Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... Peptide hormones: 3 to 2000 or more amino acid; insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin; precursor to active form; release by exocytosis; a large amount of hormone release suddenly; bind to receptor; generate second messenger Insulin : preproinsulin (singnal p.p.) proinsulin (secretary vesicle in pan ...
... Peptide hormones: 3 to 2000 or more amino acid; insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin; precursor to active form; release by exocytosis; a large amount of hormone release suddenly; bind to receptor; generate second messenger Insulin : preproinsulin (singnal p.p.) proinsulin (secretary vesicle in pan ...
Stable Isotope and Metabolomics Core Facility
... AECOM Diabetes Center The Einstein Stable Isotope & Metabolomics Core is within the NIH funded Diabetes Research Center at Einstein and anchors the CMCR Metabolomics Core. The Core uses stable isotope flux and metabolite profiling to help formulate and test hypotheses about the metabolic consequence ...
... AECOM Diabetes Center The Einstein Stable Isotope & Metabolomics Core is within the NIH funded Diabetes Research Center at Einstein and anchors the CMCR Metabolomics Core. The Core uses stable isotope flux and metabolite profiling to help formulate and test hypotheses about the metabolic consequence ...
Glycolysis
... proteins, and carbs (potential) • liberate energy – break bonds – release energy, CO2 and H20 – Energy is transferred to ATP for use in the body ...
... proteins, and carbs (potential) • liberate energy – break bonds – release energy, CO2 and H20 – Energy is transferred to ATP for use in the body ...
classsssssss
... male who suffers from periodic hemolysis demonstrate a low activity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Deficiency of which of the following erythrocyte enzymes has the same pathophysiology as this patient’s condition? • A. bisphosphoglycerate mutase • B. pyruvate kinase • C. hexokinase • D. trans ...
... male who suffers from periodic hemolysis demonstrate a low activity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Deficiency of which of the following erythrocyte enzymes has the same pathophysiology as this patient’s condition? • A. bisphosphoglycerate mutase • B. pyruvate kinase • C. hexokinase • D. trans ...
fatty acid synthesis
... synthesis. Phosphorylation of ACC, for example a result of activation of PKA by stress or exercise switches on fatty acid oxidation (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ACC-2 resulting in decreased malonyl CoA levels) while switching off fatty acid synthesis (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ...
... synthesis. Phosphorylation of ACC, for example a result of activation of PKA by stress or exercise switches on fatty acid oxidation (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ACC-2 resulting in decreased malonyl CoA levels) while switching off fatty acid synthesis (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ...
Remember: Condensation makes bonds: Hydrolysis breaks bonds.
... Condensation of monosaccharides is a polymerization reaction. It can continue to create a longer chain of saccharides (a carbohydrate). These building reactions are anabolic metabolism. c. Annotate and complete diagram below to outline how two monosaccharides are converted into a disaccharide throug ...
... Condensation of monosaccharides is a polymerization reaction. It can continue to create a longer chain of saccharides (a carbohydrate). These building reactions are anabolic metabolism. c. Annotate and complete diagram below to outline how two monosaccharides are converted into a disaccharide throug ...
Energy metabolism
... Phosphocreatine + ADP = ATP + Creatine Lactate is transported to liver via blood where it is converted to glucose through gluconeogenesis, and glucose is transported back to muscle. This inter-organic metabolic pathway is referred as Cori cycle. ...
... Phosphocreatine + ADP = ATP + Creatine Lactate is transported to liver via blood where it is converted to glucose through gluconeogenesis, and glucose is transported back to muscle. This inter-organic metabolic pathway is referred as Cori cycle. ...
nutritional terminology
... amino acids, along with 14 non-essential amino acids which together form human protein. ...
... amino acids, along with 14 non-essential amino acids which together form human protein. ...
碩命題橫式 - 國立彰化師範大學圖書館
... 10. The direct sources of nitrogen that are used to make urea via the Urea Cycle are: (a). citrulline and ornithine (b). arginine and aspartate (c). arginine and citrulline (d). ammonia and arginine (e). aspartate and ammonia 11. Which product in glycolysis also involve in serine synthesis? (a) G6P. ...
... 10. The direct sources of nitrogen that are used to make urea via the Urea Cycle are: (a). citrulline and ornithine (b). arginine and aspartate (c). arginine and citrulline (d). ammonia and arginine (e). aspartate and ammonia 11. Which product in glycolysis also involve in serine synthesis? (a) G6P. ...
Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in
... plants or seeds be better for generating metabolic water? Why? ...
... plants or seeds be better for generating metabolic water? Why? ...
Overview of Absorptive/Post-Absorptive States
... until liver stores are met (about 5% by weight) and also use the glucose for its energetic needs (glycolysis). If excess glucose remains in the blood, hepatocytes will convert it to triglycerides an ...
... until liver stores are met (about 5% by weight) and also use the glucose for its energetic needs (glycolysis). If excess glucose remains in the blood, hepatocytes will convert it to triglycerides an ...
Pertubation of metabolism in IDD Q3-5 Joe - PBL-J-2015
... 3. Indicate the mechanisms by which beta ketoacid production is increased in response to oversupply of fatty acid to the liver, including the steps of the pathways of fatty acid metabolism that are up regulated The oversupply of fatty acids in the liver cells (in the absence of insulin) leads to the ...
... 3. Indicate the mechanisms by which beta ketoacid production is increased in response to oversupply of fatty acid to the liver, including the steps of the pathways of fatty acid metabolism that are up regulated The oversupply of fatty acids in the liver cells (in the absence of insulin) leads to the ...
BIOMEDICAL IMPORTANCE Fatty acids are synthesized by an
... and acetyl-CoA to fat, assisting the anabolic phase of this feeding cycle. The nutritional state of the organism is the main factor regulating the rate of lipogenesis. Thus, the rate is high in the well-fed animal whose diet contains a high proportion of carbohydrate. It is depressed under conditio ...
