* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes on Schmidt Trigger Physics 120, David Kleinfeld, Spring 2015
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Control theory wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
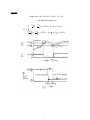
Notes on Schmidt Trigger Physics 120, David Kleinfeld, Spring 2015 This circuit uses feedback to minimize the effect of noise on a threshold transition. It involves hysteresis (shown below), in terms of a higher level for the up than down transition, with the output from the comparator. First, the case without feedback: Add feedback resistor R4. 1 K V L gives !! !!! !! ! + !! + ! !! !!!"# !! =0 Case of Vout = 0 The NPN output transistor acts as a short, so K V L gives V! − V! V! V! + + =0 R! R! R! so V! = R!R! V R ! R! + R ! R! + R ! R ! ! Usually R4 is large (the fedback voltage is small) so that, expanding to order (1/R4), V! ≈ R! R ! R! 1− R! + R ! R ! R! + R ! V! and we see that the feedback lowers the lower threshold relative to the case without feedback. Case of Vout ≠ 0 The NPN output transistor acts as an open circuit, so K V L gives V! − V! V! V! − 𝑉!"# + + =0 R! R! R! and This leads to a morass of algebra 𝑉! = V!"# − V! V!"# − V! + =0 R! R! R! + R ! 𝑅! 𝑅! 𝑅! 𝑅! 𝑅! + 𝑅! 𝑅! + 𝑅! 𝑅! R! + R ! − 𝑅! 𝑅! 𝑅! 𝑉! 𝑉! + R! R! + R ! that simplifies when R4 is large and becomes: 𝑉! ≈ R! R! V! 1+ V R! + R ! R ! V! ! and we see that the feedback raises the upper threshold relative to the case without feedback. • When the value of the input heads from high to low, the "0" to "VP" transition causes an increase in threshold that adds hysteresis and prevents jitter. • When the value of the input heads from low to high, the "VP" to "0" transition causes a decrease in threshold that adds hysteresis and prevents jitter. 2 Example Simple case is R! = R ! ; R ! = 10R! ; V! = V! ∴ the threshold voltages are: V! = 𝑉! 1 1− ≈ 0.45 𝑉! ; 𝑉!"# 𝑡 = 0! = 0 2 10 𝑉! 1 1+ ≈ 0.55 𝑉! ; 𝑉!"# 𝑡 = 0! ≈ 1.05 𝑉! 2 10 3