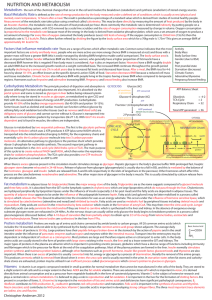
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1II 1. Enzymes are very potent catalysts
... enzyme phosphoglycerate kinase in the presence of an excess of ADP and ATP, the final mixture contains approximately 1750 molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate for every 1 molecule of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. Estimate the ΔG’0 of the reaction below (R = 8.315 J/mol·K and T = ...
... enzyme phosphoglycerate kinase in the presence of an excess of ADP and ATP, the final mixture contains approximately 1750 molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate for every 1 molecule of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. Estimate the ΔG’0 of the reaction below (R = 8.315 J/mol·K and T = ...
glyoxylate cycle
... other tissues for starch storage. In some plant seeds, stored fats are converted to glucose and sucrose upon germination and used to make cell wall cellulose. Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose. ...
... other tissues for starch storage. In some plant seeds, stored fats are converted to glucose and sucrose upon germination and used to make cell wall cellulose. Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose. ...
Nutrition and Metabolism
... and fibrinogen which is the precursor for fibrin at the end of the coagulation pathways. Most of the plasma protiens are formed in the liver. Insulin normally stimulates protien synthesis and maintains protien balance, although other hormones such as growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor, gluco ...
... and fibrinogen which is the precursor for fibrin at the end of the coagulation pathways. Most of the plasma protiens are formed in the liver. Insulin normally stimulates protien synthesis and maintains protien balance, although other hormones such as growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor, gluco ...
2-A Chemical Compounds of Life Organic Compounds
... a)Used to store energy & for building cell structures b)Built from 1 glycerol & 3 fatty acids c)During dehydration synthesis three H2O molecules are released (1 for each fatty acid) fatty acid Glycerol fatty acid fatty acid ...
... a)Used to store energy & for building cell structures b)Built from 1 glycerol & 3 fatty acids c)During dehydration synthesis three H2O molecules are released (1 for each fatty acid) fatty acid Glycerol fatty acid fatty acid ...
2008b(12): Detail the protective and regulatory roles of the liver
... General: the liver is the largest gland in the body and has multiple functions involved in many essential processes in the body. It is the interface between the gut and the body and therefore has a role in protection from organisms and toxins and regulation of nutrient levels. Protective: - involved ...
... General: the liver is the largest gland in the body and has multiple functions involved in many essential processes in the body. It is the interface between the gut and the body and therefore has a role in protection from organisms and toxins and regulation of nutrient levels. Protective: - involved ...
Gluconeogenesis
... -The overall equilibrium of the glycolysis favors the formation of glycolysis - Most precursors must enter the Krebs cycle at some point to be converted to oxaloacetate. - Oxaloacetate is the starting material for gluconeogenesis ...
... -The overall equilibrium of the glycolysis favors the formation of glycolysis - Most precursors must enter the Krebs cycle at some point to be converted to oxaloacetate. - Oxaloacetate is the starting material for gluconeogenesis ...
METABOLIC COMPARTMENTATION
... The inner mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to NADH Electrons from NADH in the cytosol are transferred by electron shuttles. In the glycerol phosphate shuttle, NADH in the cytosol is used to reduce dihydoxyacetone phosphate in the reaction catalyzed by cytosolic glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenas ...
... The inner mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to NADH Electrons from NADH in the cytosol are transferred by electron shuttles. In the glycerol phosphate shuttle, NADH in the cytosol is used to reduce dihydoxyacetone phosphate in the reaction catalyzed by cytosolic glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenas ...
C483 Final Exam Study Guide The final will be held in CH 001 at 8
... the way to being made into fat. Write all the enzymes in the list below into the proper places in the figure below. If the enzyme is not used, write its name in the “not used” box. If it is used, write the enzyme in the order that the carbon atoms from glucose encounter the enzymes. ...
... the way to being made into fat. Write all the enzymes in the list below into the proper places in the figure below. If the enzyme is not used, write its name in the “not used” box. If it is used, write the enzyme in the order that the carbon atoms from glucose encounter the enzymes. ...
3. Related Pathways
... Organisms are able to metabolize nutrients other than carbohydrates during times of starvation Once broken down, these monomers are able to feed into various parts of glycolysis or the Krebs cycle (Fig.1, p.117) ...
... Organisms are able to metabolize nutrients other than carbohydrates during times of starvation Once broken down, these monomers are able to feed into various parts of glycolysis or the Krebs cycle (Fig.1, p.117) ...
Biology 12 - Biologically Important Molecules – Review Worksheet
... a polymer of glucose, used as a structural component of plant cell walls a polymer of glucose, used as a storage form for glucose in animals a polymer of glucose, used as a storage form for glucose in plants a loss of Hydrogen atoms (or electrons) a lipid that is an important component of cell membr ...
... a polymer of glucose, used as a structural component of plant cell walls a polymer of glucose, used as a storage form for glucose in animals a polymer of glucose, used as a storage form for glucose in plants a loss of Hydrogen atoms (or electrons) a lipid that is an important component of cell membr ...
peptides - WordPress.com
... Glucose provides carbon skeletons for the glycerol of triacylglycerols and nonessential amino acids. Water-soluble products of digestion are transported directly to the liver via the hepatic portal vein. The liver regulates the blood concentrations of glucose and amino acids. Pathways are com ...
