* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NATURE`S BIOLOGICAL BUILDING BLOCKS
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
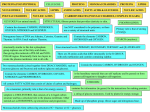
NATURE'S BIOLOGICAL BUILDING BLOCKS CARBOHYDRATES Composition: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen Monosaccharides - usually 3-6 carbon atoms These are the simplest sugars. Hexoses: (6 C sugars) - glucose, fructose Pentoses: (5 C sugars) - ribose, deoxyribose Disaccharides - 2 monosaccharides joined together sucrose = glucose + fructose maltose = glucose + glucose lactose = glucose + galactose Polysaccharides - many monosaccharides joined in large molecule cellulose - main component of wood glycogen - main storgae form of glucose in liver starch - main storage form of glucose in plants chitin - main component of exoskeleton of insects, crayfish, lobsters, crabs and other arthropods LIPIDS Composition: mostly carbon and hydrogen with some oxygen Includes fatty, greasy and waxy compounds relatively insoluble in water, but soluble in organic solvents such as ether and benzene. Neutral Fats - high energy molecules consisting of glycerol and fatty acids. Phospholipids - neutral fat with one fatty acid molecule replaced by phosphate, choline, or other group. Important to membrane structure. Carotenoids - red and yellow plant pigments such as carotene in carrots. Steroids - lipids with carbon atoms arranged in four interlocking rings with side groups attached. Includes cholesterol, bile salts, and sex hormones. PROTEINS Composition: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sometimes sulfur. Composed of subunits (molecules) called amino acids joined together by a peptide bond. Proteins may be structural (as in muscle tissue and connective tissue) or enzymatic. They may also function as hormones. ENZYMES: a group of proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. Enzymes facilitate a reaction, but are not chemically altered by that reaction. Enzymes have an active site that orients the reacting molecules and each enzyme is very specific for which reaction it will catalyze. Almost all enzymes are protein; however, there are many proteins that are not enzymes (see above). NOTE: It has recently been discovered that there are ribonucleic acids with enzymatic activity. Prior to this discovery, it was thought that all enzymes were protein. NUCLEIC ACIDS Atomic composition: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus Molecular composition: polymers of nucleotides nucleotide consists of: nucleic acid base (purine: adenine, guanine) (pyrimidine: cytosine, thymine, uracil) pentose (5 C sugar) phosphate group Examples: DNA is composed of A, T, G, C RNA is composed of A, U, G, C Nucleic acids store information. Nucleotides store energy (ATP), and act as hormones (cAMP).