... and acetyl-CoA to fat, assisting the anabolic phase of this feeding cycle. The nutritional state of the organism is the main factor regulating the rate of lipogenesis. Thus, the rate is high in the well-fed animal whose diet contains a high proportion of carbohydrate. It is depressed under conditio ...
JVB112 gluconeogenesis[1]
... -The biosynthesis of new glucose -Substrates for gluconeogenesis include lactate, pyruvate, glycerol and glucogenic amino acids -Under normal circumstances, the liver is responsible for 85%95% of the glucose that is made **during starvation or metabolic acidosis, the kidney is capable of making gluc ...
... -The biosynthesis of new glucose -Substrates for gluconeogenesis include lactate, pyruvate, glycerol and glucogenic amino acids -Under normal circumstances, the liver is responsible for 85%95% of the glucose that is made **during starvation or metabolic acidosis, the kidney is capable of making gluc ...
JVB112 gluconeogenesis[1]
... 1. interconversion of lactate and pyruvate is catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), an oxidized NAD+dependent enzyme Lactate + NAD+ <-> pyruvate +NADH + H+ a. In gluconeogenic tissues (liver), LDH usually runs this reaction in the direction of pyruvate formation b. In muscle cells and erythrocyt ...
... 1. interconversion of lactate and pyruvate is catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), an oxidized NAD+dependent enzyme Lactate + NAD+ <-> pyruvate +NADH + H+ a. In gluconeogenic tissues (liver), LDH usually runs this reaction in the direction of pyruvate formation b. In muscle cells and erythrocyt ...
lecture_22 - WordPress.com
... Ketone bodies can be regarded as a watersoluble, transportable form of acetyl units, ...
... Ketone bodies can be regarded as a watersoluble, transportable form of acetyl units, ...
File
... Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Can occur in the cytoplasm of most animal cells, but the liver is the major site for this process Fatty acids are synthesized when the diet is low in fat or high in carbohydrate or protein (most from glucose via pyruvate) A large quantity of NADPH is needed for this process a ...
... Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Can occur in the cytoplasm of most animal cells, but the liver is the major site for this process Fatty acids are synthesized when the diet is low in fat or high in carbohydrate or protein (most from glucose via pyruvate) A large quantity of NADPH is needed for this process a ...
Biochemistry II Test 2Q
... The long chain fatty acids (__c), except for ___ are produced by FA elongation with _____. Where does FA elongation occur, what is its enzyme, substrate, and dependence? The short chain FAs have how many carbons? Since short chain production occurs in the mitochondria, the substrate is naturally ___ ...
... The long chain fatty acids (__c), except for ___ are produced by FA elongation with _____. Where does FA elongation occur, what is its enzyme, substrate, and dependence? The short chain FAs have how many carbons? Since short chain production occurs in the mitochondria, the substrate is naturally ___ ...
Document
... • Lung surfactant • Hormone second messengers • Platelet-activating factor • cell adhesion and cell recognition • as receptors for bacterial toxins • ABO blood group substances • Glycolipid storage diseases ...
... • Lung surfactant • Hormone second messengers • Platelet-activating factor • cell adhesion and cell recognition • as receptors for bacterial toxins • ABO blood group substances • Glycolipid storage diseases ...
Lipids General function
... a- Insolubility in water and solubility in organic solvents like chloroform-,etc b- some relation to fatty acids esters, either actual or potential phospholipids have very little solubility in water total body lipid in man is ...
... a- Insolubility in water and solubility in organic solvents like chloroform-,etc b- some relation to fatty acids esters, either actual or potential phospholipids have very little solubility in water total body lipid in man is ...
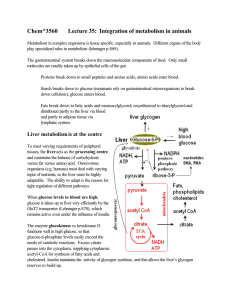
Chem*3560 Lecture 35: Integration of metabolism in animals
... ← direction during intense bursts of activity There is constant physical damage and repair of muscle fibres especially during vigorous activity. Repair enlarges and generates stronger muscles, and is the basis of body building. Because this involves very active protein degradation and resynthesis, q ...
... ← direction during intense bursts of activity There is constant physical damage and repair of muscle fibres especially during vigorous activity. Repair enlarges and generates stronger muscles, and is the basis of body building. Because this involves very active protein degradation and resynthesis, q ...
control of intermediary metabolism
... AEROBIC METABOLISM PYRUVIC ACID (3 C FRAGMENT) ENTERS MITOCHONDRIA COMBINES WITH COENZYME A LOOSING A CO2 AND BECOMING ACETYL COENZYME A (2 C FRAGMENT) THIS FRAGMENT ENTERS A CYCLIC REACTION SCHEME, THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE, ATP IS PRODUCED PRODUCTS OF THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE ENTER THE ELECTRON ...
... AEROBIC METABOLISM PYRUVIC ACID (3 C FRAGMENT) ENTERS MITOCHONDRIA COMBINES WITH COENZYME A LOOSING A CO2 AND BECOMING ACETYL COENZYME A (2 C FRAGMENT) THIS FRAGMENT ENTERS A CYCLIC REACTION SCHEME, THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE, ATP IS PRODUCED PRODUCTS OF THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE ENTER THE ELECTRON ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.













![JVB112 gluconeogenesis[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000939420_1-ae0fa12f0b4eac306770097ba9ecae40-300x300.png)
![JVB112 gluconeogenesis[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005255251_1-e457e3f80be2f5d8ecf577d50c416034-300x300.png)