermentation occurs… Pyruvate (3C) Pyruvate (3C) CO2 Acetaldehyde (2C) NADH + H+ NAD+ NADH + H+ NAD+ Ethanol Glycogen in the liver is a reserve of glucose. When blood sugar levels drop below 4 to 5 mM glycogen phosphorylase is activated Lactic Acid Liver Glucose • Fermentation generates 0ATP, so what is it’s usefulness? • How did the first anaerobic heterotrophs make E? • NAD+ is needed for glycolysis • Pyruvic acid generates NADH from NAD+, fermentation regenerates NAD+ • Which is more efficient, aerobic or anaerobic respiration? What is the evolutionary significance of this? Alternative Energy Sources for Muscles • Hydrolysis of Sucrose in Intestines • Fatty Acid Metabolism RESPIRATION PROTEINS CYTOPLASM GLYCOLOSIS HAPPENS HERE! CARBO’S (SUGARS) FATS (LIPIDS) AMINO ACIDS GLUCOSE C6H12O6 GLYCOLOSIS IN CYTOPLASM NO OXYGEN! ATP TOTALS GLYCOLOSIS=2 PYRUVIC ACID RESPIRATION=34 BOTH=36! MAKES 2 ATPS ACETYL-CoA CO2 IS RELEASED O2 ENTERS HERE MITOCHONDRIA RESPIRATION HAPPENS IN THIS ORGANELLE! KREBS CYCLE AND ELECTRON TANSPORT MAKES 34 ATPS Gluconeogenesis • Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources. Glucose must be synthesized after 12-24 hours of fasting or during prolonged exercise to maintain blood glucose concentration. • The brain prefers to use glucose as fuel, although after a long period of starvation it can derive some of its energy requirements from ketone bodies. • RBCs have an absolute requirement for glucose since they have no mitochondria and can not utilize ketone bodies. • Occurs in the liver (& kidney cortex after prolonged starvation), in cytosol &mitochondria. Glycolysis Where it occurs Co-Enzymes used Co-Enzymes produced ATP Used ATP Produced MISC Inputs MISC Outputs Pyruvate TCA Cycle Intermediate E- Transport FermenChain tation References • • • • • • • • • • • • Hibernation: Krebs cycle Tutorial Citric Acid Cycle tutorial A&P Animations & Quizzes ATP & Energy Storage Fermentation & Irritable Bowel Syndrome Step by Step Glycolysis Interactive Biochemistry Animations Overview of Glycolysis Heavy Chemistry Fundamentals of Biochemistry Animations Glycolysis with Redox Reactions Cellular Respiration Animation: Summary