Microbiology
... disease has been shown in multiple studies (Hartiala et al., 2014; Koeth et al., 2013; Kuka et al., 2014), but is still up for discussion in the scientific and medical communities (Johri et al., 2014). However, there is no debate that bacteria, intestinal and otherwise, utilize carnitine in many dif ...
... disease has been shown in multiple studies (Hartiala et al., 2014; Koeth et al., 2013; Kuka et al., 2014), but is still up for discussion in the scientific and medical communities (Johri et al., 2014). However, there is no debate that bacteria, intestinal and otherwise, utilize carnitine in many dif ...
EFFECTS OF BIOREACTOR OPERATION PARAMETERS ON
... oxygen uptake rates and the liquid phase mass transfer coefficient values were determined. The highest β-lactamase activity was obtained at 0.5 vvm 500 min-1 and at 0.2 vvm 500 min-1 conditions as ca. A=90 U cm-3 while the highest cell concentration was obtained as Cx=0.67 kg m-3 at 0.5 vvm 750 min ...
... oxygen uptake rates and the liquid phase mass transfer coefficient values were determined. The highest β-lactamase activity was obtained at 0.5 vvm 500 min-1 and at 0.2 vvm 500 min-1 conditions as ca. A=90 U cm-3 while the highest cell concentration was obtained as Cx=0.67 kg m-3 at 0.5 vvm 750 min ...
Floriculture Test Bank B
... ____ 14. _______ induces adventitious roots to form on stems while they are still attached to the parent plant. a. Division c. Layering b. Budding d. Grafting ____ 15. ________ is used in research to study physiological processes or plant diseases. a. Grafting c. Layering b. Division d. Budding ____ ...
... ____ 14. _______ induces adventitious roots to form on stems while they are still attached to the parent plant. a. Division c. Layering b. Budding d. Grafting ____ 15. ________ is used in research to study physiological processes or plant diseases. a. Grafting c. Layering b. Division d. Budding ____ ...
7vВyВtvphy hБq purАvphy АrpuhБvЖАЖ Вs ЕrqИpЗvЙr
... in that the Oxidized Form has higher oxidation state than Reduced Form via electron donation. An oxidation or a reduction cannot occur in isolation. A redox reaction, i.e. a reaction with coupled oxidation and reduction, must necessarily involve two redox pairs. The redox potential is an electrochem ...
... in that the Oxidized Form has higher oxidation state than Reduced Form via electron donation. An oxidation or a reduction cannot occur in isolation. A redox reaction, i.e. a reaction with coupled oxidation and reduction, must necessarily involve two redox pairs. The redox potential is an electrochem ...
1 spirulina (arthrospira): an edible
... Cyanobacteria and Prochlorales (Castenholz and Waterbury, 1989; Whitton, 1992), which are, by phylogeny, related to the sequence of the rARN (ribosomal ribonucleic acid) sub-unit 16S. As a function of the sequence data of this sub-unit and the rRNA sub-unit 5S, these prokaryotes are classified withi ...
... Cyanobacteria and Prochlorales (Castenholz and Waterbury, 1989; Whitton, 1992), which are, by phylogeny, related to the sequence of the rARN (ribosomal ribonucleic acid) sub-unit 16S. As a function of the sequence data of this sub-unit and the rRNA sub-unit 5S, these prokaryotes are classified withi ...
The interaction between cyanobacteria and zooplankton in a more
... elusive. Historically, the focus has been on studying the grazing defenses of cyanobacteria and their effects of zooplankton. Several cyanobacterial secondary metabolites, such as microcystins (MCs), were shown to have negative physiological effects on zooplankton (Rohrlack et al., 1999; Lürling an ...
... elusive. Historically, the focus has been on studying the grazing defenses of cyanobacteria and their effects of zooplankton. Several cyanobacterial secondary metabolites, such as microcystins (MCs), were shown to have negative physiological effects on zooplankton (Rohrlack et al., 1999; Lürling an ...
Rate at which glutamine enters TCA cycle influences carbon atom
... Because no stimulators of aminotransferase activity were known, we approached this with the glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) stimulator BCH. Although glutamine carbon has been thought to enter the TCA cycle primarily via aminotransferase pathways, there is evidence of flux through GDH (2, 6). Previous ...
... Because no stimulators of aminotransferase activity were known, we approached this with the glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) stimulator BCH. Although glutamine carbon has been thought to enter the TCA cycle primarily via aminotransferase pathways, there is evidence of flux through GDH (2, 6). Previous ...
AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF
... from approximately 5 to 10 ft bgs. Primarily sand with some silty sand and silt extends below the clay layer to a depth of 85 to 90 ft bgs. Site investigations have resulted in the installation of 51 monitoring wells screened in three separate zones of the Semiperched Aquifer throughout IRP Site 24. ...
... from approximately 5 to 10 ft bgs. Primarily sand with some silty sand and silt extends below the clay layer to a depth of 85 to 90 ft bgs. Site investigations have resulted in the installation of 51 monitoring wells screened in three separate zones of the Semiperched Aquifer throughout IRP Site 24. ...
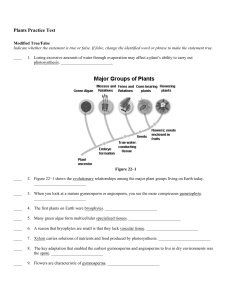
Plants Practice Test
... ____ 14. If a seed has two cotyledons, it will have fibrous roots. _________________________ ____ 15. Biennials are pollinated during their first year of growth. _________________________ ____ 16. In plants, the main organs in which photosynthesis takes place are leaves. _________________________ __ ...
... ____ 14. If a seed has two cotyledons, it will have fibrous roots. _________________________ ____ 15. Biennials are pollinated during their first year of growth. _________________________ ____ 16. In plants, the main organs in which photosynthesis takes place are leaves. _________________________ __ ...
Powerpoint
... discriminative, the •OH radical attacks different molecules or different sites in the same molecule producing lower yields of a specific product. In the case of Tyr, the •OH radical can add and oxidize the amino acid producing at least two different products (nitrated and hydroxylated Tyr). In contr ...
... discriminative, the •OH radical attacks different molecules or different sites in the same molecule producing lower yields of a specific product. In the case of Tyr, the •OH radical can add and oxidize the amino acid producing at least two different products (nitrated and hydroxylated Tyr). In contr ...
Question Bank (Class XI - Chemistry)
... Ans. A substance which contains only one kind of atom or molecule is called a pure substance . Q4- Define average atomic mass. (L-1) Ans. Average atomic mass is the average of atomic mass of all the isotopes of an element. Q5- What is one a.m.u. or one ‘u ,? (L-1) Ans:- One a.m.u. or u is equal to 1 ...
... Ans. A substance which contains only one kind of atom or molecule is called a pure substance . Q4- Define average atomic mass. (L-1) Ans. Average atomic mass is the average of atomic mass of all the isotopes of an element. Q5- What is one a.m.u. or one ‘u ,? (L-1) Ans:- One a.m.u. or u is equal to 1 ...
this 40 page pdf file .
... Blue-green algae are cyanobacteria Many people have asked about differences between two kinds of blue-green algae spirulina and aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Blue-green algae is also called cyanobacteria. Some can fix atmospheric nitrogen into organic forms. Organic nitrogen is essential for building pr ...
... Blue-green algae are cyanobacteria Many people have asked about differences between two kinds of blue-green algae spirulina and aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Blue-green algae is also called cyanobacteria. Some can fix atmospheric nitrogen into organic forms. Organic nitrogen is essential for building pr ...
Worksheets - cloudfront.net
... laws of motion allowed him to explain why objects move as they do. ...
... laws of motion allowed him to explain why objects move as they do. ...
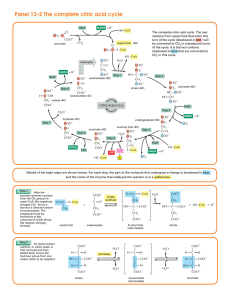
Panel 13–2 The complete citric acid cycle
... carbons from acetyl CoA that enter this turn of the cycle (shadowed in red ) will be converted to CO2 in subsequent turns of the cycle: it is the two carbons shadowed in blue that are converted to CO2 in this cycle. ...
... carbons from acetyl CoA that enter this turn of the cycle (shadowed in red ) will be converted to CO2 in subsequent turns of the cycle: it is the two carbons shadowed in blue that are converted to CO2 in this cycle. ...
Systematic metabolic analysis of recombinant Pichia pastoris UNIVERSITAT AUTÒNOMA DE BARCELONA
... Nutrients are transported through the cell membrane using different mechanism in order to be available to be catabolised. Once there are inside, these nutrients are the precursors to generate all the energy and reducing power to synthesize all the cell components required. The metabolic pathways ens ...
... Nutrients are transported through the cell membrane using different mechanism in order to be available to be catabolised. Once there are inside, these nutrients are the precursors to generate all the energy and reducing power to synthesize all the cell components required. The metabolic pathways ens ...
Chassahowitzka WMA Rare Plants Survey
... ecristata). One plant species located during the survey, Chapman’s skeletongrass (Gymnopogon chapmanianus), is tracked by FNAI, but not listed by the state. Several locations were recorded for four species listed by the state as commercially exploited: Florida butterfly orchid (Encyclia tampensis), ...
