Towards functional effects of polyphenols : modulation of energy
... roots and symbiotic root nodules are formed that can convert nitrogen from the soil into ammonia used for amino acid production for plant growth [6]. The small molecule signal that initiates the interaction is a polyphenol [7]. The biochemical mechanism by which polyphenols initiate the interaction ...
... roots and symbiotic root nodules are formed that can convert nitrogen from the soil into ammonia used for amino acid production for plant growth [6]. The small molecule signal that initiates the interaction is a polyphenol [7]. The biochemical mechanism by which polyphenols initiate the interaction ...
Elucidating Flux Regulation of the Fermentation Modes of
... It is impossible to complete my PhD study without the help of many people. First of all, I must express my sincerest gratitude to my supervisors, Christian Solem and Peter Ruhdal Jensen. Christian has taught me numerous principles, skills and knowledge in practical as well as theoretical molecular b ...
... It is impossible to complete my PhD study without the help of many people. First of all, I must express my sincerest gratitude to my supervisors, Christian Solem and Peter Ruhdal Jensen. Christian has taught me numerous principles, skills and knowledge in practical as well as theoretical molecular b ...
University of Groningen Citrate driven transamination for
... pta) and acetate kinase (ACK) (encoded by ackA1 and ackA2). The pathway from pyruvate to acetate via acetate kinase produces metabolic energy in the form of ATP. A shift from homolactic fermentation (L-lactate) to mixed-acid fermentation (ethanol and acetate) has been observed under certain growth c ...
... pta) and acetate kinase (ACK) (encoded by ackA1 and ackA2). The pathway from pyruvate to acetate via acetate kinase produces metabolic energy in the form of ATP. A shift from homolactic fermentation (L-lactate) to mixed-acid fermentation (ethanol and acetate) has been observed under certain growth c ...
13C MRS: An outstanding tool for metabolic studies
... variety of metabolic pathways in cells, animals, and humans. These include glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis and degradation, gluconeogenesis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, ketogenesis, ureogenesis and the glutamate, glutamine, GABA cycle in brain, and others (see refe ...
... variety of metabolic pathways in cells, animals, and humans. These include glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis and degradation, gluconeogenesis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, ketogenesis, ureogenesis and the glutamate, glutamine, GABA cycle in brain, and others (see refe ...
Rate at which glutamine enters TCA cycle influences carbon atom
... Because no stimulators of aminotransferase activity were known, we approached this with the glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) stimulator BCH. Although glutamine carbon has been thought to enter the TCA cycle primarily via aminotransferase pathways, there is evidence of flux through GDH (2, 6). Previous ...
... Because no stimulators of aminotransferase activity were known, we approached this with the glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) stimulator BCH. Although glutamine carbon has been thought to enter the TCA cycle primarily via aminotransferase pathways, there is evidence of flux through GDH (2, 6). Previous ...
Carnitine-Metabolism and Functions
... In all species it is found in the liver. In the rat it is also found to a small extent in the testis, but it is absent from all other tissues (38,95, 128,178). It is present in the kidneys in hamster, rabbit, rhesus monkey, and cat but not in the kidneys of dog, guinea pig, mouse, or rat (145). In h ...
... In all species it is found in the liver. In the rat it is also found to a small extent in the testis, but it is absent from all other tissues (38,95, 128,178). It is present in the kidneys in hamster, rabbit, rhesus monkey, and cat but not in the kidneys of dog, guinea pig, mouse, or rat (145). In h ...
Chapter 4 - University of Amsterdam
... In animal species, carnitine uptake by food is thought to be an important contributor to total carnitine levels but is dependent on diet, as meat and dairy products contain high levels of carnitine, while food sources derived from plants contribute very little (26). Although carnitine can be obtaine ...
... In animal species, carnitine uptake by food is thought to be an important contributor to total carnitine levels but is dependent on diet, as meat and dairy products contain high levels of carnitine, while food sources derived from plants contribute very little (26). Although carnitine can be obtaine ...
ESTUDIO DE LOS MECANISMOS DE INHIBICIÓN DE LA ACTIVIDAD CARNITINA PALMITOILTRANSFERASA 1
... The enzyme carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT)1 I catalyzes the conversion of long chain fatty acyl-CoAs to acylcarnitines, which is the first step in the transport of fatty acyl-CoA groups from the cytosol to mitochondria where they undergo -oxidation. This reaction is inhibited by malonyl-CoA, a ...
... The enzyme carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT)1 I catalyzes the conversion of long chain fatty acyl-CoAs to acylcarnitines, which is the first step in the transport of fatty acyl-CoA groups from the cytosol to mitochondria where they undergo -oxidation. This reaction is inhibited by malonyl-CoA, a ...
