* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reactions of the TCA Cycle
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oligonucleotide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
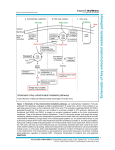
Common Metabolic pathway for energy Provision from CHO, lipids and Amino acids (TCA Cycle/ Krebs Cycle) • • • • • • • • • • Objectives By the end of the lecture the student should be able to: Enlist common metabolic pathways of carbohydrate metabolism Define TCA Enlist Functions of TCA Describe different steps of TCA cycle Discuss its biomedical importance Definition TCA cycle, Krebs cycle, citric acid cycle Cyclic process Sequence interMitochondrial matrix, aerobic 2 H2O Functions of TCA • • • Provides energy Major pathway to oxidize acetyl Co-A formed from the oxidation of – Glucose – Amino acids – Fatty acids Provides substrates for – Gluconeogenesis – Heme – Non-essential amino acids – Fatty acids Key Co-Enzymes • • • Niacin – NAD Riboflavin – FAD Thiamine – TPP – Coenzyme A – CoA • • • • • • • • • Reactions of the TCA Cycle Oxidative decarboxylation of Pyruvate Synthesis of citrate from acetyl CoA and Oxaloacetate Isomerization of Citrate Oxidation and decarboxylation of isocitrate Oxidative decarboxylation of α- ketoglutarate Cleavage of Succinyl CoA Oxidation of succinate Hydration of fumerate Oxidation of malate • • • Biomedical Importance Final common pathway CHO, proteins fats through formation of 2 C unit acetyl CoA Catabolic role-> acetyl CoA ->oxidized ->CO2 , H2O-> energy Intermediate-> heme, non-essential aa, FA synthesis, cholesterol and steroid synthesis References Lippincott’s biochemistry 5 ed. page 109 Harper’s Biochemistry th • • -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------