Slide 1
... are transported in blood to liver to be converted to pyruvate then to glucose (Cori cycle) 4- Glycerol ...
... are transported in blood to liver to be converted to pyruvate then to glucose (Cori cycle) 4- Glycerol ...
NME2.29 - Fat and Carbohydrate Metabolism 2
... Blood glucose homeostasis is maintained principally by the liver through: o Glycogenolysis – breakdown of glycogen to form glucose o Gluconeogenesis – biosynthesis of glucose from substrates when glycogen stores are low Gluconeogenesis requires ATP and is conducted in the liver from a number of subs ...
... Blood glucose homeostasis is maintained principally by the liver through: o Glycogenolysis – breakdown of glycogen to form glucose o Gluconeogenesis – biosynthesis of glucose from substrates when glycogen stores are low Gluconeogenesis requires ATP and is conducted in the liver from a number of subs ...
Regulation of metabolism by PPARs and Angiopoietin like proteins
... serving as signalling molecules. An important mechanism of fatty acid sensing is via stimulation of DNA transcription via activation of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors. One of the genes that is consistently and very significantly upregulated by fatty acids via PPARs in numerous organs e ...
... serving as signalling molecules. An important mechanism of fatty acid sensing is via stimulation of DNA transcription via activation of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors. One of the genes that is consistently and very significantly upregulated by fatty acids via PPARs in numerous organs e ...
Q4 Describe the body`s mechanisms for regulating
... pyruvate and lactate, using the pyruvate for the Krebs cycle and transporting the lactate to the liver for gluconeogenesis via the Cori cycle Inhibits cellular utilization of glucose during hypoglycaemia, cau ...
... pyruvate and lactate, using the pyruvate for the Krebs cycle and transporting the lactate to the liver for gluconeogenesis via the Cori cycle Inhibits cellular utilization of glucose during hypoglycaemia, cau ...
PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression
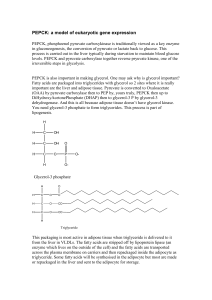
... PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression PEPCK, phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase is traditionally viewed as a key enzyme in gluconeogenesis, the conversion of pyruvate or lactate back to glucose. This process is carried out in the liver typically during starvation to maintain blood glucose lev ...
... PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression PEPCK, phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase is traditionally viewed as a key enzyme in gluconeogenesis, the conversion of pyruvate or lactate back to glucose. This process is carried out in the liver typically during starvation to maintain blood glucose lev ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.