* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8.3 The Process of Photosynthesis I. Light Dependent Reactions
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
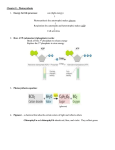
8.3 The Process of Photosynthesis I. Light Dependent Reactions - A. - Photosynthesis involves 2 sets of reactions: light dependent and light independent The light dependent reactions use energy from sunlight to produce oxygen and convert ADP and NADP+ into the energy carriers ATP and NADPH Light dependent reactions occur in the thylakoids of chloroplasts which contain photosystems o Photosystems: clusters of chlorophyll and proteins Photosystem II Light energy absorbed by pigments in photosystem II produces high energy electrons Electrons are moved across thylakoid by electron transport chain Electron transport chain: series of electron carrier proteins that move electrons Replacement electrons are formed by the splitting of water molecules o H+ ions move into thylakoid space, oxygen atoms leave thylakoid B. Electron Transport Chain - Energy from electrons moving down chain is used to pump more H+ ions into thylakoid space o Chain ends at photosystem I C. Photosystem I - Pigments in photosystem I absorb light, which is used to recharge the electrons that have passed along chain - Electrons leave thylakoid using a second transport chain and get picked up by NADP+ o NADP+ also picks up a H+ to become NADPH D. Hydrogen Ion Movement and ATP Formation - Hydrogen ions are built up in thylakoid space, making the stroma “negatively” charged (by comparison) - H+ gradient is solved by H+ ions leaving thylakoid through a protein called ATP synthase o When H+ moves through, ATP synthase rotates - While rotating, ATP synthase binds ADP to a phosphate group to form ATP o Process called chemiosmosis E. Summary of Light-Dependent Reactions - Light dependent reactions produce oxygen gas and converts ADP and NADP+ to ATP and NADPH II. The Light-Independent Reactions: Producing Sugars - Energy stored in ATP and NADPH can only last for a short period of time In the Calvin cycle (light independent reaction), ATP and NADPH are used to form glucose- a more stable form of energy storage A. Carbon Dioxide Enters the Cycle - An enzyme in the stroma combines carbon dioxide molecules with 5-carbon compounds that are already present o This produces 3-carbon compounds that continue into cycle - For every 6 CO2 molecules that enter cycle, 12 3-carbon compounds are produced B. Sugar Production - During the cycles, 2 out of the 12 3-carbon compounds molecules are removed o They are used to produce sugars, lipids, amino acids and other compounds - The other 10 3-carbon compound molecules are converted back into six 5-carbon compound molecules o These later combine with carbon dioxide molecules and continue the cycle C. Summary of the Calvin Cycle - The Calvin cycle uses 6 carbon dioxide molecules to create one sugar molecule - Conversion is powered by the products of the light-dependent reaction III. Factors Affecting Photosynthesis A. Temperature, Light and Water - Among the most important factors that affect photosynthesis are temperature, light intensity, and the availability of water o Reactions of photosynthesis use reactions that function between 0 and 35 degrees Celsius o Higher light intensity= higher rate of photosynthesis There is however, a maximum rate of photosynthesis o Shortage of water can slow photosynthesis and damage plant tissues Some plants in desert areas have a waxy coating on their leaves to prevent water loss