Photosynthesis Powerpoint
... 1. Light is absorbed by Chlorophyll in the thylakoid stacks 2. Hydrogen is released during the breakdown of water and is used to create ATP 3. The oxygen is released into the environment as a byproduct ...
... 1. Light is absorbed by Chlorophyll in the thylakoid stacks 2. Hydrogen is released during the breakdown of water and is used to create ATP 3. The oxygen is released into the environment as a byproduct ...
Unit 2 Test Study Guide
... capture light energy and use it to make food from carbon dioxide and water. Chlorophyll - a substance that gives chloroplasts their green color and captures energy from sunlight and uses it to produce food. Stoma – the small openings on the undersides of leaves through which oxygen and carbon dioxid ...
... capture light energy and use it to make food from carbon dioxide and water. Chlorophyll - a substance that gives chloroplasts their green color and captures energy from sunlight and uses it to produce food. Stoma – the small openings on the undersides of leaves through which oxygen and carbon dioxid ...
Graphic Organizer #1 Graphic Organizer #2
... Graphic Organizer #2 Create a Venn Diagram. Label one circle PLANT CELLS, label the other circle ANIMAL CELLS. Use all 11 of the terms/statements below. 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy photosynthesis energy in the form of ATP ...
... Graphic Organizer #2 Create a Venn Diagram. Label one circle PLANT CELLS, label the other circle ANIMAL CELLS. Use all 11 of the terms/statements below. 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy photosynthesis energy in the form of ATP ...
Cellular Respiration
... http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/cellresp/intro.html 1. _______________________________________________ is the process by which the chemical energy of “food” molecules is released and partially captured in the form of ATP. 2. The most common fuel for cellular respiration is____ ...
... http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/cellresp/intro.html 1. _______________________________________________ is the process by which the chemical energy of “food” molecules is released and partially captured in the form of ATP. 2. The most common fuel for cellular respiration is____ ...
Energy flow graphic notes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration
... Chloroplasts use Red and Blue light Energy and reflects Green light energy The process of Photosynthesis re-arranges C, O, and H from carbon dioxide and water to produce… ...
... Chloroplasts use Red and Blue light Energy and reflects Green light energy The process of Photosynthesis re-arranges C, O, and H from carbon dioxide and water to produce… ...
Photosynthesis Learning Activity
... There are three types of photosynthesis, C3, C4 and CAM. Each plant has evolved to do one of the three types depending on its interaction with its environment. Most grassland plants will do C3, most succulents do CAM and plants in very humid areas do C4. The main differences between them is in how t ...
... There are three types of photosynthesis, C3, C4 and CAM. Each plant has evolved to do one of the three types depending on its interaction with its environment. Most grassland plants will do C3, most succulents do CAM and plants in very humid areas do C4. The main differences between them is in how t ...
Week 4:
... Stroma filling the space outside of the grana. Light reactions can be divided into 2 “photosystems”: “Water splitting” and “NADPH producing”. These two photosystems both take in light energy, one produces ATP via electron transport chain, the other produces NADPH. These products are both used in the ...
... Stroma filling the space outside of the grana. Light reactions can be divided into 2 “photosystems”: “Water splitting” and “NADPH producing”. These two photosystems both take in light energy, one produces ATP via electron transport chain, the other produces NADPH. These products are both used in the ...
Photosynthesis notes
... Q: Do plants undergo cellular respiration or just photosynthesis? A: Plants do both. - They are producers (autotrophs) and make sugars from CO2 in the atmosphere - They have to break down the sugar into ATP (cell fuel) to run cell activities just like consumers (heterotrophs – organisms that can't ...
... Q: Do plants undergo cellular respiration or just photosynthesis? A: Plants do both. - They are producers (autotrophs) and make sugars from CO2 in the atmosphere - They have to break down the sugar into ATP (cell fuel) to run cell activities just like consumers (heterotrophs – organisms that can't ...
Energy Processing in Plants A. 1.
... A. Materials for Plant Processes 1. To survive, plants must be able to move materials throughout their , make their own down food into a usable form of energy. ...
... A. Materials for Plant Processes 1. To survive, plants must be able to move materials throughout their , make their own down food into a usable form of energy. ...
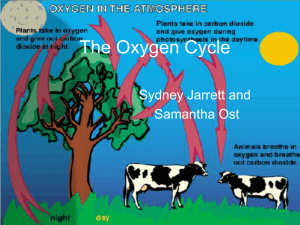
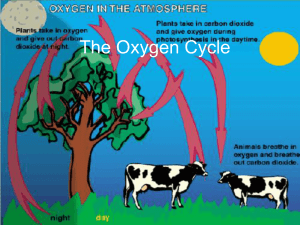
The Oxygen Cycle - EDHSGreenSea.net
... they have been buried in the ground gets absorbed by the soil. ...
... they have been buried in the ground gets absorbed by the soil. ...
Slide 1 - willisworldbio
... __________, such as plants and some other organisms are able to use the energy from the sun to make their food. ...
... __________, such as plants and some other organisms are able to use the energy from the sun to make their food. ...
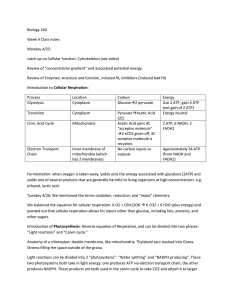
The Oxygen Cycle
... cycle begins with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. • Animals breathe that oxygen and both plants and animals use the sugars for energy. ...