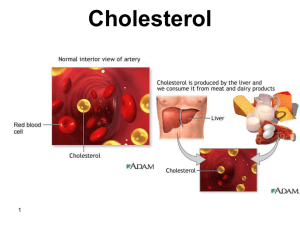
What is Cholesterol?......cont. - Home
... should aim to decrease their weight with regular physical activity and a balanced, healthy diet. Weight management and cholesterol control go hand in hand. ...
... should aim to decrease their weight with regular physical activity and a balanced, healthy diet. Weight management and cholesterol control go hand in hand. ...
Glycogen branches out: new perspectives on the role of glycogen
... phosphorylase is also allosterically activated by increased [Pi] within the cell, which rises as ATP levels fall, reflecting an energy deficit. As activity continues, glycogen phosphorylase may also be activated in response to increased extracellular epinephrine levels, which result in activation of ...
... phosphorylase is also allosterically activated by increased [Pi] within the cell, which rises as ATP levels fall, reflecting an energy deficit. As activity continues, glycogen phosphorylase may also be activated in response to increased extracellular epinephrine levels, which result in activation of ...
Training Carnitine - Overview
... • Acute metabolic decompensation with hypoketotic or nonketotic hypoglycemia usually occurs in infancy, whereas cardiac and skeletal muscle disease manifest later. Patients may have a history of developmental ...
... • Acute metabolic decompensation with hypoketotic or nonketotic hypoglycemia usually occurs in infancy, whereas cardiac and skeletal muscle disease manifest later. Patients may have a history of developmental ...
Lactic acidosis - Medical School
... effective transport of hydrogen ions, referred to as reducing can enter the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and the electron equivalents, across the mitochondrial membrane and the reoxi- transfer/oxidative phosphorylation pathway for complete oxidation of cytosolic NADH. The two best-studied such sys ...
... effective transport of hydrogen ions, referred to as reducing can enter the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and the electron equivalents, across the mitochondrial membrane and the reoxi- transfer/oxidative phosphorylation pathway for complete oxidation of cytosolic NADH. The two best-studied such sys ...
Sucrose breakdown in the potato tuber - publish.UP
... In this work different approaches are undertaken to improve the understanding of the sucroseto-starch pathway in developing potato tubers. At first an inducible gene expression system from fungal origin is optimised for the use of studying metabolism in the potato tuber. It is found that the alc sys ...
... In this work different approaches are undertaken to improve the understanding of the sucroseto-starch pathway in developing potato tubers. At first an inducible gene expression system from fungal origin is optimised for the use of studying metabolism in the potato tuber. It is found that the alc sys ...
Presentation part1-201210091211
... regulated physiologically. For example, during lactation, carnitine is preferentially distributed to the nursing mother's breast through increased expression of its carriers at the expense of the liver, because mother's milk is the only source of carnitine for the infant and is essential for the sur ...
... regulated physiologically. For example, during lactation, carnitine is preferentially distributed to the nursing mother's breast through increased expression of its carriers at the expense of the liver, because mother's milk is the only source of carnitine for the infant and is essential for the sur ...
Role of the glutamine transaminase-m-amidase
... different growth conditions. Asn, asparagine; Asp, aspartate; Gln, glutamine; Glu, glutamate; Gly, glycerol; glu, glucose; SUC, succinate. ...
... different growth conditions. Asn, asparagine; Asp, aspartate; Gln, glutamine; Glu, glutamate; Gly, glycerol; glu, glucose; SUC, succinate. ...
allyl cysteine sulphoxide
... for the production of cis- propenyl cysteine sulphoxide, however it should theoretically to produce both ‘cis’ and ‘trans’ isomers. It was decided to search the reaction products for the biological ‘trans’ isomer. This was successful and this synthetic method has been used, together with repeated ...
... for the production of cis- propenyl cysteine sulphoxide, however it should theoretically to produce both ‘cis’ and ‘trans’ isomers. It was decided to search the reaction products for the biological ‘trans’ isomer. This was successful and this synthetic method has been used, together with repeated ...
DMD #620 1 Identification of di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate
... 1994), were raised in male Japanese white rabbits (2.5 – 3.0 kg in body weight) according to a previously described procedure (Hosokawa et al., 1987). Anti-CES RL1 antibodies and anti-CES D1 antibodies were prepared as previously described (Hosokawa et al., 1990; Hosokawa et al., 2001). The IgG frac ...
... 1994), were raised in male Japanese white rabbits (2.5 – 3.0 kg in body weight) according to a previously described procedure (Hosokawa et al., 1987). Anti-CES RL1 antibodies and anti-CES D1 antibodies were prepared as previously described (Hosokawa et al., 1990; Hosokawa et al., 2001). The IgG frac ...
