* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study guide for Midterm 3.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
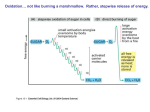
Study guide for Midterm 3. 1. Isolated mitochondria are suspended in a buffer containing ADP, Pi, and an oxidizable substrate such as succinate. According to the graph below, the lower (red) line indicates the ATP production and the above (black) line the consumption of oxygen. a. Why there is neither O2 consumed nor ATP synthesized until ADP and Pi are added to the succinate solution? b. Explain the effect of Venturicidin or oligomycin to the respiratory chain. If they block the respiratory chain, why there is no ATP synthesized? c. DNP is a hydrophobic acid molecule. Explain its effect. 2. The acetyl group of acetyl-CoA, produced by the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate in the mitochondrion, is transferred to the cytosol by the acetyl group shuttle outlined in Figure 21-10. a. Write the overall equation for the transfer of one acetyl group from the mitochondrion to the cytosol. b. What is the cost of this process in ATPs per acetyl group? c. In Chapter 17 we encountered an acyl group shuttle in the transfer of fatty acyl–CoA from the cytosol to the mitochondrion in preparation for β oxidation (see Fig. 17-6). One result of that shuttle was separation of the mitochondrial and cytosolic pools of CoA. Does the acetyl group shuttle also accomplish this? Explain. 3. Consider a preparation that contains all the enzymes and cofactors necessary for fatty acid biosynthesis from added acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA. a. If [2-2H]acetyl-CoA (labeled with deuterium, the heavy isotope of hydrogen) and an excess of unlabeled malonyl-CoA are added as substrates, how many deuterium atoms are incorporated into every molecule of palmitate? What are their locations? Explain. b. If unlabeled acetyl-CoA and [2-2H]malonyl-CoA are added as substrates, how many deuterium atoms are incorporated into every molecule of palmitate? What are their locations? Explain 4. When an animal confronts a “fight-or-flight” situation, the release of epinephrine promotes glycogen breakdown in the liver, heart, and skeletal muscle. The end product of glycogen breakdown in the liver is glucose; the end product in skeletal muscle is pyruvate. What is the reason for the different products of glycogen breakdown in the two tissues? 5. Why does citrate inhibit phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)? 6. After few days of starvation the concentration of glucose in blood decreases and the concentration of ketone bodies increase. Are these two phenomena connected? Why? 7. Associate all the conditions that apply for each pathway: Conditions a. Happens in the cytosol b. Happens in mitochondria c. Happens in mitochondrial inner membrane d. Uses NADPH as reactant e. Uses FADH2 as reactant f. Uses NAD+ as reactant g. Uses NADP+ as reactant h. Uses FAD as reactant i. j. k. l. Takes place in the liver between meals and during fasting Takes place in the liver right after a meal The pathway uses CO2 to activate a molecule It requires a shuttle to transport an electron carrier across the mitochondrial membrane. m. It requires a shuttle to transport some of the necessary metabolites across the mitochondrial membrane. n. It’s a cycle that takes place between different organs. Pathways I. Glycolysis: From glucose to pyruvate. II. Gluconeogenesis. From pyruvate to glucose. III. Fatty acid biosynthesis IV. Cori Cycle V. Oxidative phosphorylation VI. Amino acid catabolism. From any amino acid to urea. VII. Alanine-glucose cycle VIII. Fatty acid beta-oxidation IX. Pentose phosphate pathway X. Fermentation. From pyruvate to lactate. XI. Formation of ketone bodies.