* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STUDY GUIDE FOR CELLULAR RESPIRATION Cellular
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
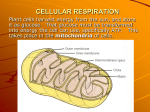
STUDY GUIDE FOR CELLULAR RESPIRATION 1. CELLULAR RESPIRATION: Transfer of energy from organic compounds (especially GLUCOSE) to ATP. 2. AEROBIC: cellular respiration WITH O2 3. ANEROBIC: cellular respiration WITHOUT O2 4. TWO STAGES OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION: a. STAGE 1: Glucose is converted to Pyruvate producing small amounts of ATP and NADH. b. STAGE 2: If O2, then: PYR and NADH make lots of ATP; if no O2, then Lactate or Ethanol and CO2 are produced. SEE FIGURE 10 FROM PAGE 104 IIN THE TEXTBOOK. http://www.google.com/imgres?q=cellular+respiration&hl=en&client=safari&sa=X&pwst=1&rls=en&biw=11 21&bih=711&tbm=isch&prmd=ivns&tbnid=6JGvIfwjrI4WHM:&imgrefurl=http://staff.jccc.net/pdecell/cell resp/respintro.html&docid=iPm9EB-AQdpqsM&w=640&h=600&ei=BnxuTqbnKKGsAKzlJXIBA&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=706&vpy=111&dur=4363&hovh=217&hovw=232&tx=107&ty=105 &page=1&tbnh=125&tbnw=133&start=0&ndsp=24&ved=1t:429,r:4,s:0 STAGE 1: BREAKDOWN OF GLUCOSE 1. Occurs in cell’s cytoplasm 2. Process of glucose breakdown is called GLYCOLOSIS 3. Glycolsis is an ANAEROBIC process that requires ENZYMES and results in a 6 carbon glucose being broken down into 2three carbon Pyruvate molecules STAGE 2: PRODUCTION OF ATP 1. IN THE PRESENCE OF O2: Pyruvate from glycolysis enters the MITOCHONDRION and is converted to a 2 carbon compound (Acetyl group). Acetyl attaches to a conenzyme A (CoA)=Acetyl-CoA 2. Acetyl-CoA enters the Krebs Cycle. ELECTRON CHAIN TRANSPORT 1. Electrons are donated NADH and FADH2 pass through an electron transport chain 2. In EUKARYOTIC cells, a. ETC is in inner mitochondrial membrane b. Electron energy pumps hydrogens out c. Hydrogens diffuse across the membrane back to the inside via a carrier protein that ads a PHOSPHATE group to ADP d. ADP + PO4 = ATP e. At the end of the chain spent electrons, Hydrogen ions and O2 combine to form H20. RESPIRATION IN THE ABSENCE OF OXYGEN 1. No O2, No ETC function. No electrons transferred from NADH therefore NAD+ is not recycled in the ETC but is recycled in ANAEROBIC METABOLISM. 2. GLUC—glycolysis yields 2 PYR. 3. Electrons from NADH are transferred to PYR yielding LACTATE (This is called LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION). [LACTIC ACID BUILD-UP IN YOUR MUSCLES CASUES THE BURN YOU EXPEREINCE IN DANCE] 4. Another type of Anaerobic Metabolism (fermentation) is ALCOHOL FERMENTATION. In this case the 2 PYR from glycolysis are broken down, releasing CO2 and forming the 2carbon compound, ETHANOL. [THIS IS HOW BEER IS MADE].