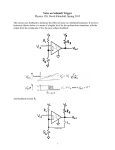
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lactic Acid and Energy from Fats and Proteins
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
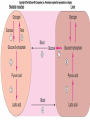
Lactic Acid Blood lactate threshold = the point where lactate levels in the blood increases suddenly beyond resting values Aka anaerobic threshold Cont... Varies from person to person Generally, untrained people have a low anaerobic threshold and reach their threshold at 50-60% of their VO2 max. Elite endurance athletes have a high threshold and do not reach their threshold until 70-80% of their VO2 max. Raising the Lactic Acid Threshold Main objective in physical training (exercise) Two ways to achieve this: 1. Use anaerobic training to extend the amount of time before lactate buildup occurs 2. Use aerobic-style (endurance) training to improve cardiorespiratory capacity This will help to increase the concentration of mitochondria + myoglobin in muscle fibres = improved efficiency of oxygen transfers The Cori Cycle Process where lactic acid is converted to pyruvate Lactate is transported (by blood) to the liver and converted back to glucose It is then converted into glycogen so that it can be used for energy Occurs during anaerobic lactic exercise The opposite of glycolysis Fats Contain large quantity of stored energy (more than 2x carbohydrates and protein) Fatty acids = types of fat found in muscle cells and adipose tissue that are used for energy Fatty acids are stored in the body as triglycerides Lipolysis = process where triglycerides are broken down and the resulting fatty acids become available to be used as an energy source Proteins Unlike carbohydrates and fats, there are no “protein reserves” in the body. It is not readily available All proteins are part of existing body tissue or actively engaged in the metabolic system Cont... Protein is comprised of about 20 different amino acids which are used to form various body tissues To be utilized as an energy source protein must first be broken down into separate amino acids The aa alanine is the main contributor It is converted to glycogen in the liver which is then transported as glucose through the bloodstream Cont... As a source of energy protein plays an important role in endurance-type activities More generally it is used in chronic conditions when glycogen stores have been significantly diminished In the absence of other energy sources the body breaks down protein as a backup In your own words... Using the section on page 89 under “protein supplementation” explain why protein supplements are taken and the ramifications of having too much protein in your body












![fermentation[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008290469_1-3a25eae6a4ca657233c4e21cf2e1a1bb-150x150.png)