Riboflavin (Vitamin B )
... Introduction (cont.) Both classes of enzymes are involved in a wide range of redox reactions, e.g. succinate dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase. oxidase During the enzymatic reactions which involving the flavoproteins, the reduced forms of FMN and FAD are formed, FMNH2 and FADH2, respectively. Phys ...
... Introduction (cont.) Both classes of enzymes are involved in a wide range of redox reactions, e.g. succinate dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase. oxidase During the enzymatic reactions which involving the flavoproteins, the reduced forms of FMN and FAD are formed, FMNH2 and FADH2, respectively. Phys ...
Metabolic downregulation during diapause in embryos of Artemia
... dehydrogenase. Trehalose is the sole source of fuel in the embryos of A. franciscana, and hence downregulation of trehalose catabolism results in severe limitation of metabolic fuel available to the embryo during diapause. Western blot data demonstrates that pyruvate dehydrogenase becomes phosphoryl ...
... dehydrogenase. Trehalose is the sole source of fuel in the embryos of A. franciscana, and hence downregulation of trehalose catabolism results in severe limitation of metabolic fuel available to the embryo during diapause. Western blot data demonstrates that pyruvate dehydrogenase becomes phosphoryl ...
7vВyВtvphy hБq purАvphy АrpuhБvЖАЖ Вs ЕrqИpЗvЙr
... between two redox half reactions. A chemical redox reaction occurs spontaneously, if ∆G<0. This indicates that a redox process is thermodynamically feasible, if a redox pair with a more negative redox potential reduces another redox pair. The free energy gainable between the two redox half reactions ...
... between two redox half reactions. A chemical redox reaction occurs spontaneously, if ∆G<0. This indicates that a redox process is thermodynamically feasible, if a redox pair with a more negative redox potential reduces another redox pair. The free energy gainable between the two redox half reactions ...
Pyruvate dehydrogenase - Wageningen UR E
... Pyruvate dehydrogenase multi-enzyme complex (PDHC) is member of a family of multienzyme complexes that catalyse the irreversible decarboxylation of various 2-oxoacid substrates totheir corresponding acyl-CoAderivatives,NADH andCO2.PDHC,liketheother members of this family, consists of an assembly of ...
... Pyruvate dehydrogenase multi-enzyme complex (PDHC) is member of a family of multienzyme complexes that catalyse the irreversible decarboxylation of various 2-oxoacid substrates totheir corresponding acyl-CoAderivatives,NADH andCO2.PDHC,liketheother members of this family, consists of an assembly of ...
Contribution of 13C-NMR spectroscopy to the elucidation of
... pyruvate and oxaloacetate are formed, respectively. These intermediates can be partially oxidized to acetate and partially reduced to propionate leading to stoichiometries as given in Table 2 (Eqs. 1 and 2). Also glutamate may be converted reductively to propionate (Table 2, Eq. 3). This was describ ...
... pyruvate and oxaloacetate are formed, respectively. These intermediates can be partially oxidized to acetate and partially reduced to propionate leading to stoichiometries as given in Table 2 (Eqs. 1 and 2). Also glutamate may be converted reductively to propionate (Table 2, Eq. 3). This was describ ...
the role of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase in glucose and ketone
... knockout (KO), PDK4 KO, and PDK2/PDK4 double knockout (DKO) mice were generated. PDK2 deficiency caused higher PDC activity and lower blood glucose levels in the fed state while PDK4 deficiency caused similar effects in the fasting state. DKO intensified these effects in both states. PDK2 deficiency ...
... knockout (KO), PDK4 KO, and PDK2/PDK4 double knockout (DKO) mice were generated. PDK2 deficiency caused higher PDC activity and lower blood glucose levels in the fed state while PDK4 deficiency caused similar effects in the fasting state. DKO intensified these effects in both states. PDK2 deficiency ...
c12) United States Patent - Rice Scholarship Home
... The metabolic pathways leading to the production of most industrially important compounds involve oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. Biosynthetic transformations involving redox reactions offer a significant economic and environmental advantage for the production of fine chemicals over conventio ...
... The metabolic pathways leading to the production of most industrially important compounds involve oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. Biosynthetic transformations involving redox reactions offer a significant economic and environmental advantage for the production of fine chemicals over conventio ...
Regulation of Exogenous and Endogenous Glucose Metabolism by
... metabolic fuels to myocardial energy production (1). Glucose plays an important role in myocardial energy metabolism, providing ATP through both glycolysis and oxidation in the citric acid cycle. Numerous studies have demonstrated that the uptake of glucose by the heart is regulated by insulin. Furt ...
... metabolic fuels to myocardial energy production (1). Glucose plays an important role in myocardial energy metabolism, providing ATP through both glycolysis and oxidation in the citric acid cycle. Numerous studies have demonstrated that the uptake of glucose by the heart is regulated by insulin. Furt ...
AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF
... remove only 50 to 60% of the added TCE after four stimulations, while propane utilizers were unable to cometabolize any TCE. Primary substrate utilization lag-times of 4 to 5 days, 0 to 0.5 days and 40 to 45 days were observed for methane, phenol and propane, respectively. Cometabolism of VC was pos ...
