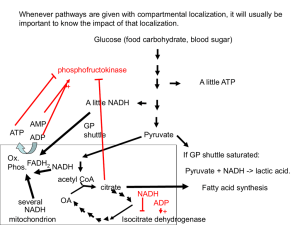
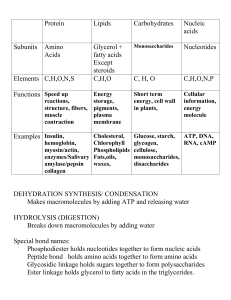
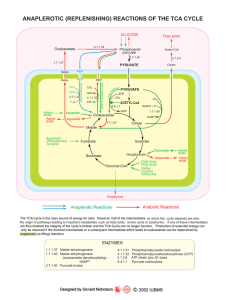
NATURE`S BIOLOGICAL BUILDING BLOCKS
... Composed of subunits (molecules) called amino acids joined together by a peptide bond. Proteins may be structural (as in muscle tissue and connective tissue) or enzymatic. They may also function as hormones. ...
... Composed of subunits (molecules) called amino acids joined together by a peptide bond. Proteins may be structural (as in muscle tissue and connective tissue) or enzymatic. They may also function as hormones. ...
Ch7METABOLISM
... Lactate is an alternative fuel that muscle cells can use, or liver cells can convert to glucose BREAKDOWN and RELEASE of ENERGY – FATS ...
... Lactate is an alternative fuel that muscle cells can use, or liver cells can convert to glucose BREAKDOWN and RELEASE of ENERGY – FATS ...
Fed State Insulin Insulin Fasted State/ Starvation
... Fructose 6-phosphate Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase ...
... Fructose 6-phosphate Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase ...
Exam 4, 2015 - Biochemistry at CSU, Stanislaus
... 14. (24 points) Describe how liver cells are controlled so that glycolysis and gluconeogenesis do not occur simultaneously in the liver. Give specific details about the regulation by insulin and glucagon. Give specific details about the reactions that are regulated. What enzyme, how is it regulated? ...
... 14. (24 points) Describe how liver cells are controlled so that glycolysis and gluconeogenesis do not occur simultaneously in the liver. Give specific details about the regulation by insulin and glucagon. Give specific details about the reactions that are regulated. What enzyme, how is it regulated? ...
Lactic Acid and Energy from Fats and Proteins
... Process where lactic acid is converted to pyruvate Lactate is transported (by blood) to the liver and converted back to glucose It is then converted into glycogen so that it can be used for energy ...
... Process where lactic acid is converted to pyruvate Lactate is transported (by blood) to the liver and converted back to glucose It is then converted into glycogen so that it can be used for energy ...
Slide 1
... know. It should make sense with respect to your understanding of the role of that tissue in support of global metabolism. If hormonal regulation is specified, that is always important to know. It should make sense with respect to what physiological state the hormone signifies. ...
... know. It should make sense with respect to your understanding of the role of that tissue in support of global metabolism. If hormonal regulation is specified, that is always important to know. It should make sense with respect to what physiological state the hormone signifies. ...
Liver- integrated lecture
... • Acetyl~CoA is mostly converted to ketone bodies (small amount is oxidized completely) • Ketone bodies and FA are preferred by many tissues over glucose; they can also suppress proteolysis and BCA oxidation in muscle • Cooperation of tissues : liversynthesizes glucose, muscle and gut supply the sub ...
... • Acetyl~CoA is mostly converted to ketone bodies (small amount is oxidized completely) • Ketone bodies and FA are preferred by many tissues over glucose; they can also suppress proteolysis and BCA oxidation in muscle • Cooperation of tissues : liversynthesizes glucose, muscle and gut supply the sub ...
Chapter 21 Biosynthetic Pathways
... • These sources are most commonly pyruvate, citric acid cycle intermediates, and glucogenic amino acids. • Gluconeogenesis is not the exact reversal of glycolysis; that is, pyruvate to glucose does not occur by reversing the steps of glucose to pyruvate. • There are three irreversible steps in glyco ...
... • These sources are most commonly pyruvate, citric acid cycle intermediates, and glucogenic amino acids. • Gluconeogenesis is not the exact reversal of glycolysis; that is, pyruvate to glucose does not occur by reversing the steps of glucose to pyruvate. • There are three irreversible steps in glyco ...
C483 Study Guide for Exam 2 Fall 2015 Basic Information Exam 3
... All papers, books, phones, and electronic devices must be in a sealed bag under your seat. The exam will cover chapters 13-15 and 17, which includes Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogen metabolism, pentose phosphate pathway Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, citric acid cycle Electron transpor ...
... All papers, books, phones, and electronic devices must be in a sealed bag under your seat. The exam will cover chapters 13-15 and 17, which includes Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogen metabolism, pentose phosphate pathway Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, citric acid cycle Electron transpor ...
STARVE-FEED CYCLE 1) WELL-FED STATE (food intake
... → used in gluconeogenesis (glucogenic amino acids) → amino nitrogen detoxicated by urea synthesis → glutamine metabolized in enterocytes ...
... → used in gluconeogenesis (glucogenic amino acids) → amino nitrogen detoxicated by urea synthesis → glutamine metabolized in enterocytes ...
pbl – night starvation - UQMBBS-2013
... (b) State whether energy stores in these organs can be used to maintain blood glucose concentrations during fasting, and if not, explain why (3 marks) Liver glycogen can be degraded into glucose and released into the blood to maintain BGL. Muscle glycogen is broken down the glucose but cannot exit ...