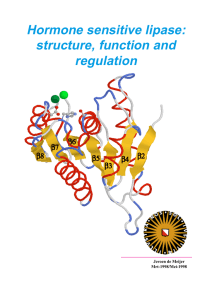
Hormone sensitive lipase: structure, function and
... Every organism continuously uses energy; not only for movement or to perform labor, but also for maintenance, regulation and almost any other process. Organisms derive their energy from the breakdown of nutrients they take up. The type of nutrients can roughly be divided in three groups: proteins, c ...
... Every organism continuously uses energy; not only for movement or to perform labor, but also for maintenance, regulation and almost any other process. Organisms derive their energy from the breakdown of nutrients they take up. The type of nutrients can roughly be divided in three groups: proteins, c ...
novel aspects of carnitine function and metabolism
... It is generally assumed that medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs) are oxidized in mitochondria independently from carnitine. However, the true contribution of the carnitine shuttle to the oxidation of MCFAs has remained elusive. We show that lauric acid, a MCFA, also depends on the carnitine shuttle to ...
... It is generally assumed that medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs) are oxidized in mitochondria independently from carnitine. However, the true contribution of the carnitine shuttle to the oxidation of MCFAs has remained elusive. We show that lauric acid, a MCFA, also depends on the carnitine shuttle to ...
New insight into the photoheterotrophic growth of the
... second compartment of the MELiSSA loop, will be used to photoassimilate these volatile fatty acids. The assimilation of carbon sources that enter central carbon metabolism through acetyl-CoA requires an alternative cycle to replenish the TCA cycle intermediates used for the synthesis of all cell com ...
... second compartment of the MELiSSA loop, will be used to photoassimilate these volatile fatty acids. The assimilation of carbon sources that enter central carbon metabolism through acetyl-CoA requires an alternative cycle to replenish the TCA cycle intermediates used for the synthesis of all cell com ...
Application of Synthetic Biology for Biopolymer
... agricultural and forest residues. As result is expected that the production cost of PHB from lignocellulosic biomass may be reduced since both glucose and xylose fractions of the substrate can be used. Although the generated yeast strains were able to consume xylose and produce PHB, the production r ...
... agricultural and forest residues. As result is expected that the production cost of PHB from lignocellulosic biomass may be reduced since both glucose and xylose fractions of the substrate can be used. Although the generated yeast strains were able to consume xylose and produce PHB, the production r ...
Free radical scavenging and antioxidant effects of lactate ion: an in
... (60 mM). Figure 1B shows the effect of lactate dissolved in plasma. Because plasma alone exhibited a scavenging activity toward 䡠OH, plasma without lactate was taken for reference 100%. Addition of lactate dissolved in plasma reduced the EPR signal intensity only at high concentration levels (30 and ...
... (60 mM). Figure 1B shows the effect of lactate dissolved in plasma. Because plasma alone exhibited a scavenging activity toward 䡠OH, plasma without lactate was taken for reference 100%. Addition of lactate dissolved in plasma reduced the EPR signal intensity only at high concentration levels (30 and ...
Adaptation and Specialization in the Evolution of Bacterial
... adaptive improvements to glucose growth resulting in tradeoffs in the ability to use other carbon sources. In fact, this has been observed in specific cases, where adaptive improvement occurred at the cost of transport of non-glucose sugars such as maltose [7], or where portions of the ribose operon ...
... adaptive improvements to glucose growth resulting in tradeoffs in the ability to use other carbon sources. In fact, this has been observed in specific cases, where adaptive improvement occurred at the cost of transport of non-glucose sugars such as maltose [7], or where portions of the ribose operon ...
Contribution of 13C-NMR spectroscopy to the elucidation of
... pyruvate and oxaloacetate are formed, respectively. These intermediates can be partially oxidized to acetate and partially reduced to propionate leading to stoichiometries as given in Table 2 (Eqs. 1 and 2). Also glutamate may be converted reductively to propionate (Table 2, Eq. 3). This was describ ...
... pyruvate and oxaloacetate are formed, respectively. These intermediates can be partially oxidized to acetate and partially reduced to propionate leading to stoichiometries as given in Table 2 (Eqs. 1 and 2). Also glutamate may be converted reductively to propionate (Table 2, Eq. 3). This was describ ...
C. jejuni
... that spans the entire cell envelope. The translocon consists of an IM ATPase-binding cassette (ABC) transporter, a membrane-fusion protein and an OM pore. Substrates of this pathway, such as alpha-haemolysin, possess an uncleaved carboxy-terminal signal sequence. ...
... that spans the entire cell envelope. The translocon consists of an IM ATPase-binding cassette (ABC) transporter, a membrane-fusion protein and an OM pore. Substrates of this pathway, such as alpha-haemolysin, possess an uncleaved carboxy-terminal signal sequence. ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.