... remove only 50 to 60% of the added TCE after four stimulations, while propane utilizers were unable to cometabolize any TCE. Primary substrate utilization lag-times of 4 to 5 days, 0 to 0.5 days and 40 to 45 days were observed for methane, phenol and propane, respectively. Cometabolism of VC was pos ...
The metabolic responses of high intensity intermittent exercise in
... followed by 36 s rest (24:36). This study showed that the 24:36 HIIE protocol induced significantly greater, but previously unaccounted for energy loss via heightened urinary lactate and purine excretion compared to the 8:12 trial. Furthermore, plasma markers indicate that the 24:36 protocol may hav ...
... followed by 36 s rest (24:36). This study showed that the 24:36 HIIE protocol induced significantly greater, but previously unaccounted for energy loss via heightened urinary lactate and purine excretion compared to the 8:12 trial. Furthermore, plasma markers indicate that the 24:36 protocol may hav ...
Panel 13–2 The complete citric acid cycle
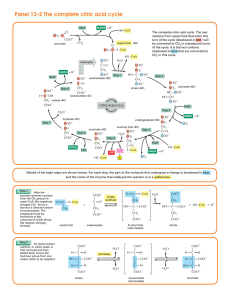
... In the third oxidation step in the cycle, FAD removes two hydrogen atoms from succinate. ...
... In the third oxidation step in the cycle, FAD removes two hydrogen atoms from succinate. ...
Acid-Base 2013 - UMF IASI 2015
... •change in PaCO2 not within this range = a mixed acid-base disturbance –ex, if the a less decrease in PaCO2 than the expected change = a primary respiratory acidosis also present ...
... •change in PaCO2 not within this range = a mixed acid-base disturbance –ex, if the a less decrease in PaCO2 than the expected change = a primary respiratory acidosis also present ...
Liver glucose metabolism in humans
... enter the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle to be oxidized or may be exported to the cytosol to synthesize fatty acids, when excess glucose is present within the hepatocyte. Finally, glucose 6-phosphate may produce NADPH and ribose 5-phosphate through the pentose phosphate pathway. Glucose metabolism s ...
... enter the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle to be oxidized or may be exported to the cytosol to synthesize fatty acids, when excess glucose is present within the hepatocyte. Finally, glucose 6-phosphate may produce NADPH and ribose 5-phosphate through the pentose phosphate pathway. Glucose metabolism s ...
Production and Utilization of Acetate in Mammals
... Initial experiments on the intracellular distribution of acetyl-CoA synthetase and acetyl-CoA hydrolase were performed by differential centrifugation of homogenates in 0.25M-sucrose (Schneider & Hogeboom, 1950). Although the particulate activities of the two enzymes were associated with the mitochon ...
... Initial experiments on the intracellular distribution of acetyl-CoA synthetase and acetyl-CoA hydrolase were performed by differential centrifugation of homogenates in 0.25M-sucrose (Schneider & Hogeboom, 1950). Although the particulate activities of the two enzymes were associated with the mitochon ...
New insight into the photoheterotrophic growth of the
... intermediate of the branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis pathway, which is activated during acetate assimilation, rather than a metabolite of the so-called citramalate cycle. ...
... intermediate of the branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis pathway, which is activated during acetate assimilation, rather than a metabolite of the so-called citramalate cycle. ...
Glutamate Dehydrogenases: Enzymology, Physiological
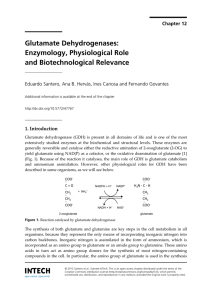
... Glutamate can be synthesized by two alternative routes: one involves catalysis of GDH in the aminating direction, but ammonium assimilation is also possible by the participation of two enzymes: glutamine synthetase (GS), and glutamate synthase, also named glutamine oxoglutarate aminotransferase or G ...
... Glutamate can be synthesized by two alternative routes: one involves catalysis of GDH in the aminating direction, but ammonium assimilation is also possible by the participation of two enzymes: glutamine synthetase (GS), and glutamate synthase, also named glutamine oxoglutarate aminotransferase or G ...
On the mechanism of action of the antifungal agent propionate
... propionate as sole carbon and energy source. Unexpectedly, growth of DmcsA on glucose was more inhibited by propionate than that of a wild-type strain [2]. This result indicated that (2S,3S)-methylcitrate or (2R,3S)-2-methylisocitrate are unlikely to be responsible for this inhibitory effect. At hig ...
... propionate as sole carbon and energy source. Unexpectedly, growth of DmcsA on glucose was more inhibited by propionate than that of a wild-type strain [2]. This result indicated that (2S,3S)-methylcitrate or (2R,3S)-2-methylisocitrate are unlikely to be responsible for this inhibitory effect. At hig ...
Application of Synthetic Biology for Biopolymer
... Plastics are versatile, cheap and durable materials that are omnipresent in modern society. Since most of them are derived from crude oil and are not biodegradable, their production leads to the depletion of fossil fuels and the accumulation of enormous amounts of plastic waste that pollutes ecosyst ...