... ecristata). One plant species located during the survey, Chapman’s skeletongrass (Gymnopogon chapmanianus), is tracked by FNAI, but not listed by the state. Several locations were recorded for four species listed by the state as commercially exploited: Florida butterfly orchid (Encyclia tampensis), ...
P fr
... • Provides information about environment • Answers 3 questions for plant – Am I in the light? – Do I have plants as neighbors or above me? – Is it time to flower? ...
... • Provides information about environment • Answers 3 questions for plant – Am I in the light? – Do I have plants as neighbors or above me? – Is it time to flower? ...
Estuarine Nutrient Cycling - The Influence of
... different plant types respond to environmental changes (for example eutrophication), but we also expect that they affect the fate of organic matter produced during photosynthesis and, thus, modify major pathways of energy, carbon and plant nutrients (especially N and P). The composition of plant com ...
... different plant types respond to environmental changes (for example eutrophication), but we also expect that they affect the fate of organic matter produced during photosynthesis and, thus, modify major pathways of energy, carbon and plant nutrients (especially N and P). The composition of plant com ...
(45)
... molecules and SWCNTs onto which they are adsorbed, has been identified as a simple, yet effective, way to modify the electronic structure of SWCNTs [10,11]. Molecular doping is advantageous because of the reversibility of the doping effect and the decreased production of impurities which can obstruc ...
... molecules and SWCNTs onto which they are adsorbed, has been identified as a simple, yet effective, way to modify the electronic structure of SWCNTs [10,11]. Molecular doping is advantageous because of the reversibility of the doping effect and the decreased production of impurities which can obstruc ...
PhD Dissertation: EFFECT OF LOW SOIL
... crop, amaranth plants could be cut for forage at an early stage, before significant floral growth. The daylength response in many lines causes flowering to occur early enough to produce a grain crop in addition to the forage crop. In some environments, this practice could aid in reducing plant heig ...
... crop, amaranth plants could be cut for forage at an early stage, before significant floral growth. The daylength response in many lines causes flowering to occur early enough to produce a grain crop in addition to the forage crop. In some environments, this practice could aid in reducing plant heig ...
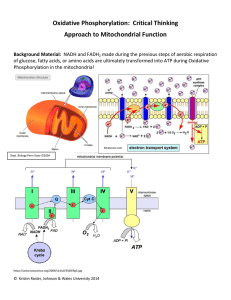
practice oxidative phosphorylation worksheet11
... * Interestingly, many animals (camels, hibernating bears) rely upon the water being produced at the end of the ETC as its source of water while metabolizing fatty acids that lead to the formation of many NADH and FADH2. * Anaerobes, on the other hand, can use alternative terminal oxidases in an indu ...
... * Interestingly, many animals (camels, hibernating bears) rely upon the water being produced at the end of the ETC as its source of water while metabolizing fatty acids that lead to the formation of many NADH and FADH2. * Anaerobes, on the other hand, can use alternative terminal oxidases in an indu ...
AP & Regents Biology
... If pillbugs prefer a moist environment, then when they are randomly placed on both sides of a wet/dry choice chamber and allowed to move about freely for 10 minutes, most will be found on the wet side. ...
... If pillbugs prefer a moist environment, then when they are randomly placed on both sides of a wet/dry choice chamber and allowed to move about freely for 10 minutes, most will be found on the wet side. ...
A network-based approach to cell metabolism: from structure to flux balances
... specific sequences of chemical reactions in order to optimize processes, thousands of reactions, tightly interconnected through common metabolites, take place simultaneously in cells, forming a network that is precisely controlled by the combined action of enzymes, genes, etc., in order to secure fu ...
... specific sequences of chemical reactions in order to optimize processes, thousands of reactions, tightly interconnected through common metabolites, take place simultaneously in cells, forming a network that is precisely controlled by the combined action of enzymes, genes, etc., in order to secure fu ...
Amino Acid Catabolism: C
... Histidine is first converted to glutamate. The last step in this pathway involves the cofactor tetrahydrofolate. Tetrahydrofolate (THF), which has a pteridine ring, is a reduced form of the B vitamin folate. Within a cell, THF has an attached chain of several glutamate residues, linked to one anothe ...
... Histidine is first converted to glutamate. The last step in this pathway involves the cofactor tetrahydrofolate. Tetrahydrofolate (THF), which has a pteridine ring, is a reduced form of the B vitamin folate. Within a cell, THF has an attached chain of several glutamate residues, linked to one anothe ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.