metabolic pathways - MPG Systems Biology Forum
... An elementary mode is a minimal set of enzymes that can operate at steady state with all irreversible reactions used in the appropriate direction All flux distributions in the living cell are non-negative linear combinations of elementary modes ...
... An elementary mode is a minimal set of enzymes that can operate at steady state with all irreversible reactions used in the appropriate direction All flux distributions in the living cell are non-negative linear combinations of elementary modes ...
Does Lactic Acid Cause Muscular Fatigue?
... Aerobic metabolism. As indicated, pyruvate and NADH, (and, perhaps, lactic acid), must be absorbed from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria of muscle fibers in order to continue being metabolized. Mitochondria are rod-shaped structures found in the cytoplasm of cells (see figure 4). They have been l ...
... Aerobic metabolism. As indicated, pyruvate and NADH, (and, perhaps, lactic acid), must be absorbed from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria of muscle fibers in order to continue being metabolized. Mitochondria are rod-shaped structures found in the cytoplasm of cells (see figure 4). They have been l ...
Citrate metabolism in lactic acid bacteria
... process that it catalyses. The citrate permease of L. lactis was found to have a narrow pH optimum with only appreciable activity between pH 5.0 and 6.0 [12]. The permeasc of Leuconostoc was found to be homologous to the L. lactis permease [13] and is likely to show a similar pH dependency as the L. ...
... process that it catalyses. The citrate permease of L. lactis was found to have a narrow pH optimum with only appreciable activity between pH 5.0 and 6.0 [12]. The permeasc of Leuconostoc was found to be homologous to the L. lactis permease [13] and is likely to show a similar pH dependency as the L. ...
enzyme
... positively charged Lys or Arg residues H2N-Gly-Ile-Val-Glu-Gln-Cys-Cys-Thr-Ser-Lys-Ile-Ser-Leu-Tyr-Gln-Leu-Glu-Asn-Tyr------ ...
... positively charged Lys or Arg residues H2N-Gly-Ile-Val-Glu-Gln-Cys-Cys-Thr-Ser-Lys-Ile-Ser-Leu-Tyr-Gln-Leu-Glu-Asn-Tyr------ ...
Anion gap metabolic acidosis
... Acetaldehyde levels increase significantly if acetaldehyde dehydrogenase inhibited by disulfiram, insecticides or a sulfonurea. ...
... Acetaldehyde levels increase significantly if acetaldehyde dehydrogenase inhibited by disulfiram, insecticides or a sulfonurea. ...
The Proposed Effects of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD
... electron transport is utilised in the formation of ATP [1]. Oxygen’s role in aerobic respiration is to act as the final hydrogen/electron accepter to form water. If this is not present the whole aerobic pathway cannot occur and so the body will rely on energy produced anaerobically. The question ins ...
... electron transport is utilised in the formation of ATP [1]. Oxygen’s role in aerobic respiration is to act as the final hydrogen/electron accepter to form water. If this is not present the whole aerobic pathway cannot occur and so the body will rely on energy produced anaerobically. The question ins ...
Fatigue During Muscular Exercise
... • Two hypothesis for peripheral fatigue • a) Exhaustion - depletion of energy substrates - eg ATP, CP, glycogen – Phosphagens are present in low quantities – Must match use with restoration from other metabolic pathways - or fatigue ...
... • Two hypothesis for peripheral fatigue • a) Exhaustion - depletion of energy substrates - eg ATP, CP, glycogen – Phosphagens are present in low quantities – Must match use with restoration from other metabolic pathways - or fatigue ...
video slide - Green River Community College
... by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate • The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a ...
... by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate • The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a ...
Metabolism
... Glycogen metabolism in liver and muscle Energy yield from glycogen breakdown The energy yield from the hydrolysis of stored glycogen and the subsequent oxidation of the released glucose is the same in muscle and liver. When glycogen is hydrolyzed, the product is glucose 1phosphate. This is easily co ...
... Glycogen metabolism in liver and muscle Energy yield from glycogen breakdown The energy yield from the hydrolysis of stored glycogen and the subsequent oxidation of the released glucose is the same in muscle and liver. When glycogen is hydrolyzed, the product is glucose 1phosphate. This is easily co ...
ppt
... 2. One C is broken off (CO2) and NAD accepts energy (NADH) 3. The second C is broken off (CO2) and NAD accepts the energy…at this point the acetyl group has ...
... 2. One C is broken off (CO2) and NAD accepts energy (NADH) 3. The second C is broken off (CO2) and NAD accepts the energy…at this point the acetyl group has ...
Part 2
... 2. One C is broken off (CO2) and NAD accepts energy (NADH) 3. The second C is broken off (CO2) and NAD accepts the energy…at this point the acetyl group has ...
... 2. One C is broken off (CO2) and NAD accepts energy (NADH) 3. The second C is broken off (CO2) and NAD accepts the energy…at this point the acetyl group has ...
