Document
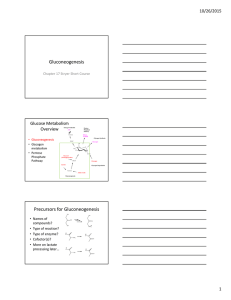
... • Site of gluconeogenesis and source of precursors depends on duration of starvation > liver is site after brief fasting > kidney is site after prolonged fasting • Carbon sources > glycerol – product of adipose triglyceride degradation; relatively minor contribution to gluconeogenesis > lactate – 10 ...
... • Site of gluconeogenesis and source of precursors depends on duration of starvation > liver is site after brief fasting > kidney is site after prolonged fasting • Carbon sources > glycerol – product of adipose triglyceride degradation; relatively minor contribution to gluconeogenesis > lactate – 10 ...
Metabolism Practice Questions
... 7. Fatty acids must be converted to ____ before entering the Krebs cycle. a. pyruvate b. acetyl CoA ...
... 7. Fatty acids must be converted to ____ before entering the Krebs cycle. a. pyruvate b. acetyl CoA ...
Metabolic Characteristics of the Major Organs and Tissues
... Because the brain contains no stored energy, it must be constantly supplied with glucose and oxygen from the circulating blood. The brain can suffer rapid irreversible loss of function when deprived of glucose, even for very short periods of time. The brain can adapt to use 3-hydroxybutyrate as an e ...
... Because the brain contains no stored energy, it must be constantly supplied with glucose and oxygen from the circulating blood. The brain can suffer rapid irreversible loss of function when deprived of glucose, even for very short periods of time. The brain can adapt to use 3-hydroxybutyrate as an e ...
Powerpoint Slides for Chapter Seven
... Inside the mitochondria, the two carbon piece left from the sugar is converted to carbon dioxide, water, and lots of ATP (TCA & ETS) ...
... Inside the mitochondria, the two carbon piece left from the sugar is converted to carbon dioxide, water, and lots of ATP (TCA & ETS) ...
Food Utilization
... • Ingested chemical used for growth, repair or maintenance • Macronutrients • Micronutrients • Recommended daily allowances (RDA) – safe estimate of daily intake for standard needs • Essential nutrients can not be synthesized – minerals, vitamins, 8 amino acids and 1-3 fatty acids ...
... • Ingested chemical used for growth, repair or maintenance • Macronutrients • Micronutrients • Recommended daily allowances (RDA) – safe estimate of daily intake for standard needs • Essential nutrients can not be synthesized – minerals, vitamins, 8 amino acids and 1-3 fatty acids ...
Metabolism08
... breaks triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids Most of the energy is stored in the fatty acids (glycerol can be converted to glucose or pyruvate) Fatty acids usually produce substantially more ATP than glucose (16 carbon fatty acid = 129 ATP) ...
... breaks triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids Most of the energy is stored in the fatty acids (glycerol can be converted to glucose or pyruvate) Fatty acids usually produce substantially more ATP than glucose (16 carbon fatty acid = 129 ATP) ...
Lipids
... 1. Carnitine Palmitoyl Transferase I, an enzyme on the cytosolic surface of the outer mitochondrial membrane, transfers a fatty acid from CoA to the OH on carnitine. 2.Carnitine acylcarnitine translocase in the inner mitochondrial membrane mediates exchange of carnitine for acylcarnitine. ...
... 1. Carnitine Palmitoyl Transferase I, an enzyme on the cytosolic surface of the outer mitochondrial membrane, transfers a fatty acid from CoA to the OH on carnitine. 2.Carnitine acylcarnitine translocase in the inner mitochondrial membrane mediates exchange of carnitine for acylcarnitine. ...
2015FallNSC408
... Most bile acids are recycled to the liver. a. True b. False What is produced from the -oxidation of an odd-chain fatty acid? a. Citrate b. Propionyl CoA c. Malonyl CoA d. Methionine Which metabolic profile would most likely lead to fatty acid synthesis? a. Increased insulin, increased glucagon b. I ...
... Most bile acids are recycled to the liver. a. True b. False What is produced from the -oxidation of an odd-chain fatty acid? a. Citrate b. Propionyl CoA c. Malonyl CoA d. Methionine Which metabolic profile would most likely lead to fatty acid synthesis? a. Increased insulin, increased glucagon b. I ...
Organic chemistry and Biological chemistry for Health Sciences
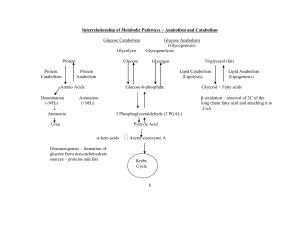
... Gluconeogenesis is not just the reverse of glycolysis. Three of the steps in glycolysis namely steps 1, 3, and 10 cannot be directly reversed. Special enzymes exist in the liver and the kidneys that create bypasses around these irreversable steps. In the bypass that gets around step 10 of glycolysis ...
... Gluconeogenesis is not just the reverse of glycolysis. Three of the steps in glycolysis namely steps 1, 3, and 10 cannot be directly reversed. Special enzymes exist in the liver and the kidneys that create bypasses around these irreversable steps. In the bypass that gets around step 10 of glycolysis ...
File
... In addition, a large amount of alanine is formed in active muscle by the transamination of pyruvate. Alanine, like lactate, can be converted into glucose by the liver. Why does the muscle release alanine? Muscle can absorb and transaminate branched-chain amino acids; however, it cannot form urea. C ...
