* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - Denton ISD
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
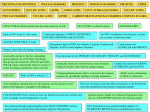
PROTEINS (POLYPEPTIDES) NUCLEOTIDES CELLULOSE: NUCLEIC ACIDS POLYSACCHARIDES LIPIDS PROTEINS AMINO ACIDS NUCLEIC ACIDS GLYCOGEN (or animal starch): MONOSACCHARIDES FATTY ACIDS & GLYCEROL LIPIDS NUCLEIC ACIDS CARBOHYDRATES (POLYSACCHARIDES, COMPLEX SUGARS) STRUCTURAL fibrous protein that provides elasticity to skin. Contain the elements CARBON, HYDROGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN and SULPHUR. Are NOT considered to be polymers, as there are a variety of structural units. Nitrogenous bases of DNA are Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine. In RNA Uracil replaces Thymine. structurally similar to fats but a phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains, thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma membrane vital to all cells. PROTEINS Contain the elements CARBON, HYDROGEN and OXYGEN. PHOSPHOLIPIDS: Primary role is that of storing of energy. STARCH (amylose): Four structural levels: PRIMARY, SECONDARY, TERTIARY and QUATERNARY. There are 20 amino acids that differ structurally in the R-GROUP, with only methionine and cysteine containing sulphur. Two monosaccharides joined together form DISACCHARIDES, such as sucrose (glucose and fructose) and maltose (glucose and glucose). Contain the elements CARBON, HYDROGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN and PHOSPHOROUS. Contain the elements CARBON, HYDROGEN and OXYGEN. is the hereditary material that can self replicate and be passed on from parent cell/organism to daughter cell/organism. All contain FATTY ACIDS that consist of chains of carbon and hydrogen. As a monomer, primarily role is that of an energy source. simplest is CHOLESTEROL that consists of a 4 ringed carbon structure and has a structural role in the plasma membrane. Other steroids act as HORMONES, eg testosterone and progesterone. STEROIDS: contains the information (in genes) for the instructions for making proteins. a string of glucose monomers. Used by plants for energy storage. Made up of phosphate group, ribose sugar and nitrogenous base. Monosaccharides form carbon-ring structures (5C= fructose or 6C = glucose).