Contents Assessment of the Risk of Zinc Deficiency in Populations
... 2.3 Methods to estimate the risk of zinc deficiency in populations .................................................................. S137 2.3.1 Assessment of dietary zinc intakes....................................................................................................... S137 2.3.2 Serum ...
... 2.3 Methods to estimate the risk of zinc deficiency in populations .................................................................. S137 2.3.1 Assessment of dietary zinc intakes....................................................................................................... S137 2.3.2 Serum ...
- The Center for Best Practices
... Although these reviewers provided many constructive comments and suggestions, they were not asked to endorse nor did they see the final draft of the book before its release and publication. The review of this report was overseen by Clyde J. Behney, who was responsible for making certain that an inde ...
... Although these reviewers provided many constructive comments and suggestions, they were not asked to endorse nor did they see the final draft of the book before its release and publication. The review of this report was overseen by Clyde J. Behney, who was responsible for making certain that an inde ...
Visit the National Academies Press online, the authoritative source
... Although these reviewers provided many constructive comments and suggestions, they were not asked to endorse nor did they see the final draft of the book before its release and publication. The review of this report was overseen by Clyde J. Behney, who was responsible for making certain that an inde ...
... Although these reviewers provided many constructive comments and suggestions, they were not asked to endorse nor did they see the final draft of the book before its release and publication. The review of this report was overseen by Clyde J. Behney, who was responsible for making certain that an inde ...
Microbiology
... is a quaternary amine compound that can be produced by all domains of life, and was discovered in muscle extract in 1905 by Gulewitsch & Krimberg (1905) and Kutscher (1905). It was shown to be essential for larval development of the mealworm Tenebrio molitor and was originally designated vitamin BT ...
... is a quaternary amine compound that can be produced by all domains of life, and was discovered in muscle extract in 1905 by Gulewitsch & Krimberg (1905) and Kutscher (1905). It was shown to be essential for larval development of the mealworm Tenebrio molitor and was originally designated vitamin BT ...
Emma Hanagan in a Rocky Ford Cantaloupe field Emma Hanagan
... Print your name and complete address including correct ZIP Code. Be sure to list the variety you want and where applicable the grade of seed. Make all money orders or checks payable to BURRELL SEED GROWERS LLC. There is no Colorado sales tax on garden seed. All offerings are subject to prior sale an ...
... Print your name and complete address including correct ZIP Code. Be sure to list the variety you want and where applicable the grade of seed. Make all money orders or checks payable to BURRELL SEED GROWERS LLC. There is no Colorado sales tax on garden seed. All offerings are subject to prior sale an ...
for Herbal Medicines
... Approved uses are presented in list fashion. Other uses are described with provisos as necessary regarding route and form of administration. • Contraindications: Although most natural remedies can be used under all medical circumstances, a few pharmacologically potent herbs must be avoided in the pr ...
... Approved uses are presented in list fashion. Other uses are described with provisos as necessary regarding route and form of administration. • Contraindications: Although most natural remedies can be used under all medical circumstances, a few pharmacologically potent herbs must be avoided in the pr ...
Readinq Texts for Enqlish : ( Dispensa ) 2010
... above. The root of a plant has two main functions. It takes in, or absorbs, water and minerals from thè soil through thè root hairs, which are single cells near thè tip of each root. The other main function of thè root is to hold, or anchor, thè plant firmly in position in thè soil. Plants such as s ...
... above. The root of a plant has two main functions. It takes in, or absorbs, water and minerals from thè soil through thè root hairs, which are single cells near thè tip of each root. The other main function of thè root is to hold, or anchor, thè plant firmly in position in thè soil. Plants such as s ...
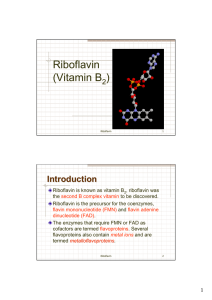
Riboflavin (Vitamin B )
... dehydrogenase [TCA cycle]) that are important in energy production. As the catalytically operating moiety within bound flavocoenzymes, riboflavin participates in oxidation-reduction reactions in numerous metabolic pathways and in energy production via the respiratory chain. Riboflavin ...
... dehydrogenase [TCA cycle]) that are important in energy production. As the catalytically operating moiety within bound flavocoenzymes, riboflavin participates in oxidation-reduction reactions in numerous metabolic pathways and in energy production via the respiratory chain. Riboflavin ...
Interallelic Complementation at the Ubiquitous
... contrast, leaf urease activity was undetectable in aj6. Consistently, urea accumulated in leaves of aj6 to levels about 65-fold over wild type. aj6 adult plants exhibited necrotic leaf tips likely due to “urea burn,” a typical trait of plants lacking leaf ubiquitous urease activity (Eskew et al., 19 ...
