* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Photosynthesis - Shelton State
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Cryptochrome wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
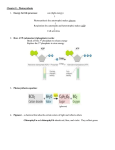
Photosynthesis Chapter 7 Photosynthesis= 6CO2+12H2O--------C6H12O6+6H2O+6O2 Who photosynthesizes? Cyanobacteria Algae Plants Flowering Plants Where does photosynthesis occur? -leaves (vegetative structures) Leaf Anatomy: -Palisade Mesophyll tissue = -Spongy Mesophyll tissue = -Stomata= -guard cells = -Chloroplast: thylakoid= Chlorophyll= grana= stroma= What is involved in Photosynthesis? 1. Visible Light = ROYGBIV -Photon= -Waves & Color -nanometers (nm)= 2. Pigments -reflection & absorption 2 primary types of plant pigments: 1. Carotenoids= 2. Chlorophylls= -chlorophyll a & b *Why does a plant look green? *What colors of light do plants use? *Why do leaves change colors? Photosynthetic Reactions Solar e + 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 -Redox Rxn: -CO2 is reduced -H2O is oxidized Two Sets of Rxns (two steps): Step 1.) Light Rxn= -light e -ATP & NADPH Step 2.) Dark Rxns (Calvin Cycle) = -CO2 Photosynthesis in Detail: Step 1: The Light Reaction -occurs on the thylakoids -involves photosystems = -photosystem I (PS I) -photosystem II (PS II) -electron acceptor = -photolysis= -electron transport chain -involves two pathways for e- to flow Noncyclic Electron Flow Light Rxn: -occurs in plants & algae - e- originate with H2O and end with NADPH -both photosystems are involved -Noncyclic Photosphosphorylation Cyclic Electron Flow Light Rxn: -occurs with all photosynthesizers - e- originate with PSI and return to PSI -only PSI is involved -only ATP –not NADPH is produced -Cyclic photophosphorylation Step 2: The Dark Reaction =Calvin Cycle =series of rxns that produce CHO and then return to the starting point. -occurs with both cyclic & noncyclic light reactions (all photosynthesizers). -uses ATP & NADPH to convert CO2 into glucose. -occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast. -occurs 6 Times to produce 1 glucose Composed of 3 Phases of rxns: 1. CO2 Fixation -RuBP 2. Reduction of CO2 -glucose formed here -ATP & NADPH used here 3. Regeneration of RuBP