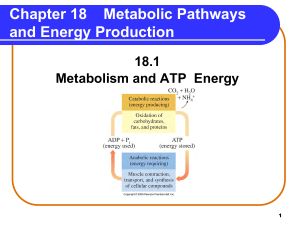
Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
... • NADH (Complex I) oxidation for 3 ATPs. NADH + 3 ADP + 3Pi NAD+ + 3 ATP • FADH2 (Complex II) oxidation for 2 ATPs. FADH2 + 2 ADP + 2Pi FAD + 2 ATP ...
... • NADH (Complex I) oxidation for 3 ATPs. NADH + 3 ADP + 3Pi NAD+ + 3 ATP • FADH2 (Complex II) oxidation for 2 ATPs. FADH2 + 2 ADP + 2Pi FAD + 2 ATP ...
Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle
... converted to FADH2 by this reaction and is regenerated by the passage of electrons to NAD+. 38. Production of acetyl-CoA (activated acetate) Page: 606 Difficulty: 2 The human disease beriberi is caused by a deficiency of thiamine in the diet. People with severe beriberi have higher than normal level ...
... converted to FADH2 by this reaction and is regenerated by the passage of electrons to NAD+. 38. Production of acetyl-CoA (activated acetate) Page: 606 Difficulty: 2 The human disease beriberi is caused by a deficiency of thiamine in the diet. People with severe beriberi have higher than normal level ...
Chapter 4 General metabolism
... pyruvate bypass that involves the synthesis of acetyl-CoA through the concerted action of pyruvate decarboxylase, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase and acetyl CoA synthetase (Figure 4.3). These reactions followed by transport of the formed acetyl CoA to the mitochondria could in principle “by-pass” the act ...
... pyruvate bypass that involves the synthesis of acetyl-CoA through the concerted action of pyruvate decarboxylase, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase and acetyl CoA synthetase (Figure 4.3). These reactions followed by transport of the formed acetyl CoA to the mitochondria could in principle “by-pass” the act ...
File
... by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate • The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a ...
... by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate • The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a ...
Perry et al., 2008
... volume and maximal capacity for carbohydrate and fat oxidation, and permits the maintenance of exercise at higher absolute power outputs (Holloszy 1967; Gollnick et al. 1973; Holloszy and Coyle 1984; Leblanc et al. 2004a). The greater mitochondrial volume also improves the sensitivity of mitochondri ...
... volume and maximal capacity for carbohydrate and fat oxidation, and permits the maintenance of exercise at higher absolute power outputs (Holloszy 1967; Gollnick et al. 1973; Holloszy and Coyle 1984; Leblanc et al. 2004a). The greater mitochondrial volume also improves the sensitivity of mitochondri ...
Dr. V. Main Powerpoint
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from f ...
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from f ...
metabolic factors in fatigue
... levels can be almost totally depleted after maximal exercise (Bogdanis et al., 1995; Casey et al., 1996), and this depletion of PCr contributes to the rapid decline in power output observed during such exercise (Sahlin et al., 1998). The recovery of power-generating ability following maximal exerci ...
... levels can be almost totally depleted after maximal exercise (Bogdanis et al., 1995; Casey et al., 1996), and this depletion of PCr contributes to the rapid decline in power output observed during such exercise (Sahlin et al., 1998). The recovery of power-generating ability following maximal exerci ...
Chapter 8: Energy generation:glycolysis
... Oxygen is used up during the reaction, so in chemical terms the process is an oxidation. Glucose oxidation is a highly exergonic reaction, yielding 2870 kJ of energy for every mole of glucose that is broken down. In biochemical terms, this is a substantial amount of energy; a typical endergonic enzy ...
... Oxygen is used up during the reaction, so in chemical terms the process is an oxidation. Glucose oxidation is a highly exergonic reaction, yielding 2870 kJ of energy for every mole of glucose that is broken down. In biochemical terms, this is a substantial amount of energy; a typical endergonic enzy ...
Lesson 8. Enzymes
... enzymes posses the catalytic power to facilitate life processes in essentially all life-forms from viruses to man. Most of the enzymes retain their catalytic potential even after extraction from the living organism. The above catalytic power of enzyme leads to commercial usage of enzymes. In ancient ...
... enzymes posses the catalytic power to facilitate life processes in essentially all life-forms from viruses to man. Most of the enzymes retain their catalytic potential even after extraction from the living organism. The above catalytic power of enzyme leads to commercial usage of enzymes. In ancient ...
Chapter 9
... by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate • The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a ...
... by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate • The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a ...
09_Lecture_Presentation
... by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate • The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a ...
... by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate • The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a ...
Lactate dehydrogenase

A lactate dehydrogenase (LDH or LD) is an enzyme found in nearly all living cells (animals, plants, and prokaryotes). LDH catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactate and back, as it converts NADH to NAD+ and back. A dehydrogenase is an enzyme that transfers a hydride from one molecule to another.LDH exist in four distinct enzyme classes. This article is about the common NAD(P)-dependent L-lactate dehydrogenase. Other LDHs act on D-lactate and/or are dependent on cytochrome c: D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)) and L-lactate (L-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)). LDH has been of medical significance because it is found extensively in body tissues, such as blood cells and heart muscle. Because it is released during tissue damage, it is a marker of common injuries and disease such as heart failure.