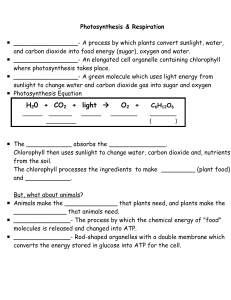
H20 + CO2 + light → O2 + C6H12O6
... The chlorophyll processes the ingredients to make _________ (plant food) and ____________. But, what about animals? Animals make the ______________ that plants need, and plants make the ______________ that animals need. _______________- The process by which the chemical energy of "food" molecule ...
... The chlorophyll processes the ingredients to make _________ (plant food) and ____________. But, what about animals? Animals make the ______________ that plants need, and plants make the ______________ that animals need. _______________- The process by which the chemical energy of "food" molecule ...
Photosynthesis - Shelton State
... -reflection & absorption 2 primary types of plant pigments: 1. Carotenoids= 2. Chlorophylls= -chlorophyll a & b *Why does a plant look green? *What colors of light do plants use? *Why do leaves change colors? Photosynthetic Reactions Solar e + 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 -Redox Rxn: -CO2 is reduced ...
... -reflection & absorption 2 primary types of plant pigments: 1. Carotenoids= 2. Chlorophylls= -chlorophyll a & b *Why does a plant look green? *What colors of light do plants use? *Why do leaves change colors? Photosynthetic Reactions Solar e + 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 -Redox Rxn: -CO2 is reduced ...
Photosynthesis and Respiration Notes
... _________________- A process of converting sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into food energy (sugar), oxygen and water. _________________- An elongated cell organelle containing chlorophyll where photosynthesis takes place. _________________- A green molecule which uses light energy from su ...
... _________________- A process of converting sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into food energy (sugar), oxygen and water. _________________- An elongated cell organelle containing chlorophyll where photosynthesis takes place. _________________- A green molecule which uses light energy from su ...
OverallQuiz2Ch5-8.doc
... used to replace these electrons? a. sunlight b. oxygen c. water d. carbon dioxide ...
... used to replace these electrons? a. sunlight b. oxygen c. water d. carbon dioxide ...
Unit_biology_2_Photosynthesis
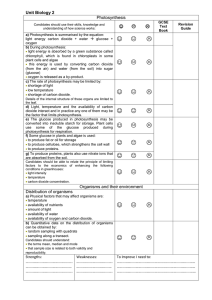
... Details of the internal structure of these organs are limited to the leaf. ...
... Details of the internal structure of these organs are limited to the leaf. ...
Chapter 7 Photosynthesis_student version
... Light hits object and is either absorbed or reflect ...
... Light hits object and is either absorbed or reflect ...
KA 7 Summary sheet
... enzyme controlled reactions. Hydrogen and ATP produced by the Light Reaction (stage 1) are used. ATP is used as the energy source. The hydrogen combines with carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to produce a sugar called glucose. The chemical energy in the glucose is available to use in a process call ...
... enzyme controlled reactions. Hydrogen and ATP produced by the Light Reaction (stage 1) are used. ATP is used as the energy source. The hydrogen combines with carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to produce a sugar called glucose. The chemical energy in the glucose is available to use in a process call ...
Quizon ch5-6-7-8new.doc
... a. the reactants have more potential energy than the products b. energy is released c. a net input of energy is not required d. all of the above e. none of the above 7. In most land plants, photosynthesis occurs in cells of the __________ of the leaves, because these cells contain the largest number ...
... a. the reactants have more potential energy than the products b. energy is released c. a net input of energy is not required d. all of the above e. none of the above 7. In most land plants, photosynthesis occurs in cells of the __________ of the leaves, because these cells contain the largest number ...
Photosynthesis - Lake Stevens School District
... absorb red and violet-blue light and reflect green ◦ each pigment absorbs a slightly different wavelength, increasing the spectrum of colors to drive photosynthesis chlorophyll a chlorophyll b carotenoids ...
... absorb red and violet-blue light and reflect green ◦ each pigment absorbs a slightly different wavelength, increasing the spectrum of colors to drive photosynthesis chlorophyll a chlorophyll b carotenoids ...
File
... 1. What is the energy molecule of the cell called? ATP 2. What macromolecule made by plants is "burned" in the mitochondria? GLUCOSE 3. Where is chlorophyll found in the chloroplast? THYLAKOIDS 4. In which part of a plant would you expect to find the most chloroplasts and why? LEAVES – HAVE THE GREA ...
... 1. What is the energy molecule of the cell called? ATP 2. What macromolecule made by plants is "burned" in the mitochondria? GLUCOSE 3. Where is chlorophyll found in the chloroplast? THYLAKOIDS 4. In which part of a plant would you expect to find the most chloroplasts and why? LEAVES – HAVE THE GREA ...
2.1 Photosynthesis I. sources of energy A. Photosynthesis 1. process
... 2.1 Photosynthesis I. sources of energy A. Photosynthesis 1. process by which a cell captures energy in sunlight and uses it make food 2. photo means “light”, and synthesis means “putting together” 3. all things obtain energy directly or indirectly from sunlight energy captured during photosynthesis ...
... 2.1 Photosynthesis I. sources of energy A. Photosynthesis 1. process by which a cell captures energy in sunlight and uses it make food 2. photo means “light”, and synthesis means “putting together” 3. all things obtain energy directly or indirectly from sunlight energy captured during photosynthesis ...
Session 15 Handout
... ii. Occurs in green plants, seaweed, algae, and certain bacteria iii. _____________________________________________ iv. Glucose is used for energy to build new ______________________________________________ ...
... ii. Occurs in green plants, seaweed, algae, and certain bacteria iii. _____________________________________________ iv. Glucose is used for energy to build new ______________________________________________ ...
Puzzle - UBC Blogs
... 1 membranous structure within chloroplast 5 pigment found in chloroplast that can be part of the antennal complex of a photosystem 7 ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate 9 organelle in which photosynthesis occurs 13 source of energy and reducing power 15 Crassulacean acid metabolism 16 spectrum of light waves ...
... 1 membranous structure within chloroplast 5 pigment found in chloroplast that can be part of the antennal complex of a photosystem 7 ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate 9 organelle in which photosynthesis occurs 13 source of energy and reducing power 15 Crassulacean acid metabolism 16 spectrum of light waves ...
Photosynthesis

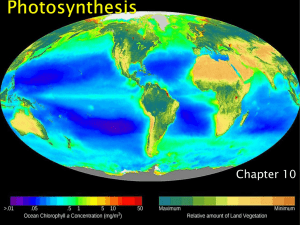
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.