... In addition, a large amount of alanine is formed in active muscle by the transamination of pyruvate. Alanine, like lactate, can be converted into glucose by the liver. Why does the muscle release alanine? Muscle can absorb and transaminate branched-chain amino acids; however, it cannot form urea. C ...
LB Fat metabolism A
... with HSL in the cytoplasm. Upon lipolytic stimulation, both perilipin and HSL become multiphosphorylated, with perilipin being displaced from the droplet, allowing access for HSL. There is also evidence that fatty acids (FA) are removed from HSL by FABPs, preventing accumulation and resultant produc ...
... with HSL in the cytoplasm. Upon lipolytic stimulation, both perilipin and HSL become multiphosphorylated, with perilipin being displaced from the droplet, allowing access for HSL. There is also evidence that fatty acids (FA) are removed from HSL by FABPs, preventing accumulation and resultant produc ...
Document
... Phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP + H+ → pyruvate + ATP Pyruvate + NADH + H+ → lactate + NAD+ In relation to this assay procedure, which one of the following statements is correct? (A)Of the two enzymes, pyruvate kinase should be in excess. (B)The reaction could be followed by measuring the increase in abso ...
... Phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP + H+ → pyruvate + ATP Pyruvate + NADH + H+ → lactate + NAD+ In relation to this assay procedure, which one of the following statements is correct? (A)Of the two enzymes, pyruvate kinase should be in excess. (B)The reaction could be followed by measuring the increase in abso ...
Document
... Pathway of conversion of (A) galactose to glucose in the liver and (B) glucose to lactose in the lactating mammary gland. ...
... Pathway of conversion of (A) galactose to glucose in the liver and (B) glucose to lactose in the lactating mammary gland. ...
Substrate Metabolism – Rest vs Stress
... - aim = to preserve plasma glucose levels for brain metabolism. REST - least expensive form of energy production utilized: carbohydrate -> fat -> protein in decreasing ratios. Carbohydrate Sources ...
... - aim = to preserve plasma glucose levels for brain metabolism. REST - least expensive form of energy production utilized: carbohydrate -> fat -> protein in decreasing ratios. Carbohydrate Sources ...
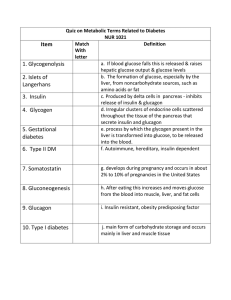
Quiz on Metabolic Terms Related to Diabetes NUR 1021 Item Match
... Quiz on Metabolic Terms Related to Diabetes NUR 1021 Match Definition Item With letter a. If blood glucose falls this is released & raises 1. Glycogenolysis hepatic glucose output & glucose levels b. The formation of glucose, especially by the 2. Islets of liver, from noncarbohydrate sources, such a ...
... Quiz on Metabolic Terms Related to Diabetes NUR 1021 Match Definition Item With letter a. If blood glucose falls this is released & raises 1. Glycogenolysis hepatic glucose output & glucose levels b. The formation of glucose, especially by the 2. Islets of liver, from noncarbohydrate sources, such a ...
Chapter 1
... • Any energy nutrient can fuel the body in the short term • TCA cycle = amphibolic pathway • Lipogenesis – CHO spares lipolysis - promotes gain – Glucose is precursor for glycerol & fatty acids ...
... • Any energy nutrient can fuel the body in the short term • TCA cycle = amphibolic pathway • Lipogenesis – CHO spares lipolysis - promotes gain – Glucose is precursor for glycerol & fatty acids ...
Unit 2: Metabolic Processes Metabolism and Energy
... - Triglycerides break down into glycerol and fatty acids - Glycerol glucose glycolysis - Glycerol DHAP (dihydroxyacetone phosphate) G3P glycolysis - Fatty Acids β-oxidation acetyl-CoA Krebs - Fats provide 38 kJ/g while carbohydrates provide 16 kJ/g ...
... - Triglycerides break down into glycerol and fatty acids - Glycerol glucose glycolysis - Glycerol DHAP (dihydroxyacetone phosphate) G3P glycolysis - Fatty Acids β-oxidation acetyl-CoA Krebs - Fats provide 38 kJ/g while carbohydrates provide 16 kJ/g ...
Role of Adipose Tissue in Lipid Metabolism
... Role of Adipose Tissue in Lipid Metabolism Adipose tissues carry all metabolic process of any active ...
... Role of Adipose Tissue in Lipid Metabolism Adipose tissues carry all metabolic process of any active ...
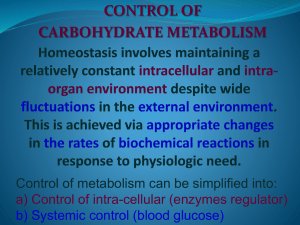
Control of intra-cellular (enzyme regulator)
... Rate-Limiting Reaction Regulates an Entire Metabolic Pathway While the flux of metabolites through metabolic pathways involves catalysis by numerous enzymes, active control of homeostasis is achieved by regulation of only a select subset of these enzymes. ...
... Rate-Limiting Reaction Regulates an Entire Metabolic Pathway While the flux of metabolites through metabolic pathways involves catalysis by numerous enzymes, active control of homeostasis is achieved by regulation of only a select subset of these enzymes. ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.