... cycle begins with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. • Animals breathe that oxygen and both plants and animals use the sugars for energy. ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration
... Chapter 10: Photosynthesis Overview: The Process That Feeds The Biosphere Concept 10.1: Photosynthesis Converts Light Energy To The Chemical Energy of Food o Chloroplasts: The Sites of Photosynthesis in Plants o Tracking Atoms Through Photosynthesis o The Two Stages of Photosynthesis: A Preview Conc ...
... Chapter 10: Photosynthesis Overview: The Process That Feeds The Biosphere Concept 10.1: Photosynthesis Converts Light Energy To The Chemical Energy of Food o Chloroplasts: The Sites of Photosynthesis in Plants o Tracking Atoms Through Photosynthesis o The Two Stages of Photosynthesis: A Preview Conc ...
Exam 2 Short Answers Ch 4-8.doc
... 5. In _______________, membranes of adjacent cells are held together by proteins and carbohydrates, much like glue. 6. In plant cells, ______________ allow for communication between cells and in animal cells the _______________ serve the same purpose. 7. ________________ are biological catalysts. 8. ...
... 5. In _______________, membranes of adjacent cells are held together by proteins and carbohydrates, much like glue. 6. In plant cells, ______________ allow for communication between cells and in animal cells the _______________ serve the same purpose. 7. ________________ are biological catalysts. 8. ...
Photosynthesis Worksheet
... Photosynthesis Chloroplasts Photosynthesis is a process in which sunlight energy is used to make glucose. The site of photosynthesis is in the chloroplast – an organelle found in the leaves of green plants. The main functions of chloroplasts are to produce food (glucose) during photosynthesis, and t ...
... Photosynthesis Chloroplasts Photosynthesis is a process in which sunlight energy is used to make glucose. The site of photosynthesis is in the chloroplast – an organelle found in the leaves of green plants. The main functions of chloroplasts are to produce food (glucose) during photosynthesis, and t ...
Chapter 5 Notes:
... the amount of light that passes through a sample of pigments. 1) As different wavelengths are passed through, some are absorbed. 2) Graph of percent of light absorbed at each wavelength is absorption spectrum. 3) Photosynthesis produces oxygen; production of oxygen is used to measure the rate of pho ...
... the amount of light that passes through a sample of pigments. 1) As different wavelengths are passed through, some are absorbed. 2) Graph of percent of light absorbed at each wavelength is absorption spectrum. 3) Photosynthesis produces oxygen; production of oxygen is used to measure the rate of pho ...
Chapter 7: Where it Starts – Photosynthesis
... - This type of photosystem uses ___________ photophosphorylation - ________ is split by _______ energy, and an e- enters the chlorophyll _____ - The chlorophyll’s original ____ is used to form ___________ - _______ is also formed; this is a much more __________ use of the energy (cyclic, light, wate ...
... - This type of photosystem uses ___________ photophosphorylation - ________ is split by _______ energy, and an e- enters the chlorophyll _____ - The chlorophyll’s original ____ is used to form ___________ - _______ is also formed; this is a much more __________ use of the energy (cyclic, light, wate ...
Exam practice answers 5
... of the thylakoid disc through channel proteins attached to molecules of the enzyme ATP synthase. The energy of their movement is used to combine ADP with a phosphate group to make ATP. (Any three correct terms from: absorbed/absorption, photosystem, thylakoid, electron transport chain, concentration ...
... of the thylakoid disc through channel proteins attached to molecules of the enzyme ATP synthase. The energy of their movement is used to combine ADP with a phosphate group to make ATP. (Any three correct terms from: absorbed/absorption, photosystem, thylakoid, electron transport chain, concentration ...
Chp 6. Autotrophs - AdventuresinScienceEducation
... • Autotrophs are organisms that are able to make their own organic molecules they need from simple inorganic molecules – they are self feeders. • Heterotrophs are unable to synthesise their own organic molecules, they must eat other living things. ...
... • Autotrophs are organisms that are able to make their own organic molecules they need from simple inorganic molecules – they are self feeders. • Heterotrophs are unable to synthesise their own organic molecules, they must eat other living things. ...
Photosynthetic Organisms
... • Contain pigment chlorophyll • Believed to have originated in bacteria modern cyanobacteria ...
... • Contain pigment chlorophyll • Believed to have originated in bacteria modern cyanobacteria ...
Cells and Energy Lesson Quiz B Completion LESSON 4
... Cells and Energy Completion Directions: On each line, write the term that correctly completes each sentence. ...
... Cells and Energy Completion Directions: On each line, write the term that correctly completes each sentence. ...
8.3 The Process of Photosynthesis I. Light Dependent Reactions
... Photosynthesis involves 2 sets of reactions: light dependent and light independent The light dependent reactions use energy from sunlight to produce oxygen and convert ADP and NADP+ into the energy carriers ATP and NADPH Light dependent reactions occur in the thylakoids of chloroplasts which contain ...
... Photosynthesis involves 2 sets of reactions: light dependent and light independent The light dependent reactions use energy from sunlight to produce oxygen and convert ADP and NADP+ into the energy carriers ATP and NADPH Light dependent reactions occur in the thylakoids of chloroplasts which contain ...
Mrs. Kristen Biology/ACC Bio Photosynthesis Worksheet What is the
... 6. How does the amount of energy in light change as the wavelength increases? ...
... 6. How does the amount of energy in light change as the wavelength increases? ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.