... contrast, leaf urease activity was undetectable in aj6. Consistently, urea accumulated in leaves of aj6 to levels about 65-fold over wild type. aj6 adult plants exhibited necrotic leaf tips likely due to “urea burn,” a typical trait of plants lacking leaf ubiquitous urease activity (Eskew et al., 19 ...
Thiamine deficiency - World Health Organization
... administration of thiamine. Thiamine deficiency occurs sporadically in people who are socially isolated, suffer loss of appetite and self neglect. In these cases ‘mixed’ vitamin deficiency syndromes are more common and respond better to vitamin B-complex treatment (Carney, 1971). Multiple vitamin B ...
... administration of thiamine. Thiamine deficiency occurs sporadically in people who are socially isolated, suffer loss of appetite and self neglect. In these cases ‘mixed’ vitamin deficiency syndromes are more common and respond better to vitamin B-complex treatment (Carney, 1971). Multiple vitamin B ...
Dietary calcium and health
... of bone; the rate of calcium deposition in bone is proportional to rate of growth. An adequate intake of calcium is one of a number of factors which are important for acquiring bone mass and attaining peak bone mass (PBM). Diets containing insufficient amounts of calcium may lead to a low bone miner ...
... of bone; the rate of calcium deposition in bone is proportional to rate of growth. An adequate intake of calcium is one of a number of factors which are important for acquiring bone mass and attaining peak bone mass (PBM). Diets containing insufficient amounts of calcium may lead to a low bone miner ...
Sub-sections Zinc Zinc Acetate Zinc Chloride Zinc Citrate
... phytate, whereas the casein in milk decreases zinc absorption. Proteins also ...
... phytate, whereas the casein in milk decreases zinc absorption. Proteins also ...
Burgerstein`s Handbook of Nutrition : Micronutrients
... beri, and rickets. However, vitamin and mineral deficiencies remain widespread. For example, there is a high prevalence of inadequate intakes of iron and folic acid among women1,2, and deficiencies of vitamin D, vitamin B12, and calcium are common among older adults.3,4 Preventive nutrition must con ...
... beri, and rickets. However, vitamin and mineral deficiencies remain widespread. For example, there is a high prevalence of inadequate intakes of iron and folic acid among women1,2, and deficiencies of vitamin D, vitamin B12, and calcium are common among older adults.3,4 Preventive nutrition must con ...
Floriculture Test Bank B
... d. Both a and b ____ 17. Two common ways to reduce the light intensity in a greenhouse are with shade cloths and shading compounds. Shade cloth is available in a variety of types which reduce light by ___ to ______% a. 5, 15 c. 12, 18 b. 13, 24 d. 25, 98 ____ 18. Yellow margins and necrotic edges, e ...
... d. Both a and b ____ 17. Two common ways to reduce the light intensity in a greenhouse are with shade cloths and shading compounds. Shade cloth is available in a variety of types which reduce light by ___ to ______% a. 5, 15 c. 12, 18 b. 13, 24 d. 25, 98 ____ 18. Yellow margins and necrotic edges, e ...
Vitamin and mineral requirements in human nutrition
... This included focusing on and revising the requirements for essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, C, D, E, and K; the B vitamins; calcium; iron; magnesium; zinc; selenium; and iodine, based on the available scientific evidence. • Secondly, the Consultation was asked to prepare a rep ...
... This included focusing on and revising the requirements for essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, C, D, E, and K; the B vitamins; calcium; iron; magnesium; zinc; selenium; and iodine, based on the available scientific evidence. • Secondly, the Consultation was asked to prepare a rep ...
species identification guide - National Plant Monitoring Scheme
... the WF symbol. A traffic light system has been used in all sections (see key opposite). An appendix at the back of this guide provides an illustration of a wildflower, fern, grass, rush and sedge with their features labelled. This should help you with identification. ...
... the WF symbol. A traffic light system has been used in all sections (see key opposite). An appendix at the back of this guide provides an illustration of a wildflower, fern, grass, rush and sedge with their features labelled. This should help you with identification. ...
Linus Pauling Institute
... contaminants, from dry cell batteries for two to three months (43). Water manganese levels were found to be 14 mg/liter almost two months after symptoms began and may have already been declining (1). A study of older adults in Greece found a high prevalence of neurological symptoms in those exposed ...