... Plastics are versatile, cheap and durable materials that are omnipresent in modern society. Since most of them are derived from crude oil and are not biodegradable, their production leads to the depletion of fossil fuels and the accumulation of enormous amounts of plastic waste that pollutes ecosyst ...
Anaerobic and aerobic pathways for salvage of proximal tubules
... and they are not mutually exclusive. One is that the same mechanisms of substrate-level phosphorylation and anaerobic respiration that prevent the lesion from developing during hypoxia are responsible. The other explanation is that, during reoxygenation, succinate, which is a product of both pathway ...
... and they are not mutually exclusive. One is that the same mechanisms of substrate-level phosphorylation and anaerobic respiration that prevent the lesion from developing during hypoxia are responsible. The other explanation is that, during reoxygenation, succinate, which is a product of both pathway ...
Liver glucose metabolism in humans
... or follow the glycolytic pathway to generate pyruvate and then acetyl-coA. Acetyl-coA may enter the tricarboxylic acid cycle to be oxidized or may be exported to the cytosol to synthesize fatty acids, when excess glucose is present within the hepatocyte. Finally, glucose 6-phosphate may produce NADP ...
... or follow the glycolytic pathway to generate pyruvate and then acetyl-coA. Acetyl-coA may enter the tricarboxylic acid cycle to be oxidized or may be exported to the cytosol to synthesize fatty acids, when excess glucose is present within the hepatocyte. Finally, glucose 6-phosphate may produce NADP ...
Electron Transport Chains of Lactic Acid Bacteria
... and inhibits growth of competitors. Indeed metabolic models of Lactobacillus plantarum demonstrated optimisation for growth rate rather than efficiency (61). The anaerobic fermentative conversion of glucose to L-lactate via glycolysis must be redox-balanced (Fig. 3). The electrons that are released ...
... and inhibits growth of competitors. Indeed metabolic models of Lactobacillus plantarum demonstrated optimisation for growth rate rather than efficiency (61). The anaerobic fermentative conversion of glucose to L-lactate via glycolysis must be redox-balanced (Fig. 3). The electrons that are released ...
Energy and Muscle Contraction
... Assuming a person is adequately nourished, the cellular respiration will proceed at a rate that is directly proportional to oxygen delivery. If oxygen delivery increases, ATP production increases. If oxygen delivery decreases, ATP production decreases. ATP will be produced by cellular respiration is ...
... Assuming a person is adequately nourished, the cellular respiration will proceed at a rate that is directly proportional to oxygen delivery. If oxygen delivery increases, ATP production increases. If oxygen delivery decreases, ATP production decreases. ATP will be produced by cellular respiration is ...
BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Problem Unit Two
... Enzymes, then, are necessary for the normal functioning of cells. Disease states may be caused by the absence or alteration of an enzyme (i.e., a genetic disease), the introduction of an enzyme inhibitor (i.e., a bacterial toxin, a chemical, etc.), the overproduction of an enzyme, or the introductio ...
... Enzymes, then, are necessary for the normal functioning of cells. Disease states may be caused by the absence or alteration of an enzyme (i.e., a genetic disease), the introduction of an enzyme inhibitor (i.e., a bacterial toxin, a chemical, etc.), the overproduction of an enzyme, or the introductio ...
Hormonal Control of Glucose Metabolism
... In a normal human living in a Western society, the 24 hours of a normal day can be divided into three periods of approximately 4 hours, corresponding to the absorption and assimilation of the principal meals and to a postabsorptive period corresponding to the 12-hour overnight fast. During these per ...
... In a normal human living in a Western society, the 24 hours of a normal day can be divided into three periods of approximately 4 hours, corresponding to the absorption and assimilation of the principal meals and to a postabsorptive period corresponding to the 12-hour overnight fast. During these per ...
Eram_SeyedMohammad - UWSpace
... native molecular weights of 260 kDa. Although the POR of T. maritima was characterized previously, its PDC activity was not reported. Since the T. hypogea genome sequence is not available, the primary structure of the genes encoding each of the POR four subunits were determined using inverse PCR and ...
... native molecular weights of 260 kDa. Although the POR of T. maritima was characterized previously, its PDC activity was not reported. Since the T. hypogea genome sequence is not available, the primary structure of the genes encoding each of the POR four subunits were determined using inverse PCR and ...
Lactate dehydrogenase

A lactate dehydrogenase (LDH or LD) is an enzyme found in nearly all living cells (animals, plants, and prokaryotes). LDH catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactate and back, as it converts NADH to NAD+ and back. A dehydrogenase is an enzyme that transfers a hydride from one molecule to another.LDH exist in four distinct enzyme classes. This article is about the common NAD(P)-dependent L-lactate dehydrogenase. Other LDHs act on D-lactate and/or are dependent on cytochrome c: D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)) and L-lactate (L-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)). LDH has been of medical significance because it is found extensively in body tissues, such as blood cells and heart muscle. Because it is released during tissue damage, it is a marker of common injuries and disease such as heart failure.