... (b) State whether energy stores in these organs can be used to maintain blood glucose concentrations during fasting, and if not, explain why (3 marks) Liver glycogen can be degraded into glucose and released into the blood to maintain BGL. Muscle glycogen is broken down the glucose but cannot exit ...
Summary of Metabolism
... amounts of alanine to get rid of ammonia (Glucose Alanine Cycle) • Resting muscle uses fatty acids to meet 85% of energy needs ...
... amounts of alanine to get rid of ammonia (Glucose Alanine Cycle) • Resting muscle uses fatty acids to meet 85% of energy needs ...
Week 4 met 2 kin 310
... 1. Describe the activation and translocation of free fatty acids into skeletal muscle that is required prior to metabolism as fuel. (do not include the regulation of translocation in your answer). 2. Describe the mobilization, circulation and uptake of free fatty acids during exercise. Why do resear ...
... 1. Describe the activation and translocation of free fatty acids into skeletal muscle that is required prior to metabolism as fuel. (do not include the regulation of translocation in your answer). 2. Describe the mobilization, circulation and uptake of free fatty acids during exercise. Why do resear ...
Citric acid Cycle:
... work, and G = - 50KJ/Mole in physiological condition. 8. Deficiency of thiamine or arsenate poisoning lead to the similar symptoms and mostly brain functions are affected in ...
... work, and G = - 50KJ/Mole in physiological condition. 8. Deficiency of thiamine or arsenate poisoning lead to the similar symptoms and mostly brain functions are affected in ...
In order to gain 1lb in body fat over 1 year a person would have to
... 1. (4pts) Give ONE physiological example of glucose sparing. What is the significance of this example to whole body energy metabolism? Glucose sparing is the utilization of substrates other than glucose for energy by tissues that are not obligatory glucose users. Examples: muscle uses FA predominate ...
... 1. (4pts) Give ONE physiological example of glucose sparing. What is the significance of this example to whole body energy metabolism? Glucose sparing is the utilization of substrates other than glucose for energy by tissues that are not obligatory glucose users. Examples: muscle uses FA predominate ...
Organ Integration and Control
... Once glycogen reserves are exhausted gluconeogenesis begins. In this mode glucose can be made from a number of sources including: 1. Glycerol from fat breakdown 2. Alanine from protein breakdown – alanine cycle 3. Lactate (Red blood cells, Muscle) – Cori Cycle ...
... Once glycogen reserves are exhausted gluconeogenesis begins. In this mode glucose can be made from a number of sources including: 1. Glycerol from fat breakdown 2. Alanine from protein breakdown – alanine cycle 3. Lactate (Red blood cells, Muscle) – Cori Cycle ...
Chapter 3: Biochemistry
... 2. Monomer: Amino Acids - 20 building blocks of proteins a) Central C with COOH group, NH2 group, H, and one other functional group b) Differences give different shapes which lead to different functions 3. Peptide bond: a) dipeptide: two amino acids b) polypepide: long chain of amino acids that form ...
... 2. Monomer: Amino Acids - 20 building blocks of proteins a) Central C with COOH group, NH2 group, H, and one other functional group b) Differences give different shapes which lead to different functions 3. Peptide bond: a) dipeptide: two amino acids b) polypepide: long chain of amino acids that form ...
MAKEUP: Briefly discuss functions of the liver
... • Once maximal glycogen stores → glucose metabolised to pyruvate → AcetylCoA → fatty acid Cholesterol / phospholipid formation o Protein synthesis Lipoproteins - Catabolic Functions: o CHO: Glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis (via acetyl CoA formation from fatty acid breakdown) → maintain BSL o Fats ...
... • Once maximal glycogen stores → glucose metabolised to pyruvate → AcetylCoA → fatty acid Cholesterol / phospholipid formation o Protein synthesis Lipoproteins - Catabolic Functions: o CHO: Glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis (via acetyl CoA formation from fatty acid breakdown) → maintain BSL o Fats ...
Study guide for Midterm 3.
... 2. The acetyl group of acetyl-CoA, produced by the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate in the mitochondrion, is transferred to the cytosol by the acetyl group shuttle outlined in Figure 21-10. a. Write the overall equation for the transfer of one acetyl group from the mitochondrion to the cytosol. ...
... 2. The acetyl group of acetyl-CoA, produced by the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate in the mitochondrion, is transferred to the cytosol by the acetyl group shuttle outlined in Figure 21-10. a. Write the overall equation for the transfer of one acetyl group from the mitochondrion to the cytosol. ...
anaplerotic (replenishing) reactions of the tca cycle - Sigma
... The TCA Cycle is the main source of energy for cells. However, half of the intermediates on which the cycle depends are also the origin of pathways leading to important metabolites such as fatty acids , amino acids or porphyrins. If any of these intermediates are thus diverted the integrity of the c ...
... The TCA Cycle is the main source of energy for cells. However, half of the intermediates on which the cycle depends are also the origin of pathways leading to important metabolites such as fatty acids , amino acids or porphyrins. If any of these intermediates are thus diverted the integrity of the c ...
Ch.24Pt.6_000
... Relationship between Lipid and Carbohydrate Metabolism Acetyl CoA is the link between lipid and carbohydrate metabolic pathways. Glucose, Glycerol, & Fatty acids all degrade into acetyl CoA Biosynthesis of fatty acids, ketone bodies, & cholesterol all use acetyl CoA. ...
... Relationship between Lipid and Carbohydrate Metabolism Acetyl CoA is the link between lipid and carbohydrate metabolic pathways. Glucose, Glycerol, & Fatty acids all degrade into acetyl CoA Biosynthesis of fatty acids, ketone bodies, & cholesterol all use acetyl CoA. ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.