... Glucose provides carbon skeletons for the glycerol of triacylglycerols and nonessential amino acids. Water-soluble products of digestion are transported directly to the liver via the hepatic portal vein. The liver regulates the blood concentrations of glucose and amino acids. Pathways are com ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... Shuttle for transfer of acetyl groups from mitochondria to the cytosol. All the aceyl-CoA used in fatty acid synthesis is formed in mitochondria from PA oxidation and from the catabolism of the a.a. Thus shuttle system is required. Acetyl-CoA from fatty acid oxidation is not a significant source of ...
... Shuttle for transfer of acetyl groups from mitochondria to the cytosol. All the aceyl-CoA used in fatty acid synthesis is formed in mitochondria from PA oxidation and from the catabolism of the a.a. Thus shuttle system is required. Acetyl-CoA from fatty acid oxidation is not a significant source of ...
March 1972 EFFECTS OF VOLATILE FA`M`Y ACIDS, KETONE
... the plasma concentration in ketotic cows, suggests an important mechanism of feedback control, in which a product derived from excessive breakdown of fatty acids participates in the regulation of fatty acid mobilization. The lack of an effect of glucose (table 1) on the release of fatty acids from b ...
... the plasma concentration in ketotic cows, suggests an important mechanism of feedback control, in which a product derived from excessive breakdown of fatty acids participates in the regulation of fatty acid mobilization. The lack of an effect of glucose (table 1) on the release of fatty acids from b ...
Gluconeogenesis
... Gluconeogenesis and starch/glycogen synthesis • In animals, lactate formed anaerobically in muscles is converted to glucose in liver and kidney and stored as glycogen or released as blood glucose. • In plants, G3P product of photosynthesis is converted to starch and stored in chloroplasts or conver ...
... Gluconeogenesis and starch/glycogen synthesis • In animals, lactate formed anaerobically in muscles is converted to glucose in liver and kidney and stored as glycogen or released as blood glucose. • In plants, G3P product of photosynthesis is converted to starch and stored in chloroplasts or conver ...
Slide 1
... occurs in muscles when starved of oxygen; bacteria produce lactate in yogurt and some cheeses – Alcohol Fermentation: pyruvate converted to ethanol via ethanal; CO2 byproduct; used in production of wine – Oxidation of NADH to NAD+ allows continued gylcolysis ...
... occurs in muscles when starved of oxygen; bacteria produce lactate in yogurt and some cheeses – Alcohol Fermentation: pyruvate converted to ethanol via ethanal; CO2 byproduct; used in production of wine – Oxidation of NADH to NAD+ allows continued gylcolysis ...
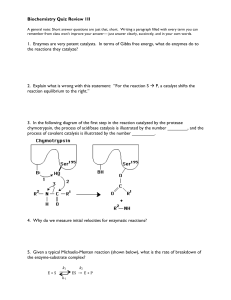
Biochemistry 3020 1. The consumption of
... 1. The consumption of alcohol (ethanol), especially after periods of strenuous activity or after not eating for several hours, result in a deficiency of glucose in the blood, a condition known as hypoglycemia The first step in the metabolism of ethanol by the liver is oxidation to acetaldehyde, cata ...
... 1. The consumption of alcohol (ethanol), especially after periods of strenuous activity or after not eating for several hours, result in a deficiency of glucose in the blood, a condition known as hypoglycemia The first step in the metabolism of ethanol by the liver is oxidation to acetaldehyde, cata ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism Updated
... They can give rise to glucose by gluconeogenesis • Transamination :Oxaloacetate and α-ketoglutarate respectively, serve as precursors for the synthesis of aspartate and glutamate by transamination which in turn are used for the synthesis of other non essential amino acids, purines and pyrimidines. • ...
... They can give rise to glucose by gluconeogenesis • Transamination :Oxaloacetate and α-ketoglutarate respectively, serve as precursors for the synthesis of aspartate and glutamate by transamination which in turn are used for the synthesis of other non essential amino acids, purines and pyrimidines. • ...
Chapter-4 part-2 Energy Metabolism
... • “Isozymes” may look different but catalyze the same reaction ...
... • “Isozymes” may look different but catalyze the same reaction ...
LB Metabolic Diseases
... • It occurs when there is a high rate of fatty acid oxidation in the liver ...
... • It occurs when there is a high rate of fatty acid oxidation in the liver ...
C483 Final Exam Study Guide The final will be held in Chemistry
... the way to being made into fat. Write all the enzymes in the list below into the proper places in the figure below. If the enzyme is not used, write its name in the “not used” box. If it is used, write the enzyme in the order that the carbon atoms from glucose encounter the enzymes. ...
... the way to being made into fat. Write all the enzymes in the list below into the proper places in the figure below. If the enzyme is not used, write its name in the “not used” box. If it is used, write the enzyme in the order that the carbon atoms from glucose encounter the enzymes. ...
CHAPTER-III CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
... example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose, glucose, and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form f ...
... example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose, glucose, and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form f ...
ENERGY METABOLISM
... The surplus amino acids ARE NOT STORED, but are either: a. released into the blood for all tissues to use in protein synthesis, b. they are with the resulting carbon skeletons being degraded by the liver pyruvate, acetyl CoA, or TCA cycle intermediates, these metabolites can be oxidized for energy o ...
... The surplus amino acids ARE NOT STORED, but are either: a. released into the blood for all tissues to use in protein synthesis, b. they are with the resulting carbon skeletons being degraded by the liver pyruvate, acetyl CoA, or TCA cycle intermediates, these metabolites can be oxidized for energy o ...
Reactions of the TCA Cycle
... Common Metabolic pathway for energy Provision from CHO, lipids and Amino acids (TCA Cycle/ Krebs Cycle) ...
... Common Metabolic pathway for energy Provision from CHO, lipids and Amino acids (TCA Cycle/ Krebs Cycle) ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.