... contaminants, from dry cell batteries for two to three months (43). Water manganese levels were found to be 14 mg/liter almost two months after symptoms began and may have already been declining (1). A study of older adults in Greece found a high prevalence of neurological symptoms in those exposed ...
please click here
... dating back to the 1700’s. Bush plants produce small jet black beans wonderful for soups, stews and refrying. PKT (100) $2 Envy Vegetable Soybean 75 days. Well established short season favorite developed by E. M. Meader, UNH. Upright 2' tall plants bear a good crop of bright green beans early for fr ...
... dating back to the 1700’s. Bush plants produce small jet black beans wonderful for soups, stews and refrying. PKT (100) $2 Envy Vegetable Soybean 75 days. Well established short season favorite developed by E. M. Meader, UNH. Upright 2' tall plants bear a good crop of bright green beans early for fr ...
Dietary oxalate and calcium oxalate stones: a theoretical or real
... Currently, there is no pharmacologic agent designed specifically to reduce urinary oxalate concentration, although cholestyramine has been prescribed with reported effect in some cases [40, 41] but not others [42]. Conjugated bile acid replacement is potentially useful in the subset of patients with ...
... Currently, there is no pharmacologic agent designed specifically to reduce urinary oxalate concentration, although cholestyramine has been prescribed with reported effect in some cases [40, 41] but not others [42]. Conjugated bile acid replacement is potentially useful in the subset of patients with ...
Calcium citrate malate as source for calcium for use in foods for
... the quantum satis principle (EC, 1995). Furthermore, calcium salts of citric acid are allowed to be used as food supplements in the EU (EC, 2002). The Scientific Committee on Food of the European Commission (SCF) evaluated the safety of use of calcium citrate and calcium malate as a food additive in ...
... the quantum satis principle (EC, 1995). Furthermore, calcium salts of citric acid are allowed to be used as food supplements in the EU (EC, 2002). The Scientific Committee on Food of the European Commission (SCF) evaluated the safety of use of calcium citrate and calcium malate as a food additive in ...
15 HS catalog 1st print 2
... Di Ciccio 50-70 days. Old reliable open pollinated Heirloom introduced in 1890. Compact plants (24-36") produce a central 3-4" head with numerous side shoots. An excellent home garden variety. Excellent for fall planting. Organic PKT (500) $2 Waltham 29 60-90 days. Widely adapted Heirloom. Developed ...
... Di Ciccio 50-70 days. Old reliable open pollinated Heirloom introduced in 1890. Compact plants (24-36") produce a central 3-4" head with numerous side shoots. An excellent home garden variety. Excellent for fall planting. Organic PKT (500) $2 Waltham 29 60-90 days. Widely adapted Heirloom. Developed ...
Manganese Bulletin
... found airborne manganese levels to be similar to those in areas where MMT was not used. A more recent Canadian study found higher concentrations of respirable manganese in an urban versus a rural area, but average concentrations in both areas were below the safe level set by the U.S. EPA. The impact ...
... found airborne manganese levels to be similar to those in areas where MMT was not used. A more recent Canadian study found higher concentrations of respirable manganese in an urban versus a rural area, but average concentrations in both areas were below the safe level set by the U.S. EPA. The impact ...
Evidence for Several Cysteine Transport Mechanisms in the
... We then measured the rate of [35S]cysteine uptake by isolated mitochondria in the first 20 s at 18 different concentrations of external cysteine (0–1,000 mM, Fig. 2C). Within the concentration range tested, cysteine uptake by isolated plant mitochondria displayed at least two phases of kinetics. The ...
... We then measured the rate of [35S]cysteine uptake by isolated mitochondria in the first 20 s at 18 different concentrations of external cysteine (0–1,000 mM, Fig. 2C). Within the concentration range tested, cysteine uptake by isolated plant mitochondria displayed at least two phases of kinetics. The ...
Plant Varieties Journal
... The PBRO accepts comments on applications. However, the scheme is managed on normal risk management lines and with an emphasis on the requirement that challengers with a commercial interest must demonstrate conclusively that an application should not be granted. All written comment will be acknowled ...
... The PBRO accepts comments on applications. However, the scheme is managed on normal risk management lines and with an emphasis on the requirement that challengers with a commercial interest must demonstrate conclusively that an application should not be granted. All written comment will be acknowled ...
catalog without prices - Pinewood Perennial Gardens
... When a cultivar name is listed within parenthesis and single quotes, it is the true cultivar name under which the plant was introduced and, in some cases, patented (PP) or plant patent applied for (PPAF). A plant selection not in single quotes [Eastern Star] is the trademarked name under which the p ...
... When a cultivar name is listed within parenthesis and single quotes, it is the true cultivar name under which the plant was introduced and, in some cases, patented (PP) or plant patent applied for (PPAF). A plant selection not in single quotes [Eastern Star] is the trademarked name under which the p ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.